In this guide, I will show you exactly how to implement ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 and ensure you pass your audit. You will get a complete walkthrough of the control, practical implementation examples, and access to the ISO 27001 templates and toolkit that make compliance easy.
I am Stuart Barker, an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor with over 30 years of experience conducting hundreds of audits. I will cut through the jargon to show you exactly what changed in the 2022 update and provide you with plain-English advice to get you certified.
Key Takeaways: ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Threat Intelligence
ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 is a new control introduced in the 2022 update that requires organizations to collect and analyze information regarding information security threats. The goal is to shift from reactive firefighting to proactive defense. By gathering intelligence on the “who, how, and when” of modern cyberattacks, organizations can implement specific mitigations before a breach occurs. This control is essential for modern risk management, ensuring your defenses are based on real-world data rather than generic assumptions.
- Sources of threat intelligence information are readily available and many are free
- Management of threats is done by risk management
- You can do it yourself with How To Create an ISO 27001 Threat Intelligence Process and Report
Core requirements for compliance include:
- Layered Intelligence: You must address threat intelligence at three levels: Strategic (high-level trends for the Board), Tactical (attacker methodologies for IT managers), and Operational (technical indicators like malicious IPs for SOC teams).
- Source Identification: You must identify and vet both Internal (logs, incident reports) and External (government alerts, vendor feeds, news sites) sources of threat data.
- Analysis & Action: It is not enough to simply “receive” a newsletter. You must prove you have analyzed the data for relevance and taken mitigation action (e.g., updating a firewall rule or patching a specific vulnerability).
- Information Sharing: Where appropriate, organizations are encouraged to share threat information with industry peers or special interest groups to improve collective defense.
- Integration with Risk Management: Relevant threats identified through intelligence must be added to your Risk Register and managed via your formal risk treatment process.
Audit Focus: Auditors will look for “The Chain of Action”:
- The Source Inventory: “Show me your list of vetted threat intelligence sources. Are they reputable and up-to-date?”
- Reporting Proof: “Show me a recent Threat Intelligence Report. Who reviewed it and what was the outcome?”
- Direct Mitigation: “Can you show me a specific security change (e.g., a new blocklist or patch) that was triggered by a threat intelligence alert?”
The 3 Layers of Threat Intelligence (Audit Prep):
| Layer | Primary Audience | Core Focus | ISO 27001 Use Case | ISO 27001:2022 Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic | Board / C-Suite. | Global trends & financial risk. | Informing ISMS Scope & Budget. | Annex A 5.7 / Clause 4.1 |
| Tactical | IT Managers. | Attack Methods (TTPs). | Tuning Firewall rules & patching. | Annex A 5.7 / 8.8 |
| Operational | Tech / Software. | Specific Data (IOCs). | Blocking bad IPs & virus updates. | Annex A 5.7 / 8.16 |
Table of Contents
- What is ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7?
- Watch the ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Video Tutorial
- ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Podcast
- Why is ISO 27001 Threat Intelligence important?
- The 3 layers of threat intelligence
- ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Implementation Guidance
- How to implement ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7
- Selecting Threat Intelligence Sources: Internal vs. External
- The threat intelligence reporting process
- The contents of the threat intelligence report
- How to create a threat intelligence process and report in under 10 minutes
- Free vs. Paid Sources Table
- How to comply
- How to pass the audit of ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7
- Top 3 Mistakes Implementing Threat Intelligence
- Applicability of ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 across different business models.
- Fast Track ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
- ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 FAQ
- Summary: Your ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Implementation Roadmap
- Further Reading
- Related ISO 27001 Controls
- ISO 27001 Controls and Attribute Values
- ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Mind Map
What is ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7?
ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Threat Intelligence is an ISO 27001 control that requires an organisation to collect and analyse information relating to information security threats and use that information take mitigation action.
Threat intelligence is used to prevent, detect or respond to threats. You can produce your own threat intelligence but as a rule you will make use of threat intelligence produced by others. It is often provided by independent providers and advisors which can include government sources and more than likely products and services will spring up around this new control to offer you it as a service, at a cost of course.
Threat Intelligence is a new control is ISO 27001:2022 and is about understanding and managing the threats to your information security. Threats to the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data.
It can be confusing when you first come to this control but I will show you what is required and some simple, practical steps you can take to implement it.
ISO 27001 Threat Intelligence is the identification and management of information security threats.
In ISO 27001 this is known as ISO27001:2022 Annex A 5.7 Threat Intelligence .
ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Purpose
ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 is preventive, detective and corrective control that ensure you provide awareness of the organisations threat environment so that the appropriate mitigation actions can be taken.
ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Definition
The ISO 27001 standard defines ISO 27001 Threat Intelligence: Annex A 5.7 as:
Information relating to information security threats should be collected and analysed to produce threat intelligence.
ISO 27001:2022 Annex A 5.7 Threat Intelligence
Watch the ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Video Tutorial
In the video ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Threat Intelligence Explained show you how to implement it and how to pass the audit. In this video, we cover:
- A walkthrough of the reporting template.
- The definition of Threat Intelligence for ISO 27001.
- How to distinguish between Internal and External sources.
ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Podcast
Listen to the ISO 27001 Threat Intelligence Deep Dive Podcast for the consultants blue print to implementing ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7.
Why is ISO 27001 Threat Intelligence important?
The purpose of this control is to provide awareness of the organisation’s threat environment so that the appropriate mitigation actions can be taken.
Taking collective knowledge of threats can lead to a collective response and that response can be based on collective best practice. If we share information we reduce the risk and impact of the emerging threats that are only ever going to increase. We cannot protect against what we do not know. As we start to know more we can increase our protection making for a safer, more secure working environment and protecting vital customer and employee data.
The 3 layers of threat intelligence
There are 3 layers to threat intelligence.
1. Strategic Threat Intelligence
High level information about the threat landscape.
Focus: High-level trends, financial impact, and global risk landscape.
Audience: Senior Management, the Board, and Policy Makers.
ISO 27001 Link: Feeds into Clause 4 (Context of the Organisation) and Clause 6.1 (Risk Assessment) to help leadership make budget and resource decisions.
2. Tactical Threat Intelligence
Intelligence on tools, techniques and attack methodologies
Focus: The “How.” It covers TTPs (Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures) used by attackers.
Audience: IT Managers, System Administrators, and Security Architects.
ISO 27001 Link: Feeds into Annex A 8.8 (Vulnerability Management) and Annex A 5.15 (Access Control) to configure defences against specific attack methods.
3. Operational Threat Intelligence
Intelligence on specific attacks and indicators.
Focus: The “Now.” It covers specific technical details like IOCs (Indicators of Compromise), malicious IP addresses, file hashes, and phishing domains.
Audience: SOC Analysts, Firewalls, and Spam Filters.
ISO 27001 Link: Feeds into Annex A 8.7 (Malware) and Annex A 8.23 (Web Filtering) for immediate blocking.
4. The 3 layers of threat intelligence comparison table
| Layer | Audience | Focus | ISO 27001 Use Case |
| Strategic | Board / C-Suite | Long-term trends & Risk | Informing the ISMS Scope & Budget |
| Tactical | IT Managers | TTPs (Attack Methods) | Tuning Firewall rules & patching priorities |
| Operational | Tech / Software | IOCs (Specific Data) | Blocking bad IPs & antivirus updates |
ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Implementation Guidance
When implementing threat intelligence you are analysing and using information and including it in your risk management process. You are using it as input to inform how you implement and configure technical controls. You are adapting information security tests and techniques based on it.
Threat intelligence is used to inform decisions and actions to precent these threats causing harm to the organisation and reduce the impact of such threats. The graphic below outlines the process from objectives to improvement.
You are going to have to ensure that
- objectives for threat intelligence production are established
- internal and external sources of information are identified, selected and vetted where necessary and appropriate
- information is collected from selected sources
- information is then prepared for analysis for example by formatting or translating it
- information is analysed to understand how it relates to you
- communication and sharing of information is done to relevant in people in a way they will understand it
Objectives of the ISO 27001 Threat Intelligence Process
When you write your threat intelligence process it will have objectives. Based on best practice real world experience the following are the objectives of the ISO 27001 Threat Intelligence process:
Identifying Existing and Emerging Threats
Through the use of internal and external data sources existing and emerging threats will be identified. In addition, the use of audit processes such as internal audit, external audit and penetration testing will be used.
Integrating Threat Intelligence into Risk Assessment
Threats will be analysed for relevance to the organisation. Where a relevant threat is identified it will be added to the risk register and managed via the risk management process.
Disseminating Threat Intelligence to Stakeholders
Threat Intelligence will be shared with the Management Review Team as part of the regular structured agenda.
Using Threat Intelligence for Continual Improvement
Threat Intelligence that identifies emerging and existing threats will be managed via the Risk Management Process and any changes or improvements will be managed via the Continual Improvement Process.
How to implement ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7
Implementing ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 requires a shift from passive security to proactive situational awareness. By formalising the collection and analysis of threat data, organisations can identify emerging risks before they manifest into incidents. This action-orientated guide provides the technical steps necessary to establish a compliant threat intelligence programme that satisfies the 2022 standard requirements.
1. Formalise the Threat Intelligence Policy and Scope
Establish a documented framework that defines the objectives, sources, and internal stakeholders for your threat intelligence activities. This action results in a standardised governance layer that ensures intelligence is collected legally, ethically, and in alignment with organisational risk appetite.
- Define the specific technical and business assets that require monitoring based on your Statement of Applicability (SoA).
- Document the “Rules of Engagement” (ROE) for how intelligence is handled and shared internally to prevent unauthorised disclosure.
- Identify Strategic, Operational, and Tactical intelligence requirements relevant to your industry vertical.
2. Provision Internal and External Intelligence Sources
Configure a diverse array of data feeds to provide a holistic view of the threat landscape. This result-focused step ensures that your security team has access to real-time indicators of compromise (IoCs) and high-level actor motives.
- Subscribe to government-backed advisories such as the NCSC (UK) or CISA (US) for national-level threat alerts.
- Provision commercial threat feeds or open-source intelligence (OSINT) tools to monitor for leaked credentials and domain masquerading.
- Integrate internal telemetry from Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) logs to identify localised attack patterns.
3. Execute Systematic Threat Analysis and Categorisation
Implement a process to filter and analyse raw data into actionable intelligence. This action results in the prioritisation of threats, ensuring that your security resources are not overwhelmed by low-fidelity alerts or irrelevant data.
- Categorise intelligence into Tactical (IoCs), Operational (TTPs), and Strategic (landscape trends).
- Utilise the MITRE ATT&CK framework to map threat actor behaviours against your existing technical controls.
- Assess the reliability and relevancy of each source to reduce false positives in your alerting systems.
4. Integrate Intelligence into Risk Assessment and Technical Controls
Apply analysed intelligence to your existing Information Security Management System (ISMS) workflows. This result-oriented step ensures that threat data leads to tangible security improvements, such as updated firewall rules or refined risk scores.
- Update your Risk Register based on emerging threats identified through Strategic intelligence reports.
- Provision automated blocklists in your Web Application Firewall (WAF) and EDR solutions using Tactical IoCs.
- Adjust Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles and MFA requirements in response to increased credential-stuffing threats.
5. Execute Continuous Monitoring and Management Review
Establish a recurring review cycle to evaluate the efficacy of your threat intelligence programme. This action ensures the programme remains effective as the threat landscape evolves and satisfies the auditor’s requirement for continuous improvement.
- Conduct monthly security briefings for management to communicate high-level Strategic threat trends.
- Audit the performance of commercial feeds to ensure they provide a high return on investment (ROI) in terms of unique detections.
- Maintain an evidence log of technical actions taken in response to intelligence for your next ISO 27001 audit.
Selecting Threat Intelligence Sources: Internal vs. External
There are free sources of threat intelligence information that you can use. These can be internal or external so let us take a look at examples of threat intelligence sources you can use:
Internal Sources of Threat Intelligence
The controls and processes that you operate will provide valuable threat intelligence information that you will identify through trend analysis and incident management. The examples include:
- Anti-Virus and Malware Protection Reports
- Information Security Incident Reports
- Phishing Reports
- Internal Audit Reports
- Helpdesk Tickets
- Log Files
External Sources of Threat Intelligence
External sources of threat intelligence are readily available from vendors and government websites. The following are examples:
- UK National Cyber Security Centre
- CISA.gov – Official website of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security
- SANS™ Internet Storm Center
- Vendor feeds
- Government alerts
- News sites
Comparing Threat Intelligence Sources
To build an effective threat intelligence capability, you cannot rely on a single source of information. ISO 27001 requires you to select a balanced mix of sources that cover both internal reality (what is happening to you now) and external risks (what is happening to others).
Relying solely on one type leaves blind spots. For example, external feeds might warn you of a new ransomware strain, but only internal logs will tell you if it has already breached your firewall. Use the comparison table below to determine which source types are relevant for your organization.
| Source Type | Examples | Best For |
| Strategic (External) | CISA Alerts, ENISA Reports | High-level risk planning |
| Tactical (External) | Vendor Feeds (CrowdStrike, etc.) | Blocking specific attacks |
| Internal | Firewall Logs, SIEM Alerts | Detecting active breaches |
| Community | ISACs, Industry Forums | Peer-to-peer warning |
The threat intelligence reporting process
When you collect the threat intelligence information you are going to report on it so you can act on it. The process for threat intelligence reporting, based on practical real world experience would be:
- A Threat Intelligence Report is created.
- The Threat Intelligence Report is shared with The Management Review Team.
- The Threat Intelligence Report is shared at least at the Management Review Team Meeting and if a significant threat is identified.
- Threat Intelligence Reports are kept for at least 12 months.
- Progress of Threat Mitigation is reported via the Risk Management Process and Continual Improvement Process as relevant.
The contents of the threat intelligence report
The Threat Intelligence Report gives a high-level threat snapshot summary. When creating the threat intelligence report it would include:
- Threat Summary: A summary in simple of terms of the threat that can be understood by someone with no technical knowledge.
- Source: The source of the threat. Either a link or a description in words of how the threat was identified.
- Threat Level: Using a simple, easy to understand rating of High / Medium and Low the initial rating is a subjective rating on the potential risk and impact to the organisation. The objective rating will be derived as part of the risk management process.
For each threat in the summary table a more detailed report is provided that includes recommendations on next steps, whether it is added to the risk register and if so a risk reference.
How to create a threat intelligence process and report in under 10 minutes
In this video tutorial I show you How to create a Threat Intelligence Process in Under 10 Minutes
If you are wanting to do this yourself I show you How To Create an ISO 27001 Threat Intelligence Process and Report in this step-by-step implementation guide.

Free vs. Paid Sources Table
| Layer | Focus | Free Source Example | Paid Source Example |
| Strategic | High-level trends for C-Suite. | ENISA Threat Landscape, Verizon DBIR. | Gartner Reports. |
| Tactical | Attack methods (TTPs) for IT Admins. | MITRE ATT&CK, Vendor Blogs (CrowdStrike). | Mandiant Advantage. |
| Operational | IP addresses/hashes for Firewalls. | AlienVault OTX, Abuse.ch. | Anomali, Recorded Future. |
How to comply
To comply with ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 you are going to implement the ‘how’ to the ‘what’ the control is expecting. In short measure you are going to:
- Establish and document objectives for threat intelligence production
- Identify, vet, list and document internal and external sources of information
- Collect the information
- Prepare the information for analysis for example by formatting or translating it
- Analyse information to understand how it relates to you
- Communicate and share information to relevant people in a way they will understand it
How to pass the audit of ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7
To pass an audit of ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Threat Intelligence you are going to make sure that you have followed the steps above in how to comply.
What will an auditor check?
The audit is going to check a number of areas. Lets go through the main ones
1. That you are gathering threat intelligence and analysing it
What this means is that you need to show that you have a list of sources of threat intelligence information, have records of collecting and show reports where you have shared and communicated it.
2. That you have taken action as a result of threat intelligence
The process may be straightforward. You may have updated a system, changed a configuration, introduced or removed a tool, had an incident that was managed via the incident management process. What ever the course of action you will have records of action taken and audit trails.
3. That threat intelligence forms part of risk management and operations
Your risk management process will factor in and evidence threat intelligence. Your risk register may take account of threat intelligence and emerging or realised risks.
Top 3 Mistakes Implementing Threat Intelligence
In my experience, the top 3 Mistakes People Make For ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Threat Intelligence are
1. You are not collecting or using threat intelligence
This is a new control so one that is easy to overlook. Make sure to follow the control requirements and be able to evidence its operation.
2. You rely only on internal threat intelligence
Internal threat intelligence is easy to collect but does not provide for the wider picture. Be sure to include external sources of threat intelligence data.
3. Your document and version control is wrong
Keeping your document version control up to date, making sure that version numbers match where used, having a review evidenced in the last 12 months, having documents that have no comments in are all good practices.
Applicability of ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 across different business models.
| Business Type | Applicability & Interpretation | Examples of Control |
|---|---|---|
| Small Businesses |
Vendor-Led Intelligence. You don’t need a SOC. Your “Threat Intel” is simply listening to your vendors (Microsoft, Apple, Xero) when they tell you to patch. Ignorance is no longer an excuse. |
• Newsletter Subscription: Subscribing to a basic alert feed like the NCSC (UK) or CISA (US) for “Critical” warnings only. |
| Tech Startups |
Dependency Scanning. Your biggest threat is likely a vulnerability in an open-source library you use. “Tactical” intelligence means knowing which |
• Automated Feeds: Using tools like GitHub Dependabot or Snyk to pull real-time CVE data directly into your Pull Requests. |
| AI Companies |
Adversarial AI Intel. Standard firewalls don’t catch “Prompt Injection” attacks. You need intelligence on how attackers are manipulating models similar to yours. |
• MITRE ATLAS: Monitoring the “Adversarial Threat Landscape for Artificial-Intelligence Systems” (ATLAS) for new attack vectors. |
Fast Track ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
For ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 (Threat intelligence), the requirement is to collect and analyze information regarding information security threats so that mitigation action can be taken. This is a new control (introduced in 2022) that focuses on being proactive rather than just reactive.
| Compliance Factor | SaaS Compliance Platforms | High Table ISO 27001 Toolkit | Audit Evidence Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy Ownership | Rents access to threat data; if you cancel the subscription, your documented threat reports and source list history vanish. | Permanent Assets: Fully editable Word/Excel Threat Intelligence Processes and Templates you own forever. | A localized “Threat Intelligence Source List” identifying specific government (CISA/NCSC) and vendor alert feeds. |
| Analytic Utility | Attempts to “automate” intelligence via generic feeds that cannot interpret how a global exploit affects your specific business risk. | Governance-First: Provides the framework for your team to triage and analyze threats that actually matter to your stack. | A completed “Threat Intelligence Report” proving that an emerging vulnerability was analyzed and mitigated. |
| Cost Efficiency | Charges an “Intelligence Feed Tax” for automated alerts that are often available for free from government and vendor sources. | One-Off Fee: A single payment covers your threat governance for 3 sources or 30, with zero recurring costs. | Allocating budget to actual security patching or firewall upgrades rather than monthly “SIEM-lite” dashboard fees. |
| Operational Freedom | Mandates rigid reporting formats that often fail to align with agile business models or unique, custom technical stacks. | 100% Agnostic: Procedures adapt to your workflow—from weekly manual reviews to dedicated security team analysis. | The ability to evolve your threat strategy (e.g., adding dark web monitoring) without reconfiguring a rigid SaaS module. |
Summary: For Annex A 5.7, the auditor wants to see a “Chain of Action”, that you have a list of sources, you analyze them, and you take action based on that analysis. The High Table ISO 27001 Toolkit provides the governance framework to satisfy this requirement immediately. It is the most direct, cost-effective way to achieve compliance using permanent documentation that you own and control.
ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 FAQ
What is ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7?
ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 is a new organisational control introduced in the 2022 update that requires organisations to collect and analyse information about information security threats to provide situational awareness.
- Focuses on identifying threat actors, their motives, and their methods.
- Requires information to be categorised into strategic, operational, and tactical levels.
- Aims to shift security posture from reactive to proactive.
- Mandates that collected intelligence is used to inform risk assessments and technical controls.
Is threat intelligence mandatory for ISO 27001:2022?
Yes, Annex A 5.7 is mandatory if it is identified as a necessary control within your Statement of Applicability (SoA) following a formal risk assessment.
- Most organisations handling digital data will find this control applicable.
- Auditors expect to see a documented process for how intelligence is gathered.
- Exclusions must be strictly justified in the SoA.
- Compliance is required for all organisations transitioning from the 2013 to the 2022 standard.
What are the three levels of threat intelligence required?
To comply with Annex A 5.7, organisations should ideally process intelligence at three distinct levels: Strategic, Operational, and Tactical.
- Strategic: High-level information about the changing threat landscape (e.g., new regulations or types of threat actors).
- Operational: Specific information about the TTPs (Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures) used by attackers.
- Tactical: Real-time technical indicators of compromise (IoCs), such as malicious IP addresses, URLs, or file hashes.
What are examples of threat intelligence sources?
Organisations can gather threat intelligence from a variety of internal, external, and community-based sources to satisfy ISO 27001 requirements.
- Government advisories such as the NCSC (UK) or CISA (US).
- Industry-specific ISACs (Information Sharing and Analysis Centres).
- Commercial threat intelligence feeds and security vendor reports.
- Open-source intelligence (OSINT) and community forums.
How do auditors check ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 compliance?
Auditors look for evidence that threat intelligence is not just being collected, but is actually being used to drive security decisions and mitigate risks.
- Verification of subscriptions to relevant threat feeds or advisory lists.
- Documented procedures for the collection and analysis of threat data.
- Evidence of meeting minutes showing threat intelligence was discussed by management.
- Proof of technical changes (e.g., firewall rule updates) made in response to specific intelligence.
What is the difference between threat intelligence and vulnerability management?
The primary difference is that vulnerability management (Annex A 8.8) focuses on internal weaknesses, while threat intelligence (Annex A 5.7) focuses on external threats.
- Threat Intelligence identifies who might attack and how they operate.
- Vulnerability Management identifies the holes in your systems that could be exploited.
- The two controls work together: TI helps prioritise which vulnerabilities to patch first.
- TI is proactive (looking outward), whereas VM is often preventative (looking inward).
Summary: Your ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Implementation Roadmap
Implementing threat intelligence is a continuous cycle of detection and response. Use the infographic below as a quick-reference guide or “Cheat Sheet” to ensure you have covered all the essential layers of threat intelligence required for your audit.

Further Reading
How to Implement ISO 27001:2022 Annex A 5.7: Turning Information into Defence
How to Audit ISO 27001:2022 Annex A 5.7: Threat Intelligence
ISO 27001:2022 Annex A 5.7 for Small Business: Security Smarts on a Budget
ISO 27001:2022 Annex A 5.7 for AI Companies: Knowing Your Enemy
ISO 27001:2022 Annex A 5.7 for Tech Startups: Smart Defense, Not Just Data
Related ISO 27001 Controls
ISO 27001 Annex A 7.5 Protecting Against Physical and Environmental Threats
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.15 Logging
ISO 27001 Clause 9.1 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis, Evaluation
ISO 27001 Controls and Attribute Values
| Control type | Information security properties | Cybersecurity concepts | Operational capabilities | Security domains |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preventive | Confidentiality | Identify | Threat and vulnerability management | Defence |
| Corrective | Integrity | Detect | Resilience | |
| Detective | Availability | Respond |
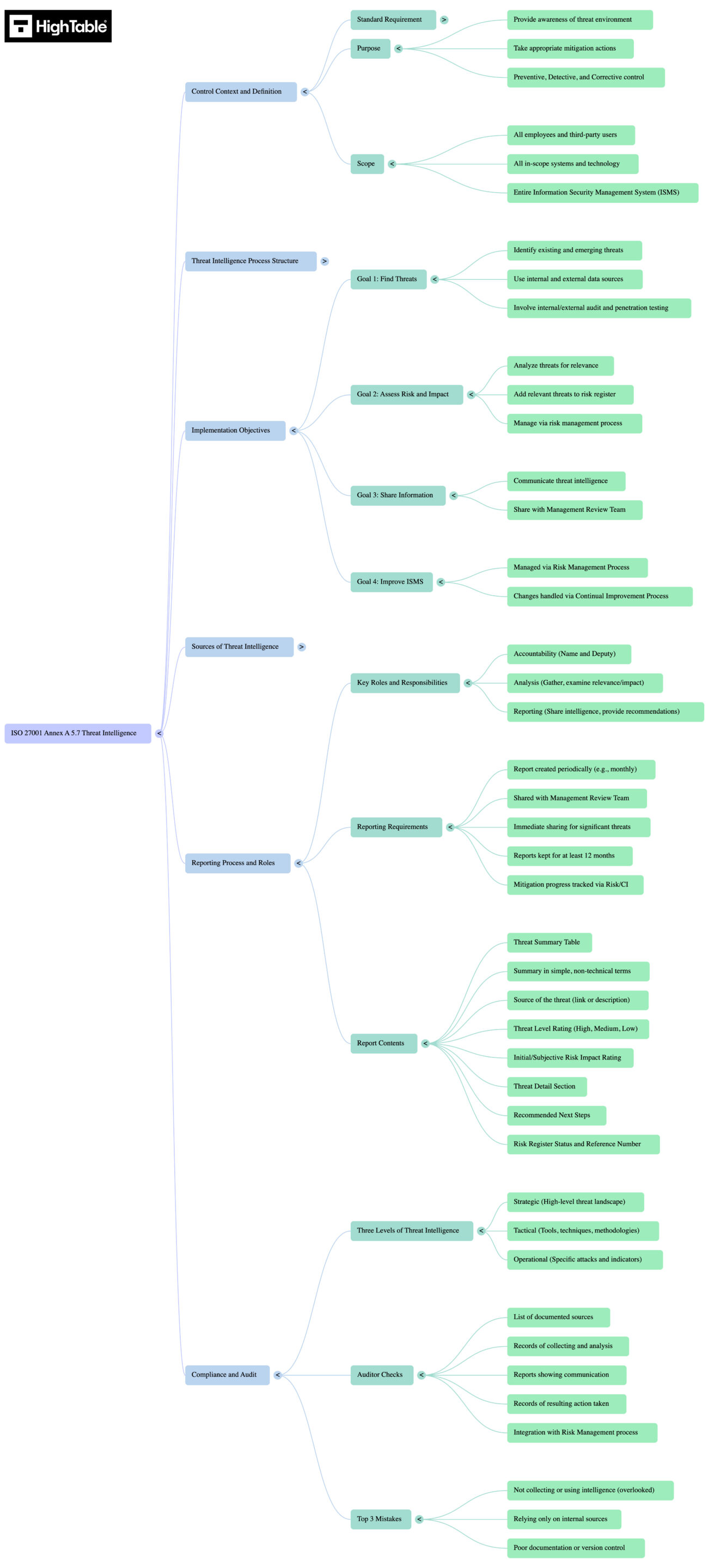
ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 Mind Map
Navigating the requirements of ISO 27001 Annex A 5.7 goes beyond simply installing antivirus software; it requires a holistic approach that links policy, technical controls, and human behaviour. To help you visualise the complete compliance landscape, the mind map below breaks down the control into six actionable pillars, ranging from the initial control context and definition to the ongoing audit process.