ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 is a security control that mandates personnel doing work under the organization’s control remain aware of the information security policy and their role. The primary implementation requirement involves structured communication and verified training to ensure a robust business benefit of human-centric risk mitigation.
In this guide, I will show you exactly how to implement ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 and ensure you pass your audit. You will get a complete walkthrough of the control, practical implementation examples, and access to the ISO 27001 templates and toolkit that make compliance easy.
I am Stuart Barker, an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor with over 30 years of experience conducting hundreds of audits. I will cut through the jargon to show you exactly what changed in the 2022 update and provide you with plain-English advice to get you certified.
Key Takeaways
- Awareness is a core requirement: The clause’s main goal is to make sure everyone in the organisation is aware of information security risks and their role in the Information Security Management System (ISMS).
- Structured approach is key: A successful awareness program requires defining clear objectives, identifying specific target audiences, and creating engaging, relevant content.
- Continuous process: Awareness is not a one-time event. It should be integrated throughout an employee’s journey, from onboarding to the end of their employment.
- Senior management responsibility: Senior management is responsible for implementing and maintaining this clause, emphasising the importance of building a strong information security culture.
Table of contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is ISO 27001 Clause 7.3?
- Applicability of ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 across different business models.
- Watch the ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Video Tutorial
- How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 7.3
- ISO 27001 Awareness Plan
- ISO 27001 Communication Plan
- How to Measure ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Effectiveness
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Awareness Templates
- How to use an Awareness and Training tool
- How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 7.3
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Audit Checklist
- How to pass the ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 audit
- Top 3 ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Mistakes and How to Fix Them
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Top Non Conformities
- Using YouTube for ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Awareness
- Fast track ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.3: Related Controls & Clauses
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Mapped to other Standards
- Awareness Triggers: Integrating Threat Intelligence
- Navigating the “Auditor’s Evidence Trap”
- Closing the “Interested Parties” Gap (Clause 4.2 Alignment)
- Integrating with Clause 4.2
- The Role-Based Awareness Matrix
- The Remote & Hybrid Awareness Nuance
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.3: Awareness FAQ
- Related ISO 27001 Controls
- Further Reading
What is ISO 27001 Clause 7.3?
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 is awareness and requires you to communicate and make people aware of the information security policy, how they contribute to information security and the consequences of not conforming to information security.
The ISO 27001 standard for ISO 27001 certification wants you to let people know what you expect, educate them and have processes in place for if things go wrong.
Purpose and Definition
The purpose of ISO 27001 clause 7.3 Awareness is to make sure people are aware of information security and what they need to do. It is part of implementing a culture of information security into the organisation.
The ISO 27001 standard defines ISO 27001 clause 7.3 Awareness as:
Persons doing work under the organisation’s control shall be aware of: a) the information security policy; b) their contribution to the effectiveness of the information security management system, including the benefits of improved information security performance; and c) the implications of not conforming with the information security management system requirements.
ISO 27001:2022 Clause 7.3 Awareness
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Requirement
The requirement is to tell people what is expected of them and explain to them the consequences of not doing what is expected when it comes to information security.
Applicability of ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 across different business models.
| Business Type | Applicability | Why it is Important | Examples of Clause 7.3 Awareness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Businesses | Applies to all staff, contractors, and third parties operating within the scope of the small business’s ISMS. | Mitigates the high risk of human error in small teams where one person often wears multiple hats. | Policy induction packs and physical security reminders in common office areas. |
| Tech Startups | Critical for developers and product teams handling proprietary source code and cloud infrastructure. | Accelerates “Enterprise Readiness” by proving the “human firewall” is as robust as the tech stack. | Secure coding workshops and automated, simulated phishing campaigns. |
| AI Companies | Essential for data scientists and ML engineers managing massive, sensitive training datasets. | Prevents accidental PII leakage or model poisoning through unauthorized data handling. | Training on data masking, PII protection, and incident response for data breaches. |
Watch the ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Video Tutorial
In this ISO 27001 tutorial How to Implement ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Awareness I show you how to implement it and how to pass the audit.
How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 7.3
There are distinct phases in the journey of staff, contractors and third parties.
Each of those phases potentially requires a different level of communication.
It is possible that one approach will work but the likelihood is you are going to have different communication styles and approaches depending on the ‘who’ and the ‘where’ they are in their journey with you.
In this step by step implementation checklist to ISO 27001 awareness I show you, based on real world experience and best practice, the best way to implement Clause 7.3.
Implementing ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 requires a transition from passive information delivery to a proactive culture of security accountability. By aligning awareness activities with specific risk profiles and technical controls, you ensure that every individual understands their role in protecting the Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Define Objectives and Formalise Policy
Provision clear, measurable goals for your awareness programme that align with the broader ISMS objectives and results from your latest risk assessment.
- Formalise an Information Security Training and Awareness Policy to set expectations for staff, auditors, and clients.
- Conduct workshops across departments to identify specific awareness needs based on functional roles and responsibilities.
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to track success, such as a targeted percentage reduction in successful simulated phishing clicks.
Identify Target Audiences and Role-Based Requirements
Categorise all personnel, including contractors and third-party stakeholders, to deliver tailored security content relevant to their specific access levels.
- Audit the Asset Register and IAM roles to identify high-risk groups, such as System Administrators or Finance teams.
- Provision specialised training for technical staff covering secure configuration, log monitoring, and incident response.
- Formalise requirements for “interested parties” and contractors, ensuring they are aware of the Rules of Engagement (ROE) and Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs).
Develop and Distribute High-Impact Content
Formalise a diverse suite of awareness materials that communicate the Information Security Policy and the personal consequences of non-conformity.
- Provision accessible versions of the Information Security Policy, highlighting sections on Acceptable Use, Home Working, and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) protocols.
- Create engaging, jargon-free content using gamification, micro-learning modules, and real-world scenarios to increase retention.
- Utilise various channels, such as internal newsletters, posters, and digital prompts, to ensure continuous engagement throughout the year.
Execute Lifecycle-Based Training
Provision mandatory security training at every stage of the employee lifecycle, from initial onboarding to final offboarding.
- Execute a dedicated face-to-face induction session for new starters covering incident reporting, policy locations, and their specific contribution to security.
- Provision annual refresher courses for general security and Data Protection (GDPR) to maintain a baseline level of vigilance across the workforce.
- Communicate contractual obligations and remaining security requirements during the offboarding process for ending employment or engagements.
Provision Technical Training Tools and Automation
Implement a dedicated information security training tool to automate scheduling, verify understanding, and generate compliance reports.
- Provision an online platform to deliver pre-built, annually refreshed content that staff can access from any location.
- Execute simulated threat exercises, such as mock phishing campaigns, to test real-world behavioural responses.
- Audit training completion logs and verification results automatically to ensure 100% participation across all departments.
Audit Effectiveness and Promote Culture
Audit the effectiveness of your awareness initiatives by measuring behavioural changes and fostering a culture of collective responsibility.
- Document all awareness activities, including attendance logs and evaluation results, within a centralised system for ISO 27001 audit readiness.
- Review incident logs to determine if training has led to an increase in proactive security event reporting and a decrease in human-error risks.
- Revoke or update outdated training materials based on emerging threats, industry trends, and lessons learned from internal security incidents.
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Implementation Checklist
Effective implementation of ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 does not require expensive Learning Management Systems (LMS) or bloated GRC platforms. In fact, relying on SaaS tools often creates complexity and vendor lock-in. The most robust audit evidence is often the simplest: a signed document or a well-maintained spreadsheet. Use this checklist to implement awareness controls using tools you already own.
| Step | Action | Common Challenge (The SaaS Trap) | The Solution (High Table Approach) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Formalise Awareness Objectives | Buying generic “Security 101” modules that don’t align with your actual business risks. | Provision targeted objectives based on your Risk Register. Focus on real-world issues like MFA usage and social engineering. |
| 2 | Execute Role-Based Inductions | Sending a mass email with a link to a PDF policy that no one reads or signs. | Formalise face-to-face or video-call inductions for new starters. Get a digital signature on an “Acceptable Use Policy” as immediate evidence. |
| 3 | Distribute Targeted Content | Paying for monthly “Security Newsletters” that end up in the spam folder or are ignored. | Provision micro-learning content via existing channels like Slack, Teams, or Town Halls. Use real internal “near-miss” examples. |
| 4 | Verify Policy Awareness | Software that tracks “clicks” but doesn’t prove the employee actually understands the policy. | Audit understanding through simple, 5-question MS Forms or Google Forms quizzes. Record the scores in a central spreadsheet. |
| 5 | Execute Simulated Threat Testing | Expensive automated phishing platforms that staff learn to “game” rather than learn from. | Provision manual, unpredictable phishing tests. Use the results to offer immediate, constructive feedback to those who fail. |
| 6 | Maintain Evidence Trail | Scattered data across multiple SaaS platforms that is difficult to export during an audit. | Formalise a single “Awareness Evidence” folder. Store signed ROE documents, quiz results, and attendance logs in one place. |
ISO 27001 Awareness Plan
An ISO 27001 Awareness Plan is a strategic roadmap designed to ensure that every individual within your organisation understands their security responsibilities. Unlike a generic training schedule, a high-performance plan focuses on continuous engagement and measurable behavioural change. By aligning awareness activities with the specific risks identified in your ISMS, you transform employees from potential security liabilities into a proactive “human firewall.”
Implementation Overview
The following plan outlines a typical 12-month cycle. It balances mandatory annual requirements with “just-in-time” training triggered by specific events (like onboarding) or emerging threats (like new phishing trends).
| Activity Type | Frequency | Target Audience | Example Content & Delivery | Objective / Clause Alignment |
| Security Induction | Upon Hire | New Starters | Provision a 30-minute face-to-face or virtual session covering Policy locations, Incident Reporting, and MFA setup. | Onboarding: Immediate compliance with Clause 7.3. |
| Annual Refresher | Annually | All Personnel | Execute a micro-learning module on Data Protection (GDPR) and the current Information Security Policy updates. | Compliance: Verifies ongoing understanding of obligations. |
| Phishing Simulation | Quarterly | All Personnel | Provision a simulated “Urgent Invoice” email. Redirect “clickers” to a 2-minute “How to Spot a Phish” video. | Behavioural: Reduces risk of social engineering. |
| Technical Deep-Dive | Bi-Annually | IT & Dev Teams | Formalise workshops on secure coding (OWASP) or IAM role-based access review procedures. | Technical: Aligns with Clause 7.2 (Competence). |
| Executive Briefing | Annually | Senior Leadership | Audit a summary of ISMS performance, resource needs, and the personal liability of directors. | Leadership: Demonstrates Top Management commitment (Clause 5). |
| Monthly Tips | Monthly | All Personnel | Distribute short “Security Spotlights” via Slack/Teams regarding Clear Desk policy or public Wi-Fi risks. | Engagement: Maintains continuous awareness culture. |
| Offboarding Review | On Departure | Leavers | Communicate remaining contractual obligations and NDAs during the exit interview. | Risk Mitigation: Prevents data leakage post-employment. |
ISO 27001 Communication Plan
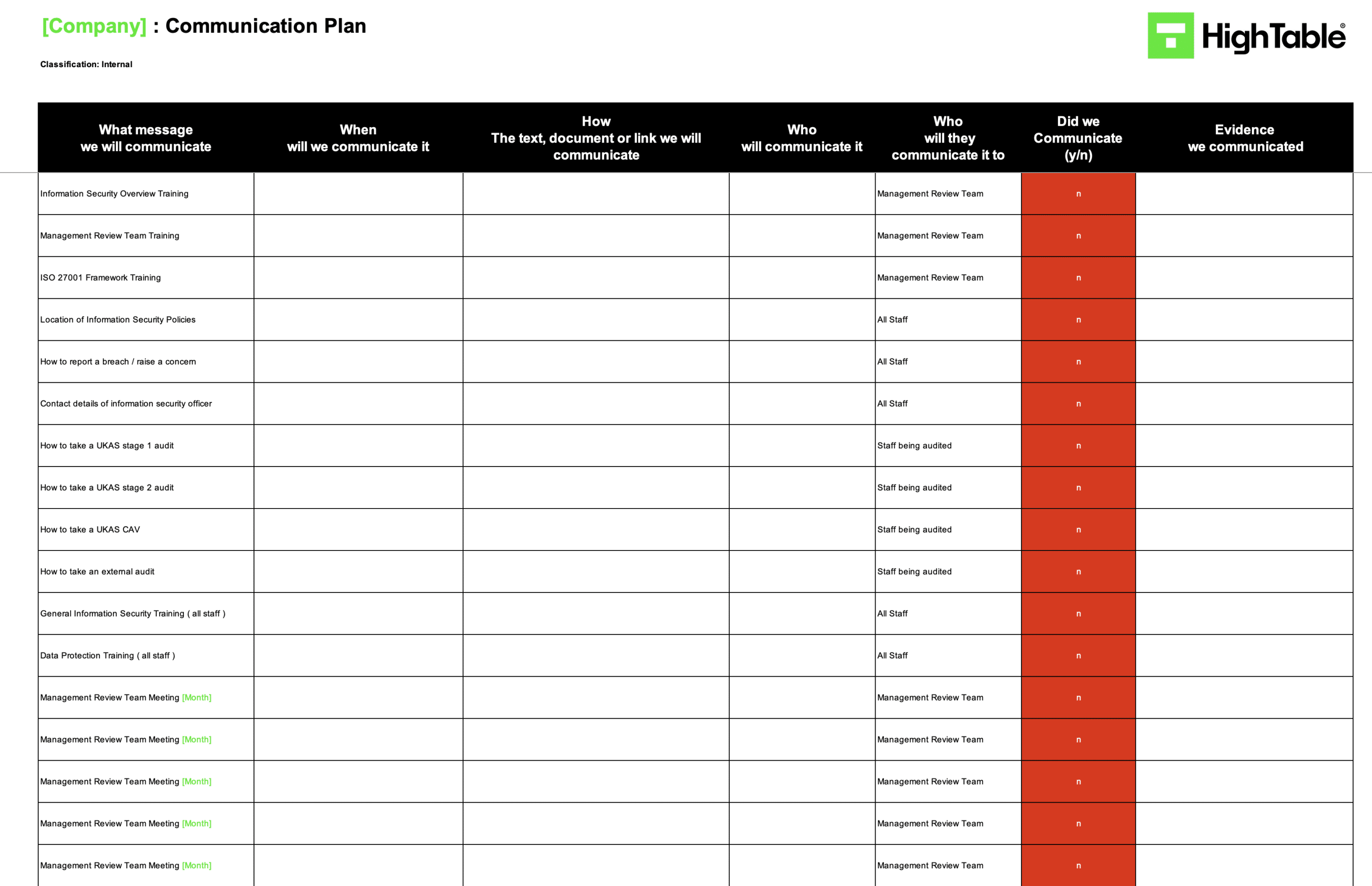
How to Measure ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Effectiveness
Measuring the effectiveness of your awareness programme is a critical requirement of ISO 27001 Clause 7.3. Auditors are no longer satisfied with simple “attendance logs”; they require evidence that the training has resulted in actual behavioural change and increased knowledge.
To satisfy the “effectiveness” requirement, you must move from quantitative metrics (how many people attended) to qualitative metrics (how much did they learn and how has their behaviour improved).
The Measurement Strategy
Effective measurement should be integrated into your internal audit cycle. By comparing baseline data (e.g., initial phishing click rates) against post-training results, you can provide objective evidence of ISMS maturity. This data-driven approach allows you to Audit the success of your programme and Revoke or update content that is failing to resonate with staff.
| Metric Category | Primary Measurement Method | Example KPI | Audit Evidence Provided |
| Knowledge Retention | Post-Training Quizzes | 85% or higher average score on the Annual Security Refresher quiz. | Formalise verified understanding of the Information Security Policy. |
| Behavioural Change | Simulated Phishing Campaigns | A 50% reduction in “click rates” over a six-month period. | Provision evidence of improved resilience against social engineering. |
| Operational Vigilance | Incident Reporting Rates | An increase in the number of “Near-Miss” or suspicious email reports sent to IT. | Audit the growth of a proactive security culture where staff take ownership. |
| Policy Compliance | Spot Checks / Physical Audits | Zero instances of unlocked screens or sensitive documents left on desks during a “Clear Desk” walkthrough. | Formalise real-world application of Acceptable Use Policies. |
| User Confidence | Periodic Awareness Surveys | 90% of staff feel “confident” or “highly confident” in identifying a security threat. | Evaluate the clarity and accessibility of your training materials. |
| Technical Competence | Helpdesk Ticket Analysis | Reduction in tickets related to forgotten passwords or MFA lockout issues post-training. | Audit the reduction in human-induced technical friction. |
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Awareness Templates
For ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Awareness the entire ISO 27001 toolkit is relevant but in particular the following templates directly support this ISO 27001 clause:
ISO 27001 Training and Awareness Policy Template
The ISO 27001 Training and Awareness Policy template sets out what you do and what must be done For ISO 27001 clause 7.3.

ISO 27001 Communication Plan Template
The ISO 27001 Communication Plan Template is used to plan communications on information security including training and awareness for the year ahead and to record evidence that those communications happened which will be required at the ISO 27001 certification audit.

How to use an Awareness and Training tool
In this day and age, one of the few times we would recommend using a tool is for information security training. These tools come with pre-built courses and allow for the automation of many required awareness tasks. Scheduling awareness training, verifying understanding, and reporting capabilities are must-haves. These tools refresh content annually, saving you time and effort, and include popular modules on relevant topics. Being online, they can be accessed by staff from anywhere. While not the only way to raise and manage awareness, they do the lion’s share of the work.
Of course, you should consider your company culture and supplement the training accordingly. Emails are useful, as are stand-up meetings, presentations at company meetings, and perhaps bringing in external resources. There’s no one-size-fits-all answer, but training tools go a long way for those who are time-poor and simply want to get the job done efficiently.
How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 7.3
To audit ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 (Awareness) effectively, an auditor must move beyond verifying that a training video was played. The goal is to confirm that the “Human Firewall” is operational and that the security culture is reflected in daily habits.
| Audit Step | Audit Objective | Audit Techniques & Evidence |
| 1. Review Awareness Objectives | Verify that the organisation has defined clear and measurable security awareness objectives aligned with the ISMS and risk assessment. | Audit documented objectives and interview management to understand the rationale. Check for alignment with overall ISMS goals and specific risk treatment plans. |
| 2. Confirm Target Audience Identification | Ensure the organisation has identified different target audiences and tailored programmes to their specific needs. | Review documentation such as role descriptions and training needs analysis. Interview employees from diverse roles to confirm they receive content relevant to their specific access levels. |
| 3. Evaluate Awareness Content | Assess the quality and relevance of materials, including presentations, videos, and communication assets. | Review materials for accuracy, clarity, and engagement. Observe a training session if possible and interview participants for feedback on content practicalities. |
| 4. Check Training Delivery Methods | Verify the use of appropriate delivery methods (e.g., face-to-face, digital, gamification) based on the audience and information type. | Provision training records to confirm completion and attendance. Interview employees regarding the effectiveness of the delivery format and their preferred learning styles. |
| 5. Assess Communication Frequency | Determine if the organisation communicates security awareness regularly and through appropriate, varied channels. | Examine communication logs, intranet posts, and newsletters. Interview employees to gauge their actual awareness of the most recent security broadcasts or “Tips of the Month.” |
| 6. Verify Reinforcement Activities | Confirm that awareness is reinforced through daily operations and a security-conscious culture. | Observe work practices (e.g., clear desk/screen). Review internal procedures for security reminders and interview staff on how security is integrated into their daily tasks. |
| 7. Evaluate Effectiveness Measurement | Check if the organisation measures success through surveys, quizzes, simulated phishing, or incident analysis. | Review reports on phishing campaign data, quiz results, and incident trends. Interview management on how this data influences the improvement of the programme. |
| 8. Confirm Review & Update Process | Verify that awareness programmes are regularly updated to maintain relevance against emerging threats. | Examine the process and frequency for updating materials. Check version control on training assets to ensure they reflect current threats (e.g., AI-driven social engineering). |
| 9. Inspect Documentation | Ensure the organisation maintains adequate, accessible records of all awareness activities. | Review training logs, communication records, and evaluation results. Verify that records are complete, accurate, and readily accessible for the audit trail. |
| 10. Assess Security Culture | Evaluate the overall security culture, including risk awareness, incident reporting, and management commitment. | Execute employee interviews and observe behaviour. Look for evidence of management “leading by example” and an environment where staff feel empowered to report security concerns. |
Audit Evidence Checklist
- Documentary Evidence: Training registers, signed Acceptable Use Policies, phishing simulation reports, and Management Review minutes.
- Observational Evidence: Clean desk checks, presence of security posters, and staff correctly using MFA during login.
- Testimonial Evidence: Staff ability to explain the process for reporting a lost laptop or a suspicious phone call.
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Audit Checklist
To audit ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 (Awareness) effectively, you must verify that security is a lived experience within the organisation rather than a checkbox on a HR portal. This checklist is designed for the “High Table Approach”, prioritising internal evidence and observed behaviour over generic SaaS reporting.
| Audit Step | Audit Action | Required Evidence (The ‘Owned’ Way) | Common Non-Conformity Flags (Red Flags) |
| 1. Policy Awareness | Verify that staff know the Information Security Policy exists and where to find it. | Audit a random sample of employees. Ask them to locate the policy on the internal server or intranet. | Personnel are unaware that a security policy exists or cannot access it without asking a manager. |
| 2. Individual Contribution | Confirm staff understand how their specific actions protect the ISMS. | Execute desk-side interviews. Ask: “How does your daily work impact the company’s security objectives?” | Staff believe security is “only an IT problem” and have no personal accountability for data protection. |
| 3. Risk of Non-Conformity | Ensure staff understand the repercussions of a security breach or policy violation. | Review training content for “consequence” slides. Verify staff can explain the impact of a lost device or data leak. | The awareness programme lacks any mention of the implications of failing to follow security protocols. |
| 4. Incident Reporting | Validate that the process for reporting a security event is universally understood. | Provision a test scenario (e.g., “You found a USB in the car park”). Observe if staff know exactly who to contact. | Employees do not know how to raise an incident or are afraid to report “near-misses” for fear of blame. |
| 5. Onboarding Controls | Check that security awareness begins on day one of employment. | Formalise a cross-check between HR joiner lists and signed “Security Induction” attendance sheets. | New starters have system access but haven’t received a security briefing or signed the Acceptable Use Policy. |
| 6. Continuous Engagement | Verify that awareness is an ongoing process, not a “once-a-year” event. | Examine your communication logs. Look for evidence of “Security Tips,” posters, or Slack/Teams broadcasts throughout the year. | The only evidence of awareness is a single training log from 11 months ago with no interim reinforcement. |
| 7. Behavioural Testing | Confirm the organisation tests the effectiveness of the training. | Audit the results of the latest simulated phishing campaign and the subsequent remediation for those who failed. | No testing is conducted, or the testing is so predictable that it doesn’t represent real-world threats. |
| 8. Record Accuracy | Ensure all awareness activities are documented and retrievable. | Inspect a central “Awareness Evidence” folder containing logs, quiz results, and signed induction records. | Gaps in attendance records where senior management or long-term contractors are missing from the logs. |
How to pass the ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 audit
The easiest way is to have a training tool that records people’s understanding by presenting with training and what you want them to be aware of and then has them take a test which you can report.
Having a communication plan that records what you communicated, when, to whom and the evidence that you did is also part of showing compliance to the clause.
There is a place for the signing of policies to accept them and the way you do this can be via traditional signature (which is clunky but doable), electronic signature, or an email to you that they have read and accept them. There are many ways to skin a cat.
The “Auditor Interview” Cheat Sheet
Auditors will randomly interview staff to verify that security awareness is a lived reality, not just a document on a server. They will not ask, “Tell me about Clause 7.3.” They will ask practical, situational questions to test the “human firewall.” Distribute this cheat sheet to your team to prepare them for an audit:
| If the Auditor asks… | Do NOT say… | DO say… |
| “Where is the company security policy?” | “I think HR has it in a folder somewhere.” | “It is available to everyone on the Company Intranet/SharePoint. I reviewed and signed the Acceptable Use Policy during my induction.” |
| “What happens if you don’t follow the security rules?” | “I’m not sure, I’ve never been in trouble.” | “The company has a formal disciplinary process outlined in our policies. Breaching security is a serious matter that affects the whole business.” |
| “How do you contribute to the security of the business?” | “I don’t really, I just do my admin/coding/sales.” | “I protect the ISMS by using MFA, following the Clear Desk Policy, and ensuring I only share sensitive data via approved, encrypted channels.” |
| “How would you report a security incident?” | “I’d probably just tell my manager or call IT.” | “I follow the Incident Reporting Procedure. I would immediately log it via the [Helpdesk/Portal/Email] so the security team can contain the risk.” |
| “Who is responsible for security here?” | “The IT Manager or the CISO.” | “We all are. Security is a collective responsibility. While [Name] manages the ISMS, I am responsible for the security of the specific data and assets I use daily.” |
| “What recent security communications have you seen?” | “I don’t recall seeing anything lately.” | “I receive the Monthly Security Spotlight via [Slack/Teams/Email]. The last one covered the risks of social engineering and how to spot deepfake phishing.” |
What an auditor looks for
The audit is going to check a number of areas for compliance with ISO 27001 Clause 7.3. Lets go through them
| Audit Focus Area | What the Auditor Checks |
| 1. The Communication Plan | The auditor verifies that a structured plan exists which defines the “Who, What, When, and How” of security messaging. They look for a schedule that ensures awareness is maintained throughout the year, rather than as a singular event. |
| 2. Evidence of Execution | The auditor checks for timestamped proof that the communications defined in your plan actually occurred. This includes examining archived newsletters, intranet posts, meeting minutes, or broadcast logs from internal messaging platforms. |
| 3. Communication of Consequences | The auditor verifies that you have explicitly told staff what will happen if they fail to follow security protocols. They check for the inclusion of disciplinary outcomes or legal ramifications within your training materials and policy documents. |
| 4. Enforcement Process | The auditor checks for a documented disciplinary process that outlines the steps the organisation takes following a security breach. Even if no breaches have occurred in the last 12 months, the auditor requires evidence that a functional process is ready to be deployed. |
| 5. Policy Acknowledgement | The auditor checks that employees have formally acknowledged the security policies (usually via a signed Acceptable Use Policy). They look for language that ties policy adherence to the contractual terms of employment or engagement. |
| 6. Understanding of Non-Conformity | Through staff interviews, the auditor checks if personnel can articulate the risks their role poses to the business and what the personal impact would be if they intentionally or negligently bypassed a security control. |
Top 3 ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Mistakes and How to Fix Them
In my experience, many organisations fail their ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 audits because they mistake “broadcasting information” for “embedding awareness”. Relying on automated tools to send emails often results in a workforce that is compliant on paper but a liability in practice.
| The Mistake | Why it Fails (The SaaS Trap) | How to Fix It (The Anti-SaaS Way) |
| 1. The “Once-a-Year” Training Event | Many organisations pay for a generic LMS video once a year. Awareness is a perishable commodity; if it’s only discussed annually, it is forgotten by month two. | Continuous Engagement. Provision a 12-month communication calendar. Use your existing Slack, Teams, or email channels to drop monthly “Security Spotlights” on current threats like MFA fatigue or deepfakes. |
| 2. Ignoring the “Consequences” Requirement | SaaS training modules often focus on “what” to do but fail to explain “why” it matters or what happens if you don’t do it. Clause 7.3 specifically requires staff to know the implications of non-conformity. | Formalise the Disciplinary Link. Explicitly include a “Consequences of Breach” section in your Information Security Policy. Ensure this is discussed during inductions so staff understand that security is a contractual obligation, not a suggestion. |
| 3. Lack of Measurable Effectiveness | Assuming that a “100% completion” report from a software tool proves awareness. Auditors want to see that the training actually changed behaviour. | Audit Real-World Behaviour. Execute manual “spot checks” or simple internal quizzes (using MS Forms/Google Forms). If staff can’t explain how to report a lost laptop during a desk-side interview, your £10k training tool has failed. |
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Top Non Conformities
Here are the top 3 audit non-conformities for ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 (Awareness). These findings often occur when organisations prioritise “the tool” over the actual “security culture” of the workforce.
| Audit Non-Conformity | The SaaS Trap (Root Cause) | The Auditor’s Finding | The Ownership Fix (Toolkit) |
| 1. Lack of Knowledge Retention | The “Play and Forget” Fallacy. SaaS platforms focus on 100% completion rates. You assume because a video was played, the person is aware. | “Training records show 100% completion, yet staff interviewed could not explain the process for reporting a security incident or locate the Information Security Policy.” | Post-Training Quizzes & Interviews. Do not rely on “Completion Logs.” Use a simple Microsoft Form to test knowledge, and conduct random internal 1-2-1 spot checks to ensure the message stuck. |
| 2. Failure to Communicate Consequences | The “Positive Vibes Only” Illusion. Generic SaaS modules often focus on “tips” but avoid the “uncomfortable” requirement of Clause 7.3(d): the implications of not conforming. | “There was no evidence that the organisation has communicated the specific consequences (e.g., disciplinary action) to personnel for failing to follow the security policy.” | Policy & Disciplinary Integration. Include a specific “Consequences of Non-Compliance” section in your Information Security Policy and Induction deck. Ensure staff sign a document acknowledging these specific risks. |
| 3. Ad-hoc/Reactive Communication | The “Broken Dashboard” Trap. You rely on the software to send automated alerts, but if the tool fails or the license expires, awareness activities stop entirely. | “The organisation lacks a proactive communication plan. Awareness activities were found to be ad-hoc, with no evidence of ongoing reinforcement outside of a single annual training event.” | 12-Month Communication Calendar. Formalise a simple spreadsheet outlining monthly topics (e.g., February: MFA; March: Clear Desk). Store screenshots of these communications in a Central Evidence Folder you own and control. |
Using YouTube for ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Awareness
A common question I get as a Lead Auditor is: “Can I use free YouTube videos to satisfy Clause 7.3?”
The answer is a definitive Yes, but with a massive caveat: YouTube is the delivery mechanism, not the evidence. Watching a video is a “Do” activity, but to pass an audit, you must also satisfy the “Check” and “Act” parts of the process.
I provide hundreds of free tutorials on the Stuart Barker YouTube Channel specifically designed to be used as high-quality awareness content for your team.
How to Turn YouTube Views into Audit Evidence
If you simply send a link to your team, you will fail your audit. To make YouTube training “audit-ready,” follow this 3-step verification process:
- The Directive (Plan): Do not just “share” a video. Provision a formal email or Slack message that says: “To comply with our 2026 Awareness Plan, all staff must watch this 5-minute brief on [Video Topic] by [Date].”
- The Verification (Check): Since YouTube doesn’t give you a list of who watched what, you must create your own log. Execute a simple 3-question Microsoft Form or Google Form that staff must complete after watching.
- The Record (Document): Store the link to the video, the date it was assigned, and the spreadsheet of quiz responses in your Central Evidence Folder.
Recommended Awareness Playlists
- For General Awareness: Use the ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Explained video to show staff what the standard actually is and why their contribution matters.
- For Policy Awareness: Use the Acceptable Use Policy Guide to explain the “Rules of the Road” for company assets.
- For Technical Teams: Use the ISO 27001 Annex A 8.28 Secure Coding tutorial to satisfy the role-specific training requirements of Clause 7.2 and 7.3.
Lead Auditor Tip: When the auditor asks, “How do you keep your staff updated on new threats?”, you can show them your internal “Security Training Library” where you have curated my latest YouTube shorts on emerging threats like AI-phishing. This shows you are using Expert Intelligence to keep your team sharp.
Fast track ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
Implementing ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 (Awareness) requires a focus on security culture, not software management. Many organisations fall into the “SaaS Trap,” paying monthly subscriptions for platforms that create complexity and vendor lock-in.
The High Table ISO 27001 Toolkit provides a leaner, high-performance alternative by giving you full ownership of your awareness assets. Below is a comparison of why an “Owned” toolkit is superior to a “Rented” SaaS platform for Clause 7.3 compliance.
| Feature | SaaS Online Platforms | High Table ISO 27001 Toolkit |
| Ownership | Rented Access: If you stop paying your monthly subscription, you lose access to your training logs and awareness evidence. | Permanent Assets: You buy the toolkit once and keep your files forever. Your evidence stays on your servers, under your control. |
| Simplicity | Learning Curve: Your team must learn to navigate a new, often bloated, interface just to complete a 10-minute awareness task. | Zero Training Required: Everyone already knows how to use Word and Excel. You can deploy the Awareness Plan and Induction records immediately. |
| Cost | Opex Burden: Expensive monthly per-user subscriptions that increase as your company grows. | One-Off Investment: A single fee for the entire toolkit. No recurring costs, no matter how many employees you hire. |
| Freedom | Vendor Lock-In: It is notoriously difficult to export your data and evidence if you want to switch providers. | Total Portability: No lock-in. Your documents are standard formats (.docx, .xlsx) that can be moved, backed up, or edited at any time. |
| Customisation | Rigid Templates: You are often stuck with generic videos and “corporate” branding that doesn’t reflect your unique culture. | Full Flexibility: Easily tailor the Awareness Plan and Policy documents to your specific risks and company tone of voice. |
| Audit Readiness | Cloud Dependency: If the platform is down during your external audit, you cannot prove compliance. | Local Availability: Your “Central Evidence Folder” is always available on your internal drive, even offline, for the auditor to review. |
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3: Related Controls & Clauses
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 does not exist in a vacuum. It is part of the “Support” block of the standard, working alongside resource management and technical controls to ensure the “Human Firewall” is effective. Understanding these dependencies is key to passing an audit, as a failure in one often indicates a failure in another.
| Related Clause / Control | Description | Why it Matters (The Link) |
| ISO 27001 Clause 7.1 Resources | Requires the organisation to determine and provide the persons necessary for the effective implementation of the ISMS. | Prerequisite. You cannot build an awareness programme if you have not resourced the people to deliver it. Clause 7.3 ensures that the resources provided in 7.1 actually understand their security obligations. |
| ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence | Ensures that people doing work under the organisation’s control are competent based on education, training, or experience. | Skill vs. Knowledge. Awareness (7.3) is knowing why security matters and what the policies are. Competence (7.2) is the ability to execute the technical tasks. You need both to prevent breaches. |
| ISO 27001 Annex A 6.3 | Information security awareness, education and training. Personnel must receive appropriate awareness and regular updates. | The Execution Component. This is the Annex A control that directly supports Clause 7.3. While 7.3 is the high-level requirement, Annex A 6.3 is the specific activity (e.g., your annual training) used to satisfy the auditor. |
| ISO 27001 Annex A 5.4 | Management responsibilities. Management must require all personnel to apply security in accordance with established policies. | Accountability. It is a management obligation to ensure awareness. If an auditor finds a lack of awareness, they will also cite A 5.4 because leadership failed to enforce the “Security Culture” from the top down. |
| ISO 27001 Annex A 5.10 | Acceptable use of information and other associated assets. Rules for the acceptable use of assets must be identified, documented, and implemented. | The Content Source. You cannot have “Awareness” without “Rules.” Annex A 5.10 provides the specific rules (AUP) that Clause 7.3 ensures everyone has actually read, understood, and signed. |
| ISO 27001 Clause 9.1 | Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation. Requires the organisation to evaluate the security performance and effectiveness of the ISMS. | Effectiveness Loop. Clause 7.3 requires you to be aware of your “contribution to the effectiveness of the ISMS.” Clause 9.1 is where you actually measure if that awareness resulted in fewer incidents or better quiz scores. |
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Mapped to other Standards
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 (Awareness) is a universal requirement that underpins almost every modern regulatory framework. While other standards might use different terminology, such as “Literacy,” “Culture,” or “Education”, the core objective remains the same: ensuring that the human element of the organisation is not the weakest link in the security chain.
| Standard / Framework | Specific Reference | Relationship to ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 (Awareness) |
| ISO/IEC 42001 (AI Management) | Clause 7.3 | The AI Awareness Mirror. Exactly mirrors 27001 but requires staff to be aware of the “implications of AI non-conformity.” Clause 7.3 in 27001 acts as the vehicle to deliver AI-specific awareness regarding data privacy and bias. |
| EU AI Act | Article 4 (AI Literacy) | Regulatory Mandate. The Act requires “AI Literacy” for all staff. ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 provides the operational framework to deliver and document this literacy, proving the organisation has met its legal obligations. |
| EU NIS2 Directive | Article 20 (Governance) | Leadership Awareness. NIS2 mandates that executives undergo regular training to identify and manage cyber risks. Your Clause 7.3 Communication Plan is the evidence that these high-level awareness sessions have occurred. |
| EU DORA | Article 13(6) (ICT Training) | Resilience Awareness. Financial entities must provide ICT security awareness to all staff. Clause 7.3 ensures that this isn’t a one-off event, but a continuous programme as required by the DORA regulation. |
| ISO 9001:2015 (Quality) | Clause 7.3 | Unified Culture. The clause text is identical. You can use a single “Awareness Communication Plan” to cover both Quality and Security, ensuring staff understand how their role affects both product quality and data safety. |
| ISO 22301:2019 (BCMS) | Clause 7.3 | Crisis Awareness. While 27001 asks if you are aware of security policies, 22301 asks if you are aware of your role during a disaster. A single awareness session can cover both “daily security” and “emergency response.” |
| ISO 20000-1:2018 (ITSM) | Clause 7.3 | Service Awareness. Focuses on awareness of service objectives. In an integrated system, Clause 7.3 ensures that Service Desk staff are aware that maintaining “Service Availability” is a core security objective. |
| SOC 2 | Criteria CC1.1 (COSO Principle 1) | Tone at the Top. SOC 2 looks for evidence that management reinforces security expectations. ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 provides the artifacts (newsletters, town hall minutes) that prove this culture is being actively promoted. |
| NIST SP 800-53 | AT-2 (Security Awareness) | Operational Baseline. NIST requires basic security awareness for all system users. Clause 7.3 satisfies this by ensuring every user acknowledges the “Rules of Behavior” (the Acceptable Use Policy). |
| PCI DSS v4.0 | Requirement 12.6 | Payment Security. Mandates a formal security awareness programme for all personnel. ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 is the “How-To” for building this programme so it meets the specific technical rigour of PCI DSS. |
| ITIL 4 | Information Security Management | Integrated Practice. ITIL 4 views awareness as a continuous “Practice.” ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 provides the structured “Plan-Do-Check-Act” lifecycle to ensure the ITIL practice is actually effective. |
| GDPR | Article 39(1)(b) | Privacy Awareness. The DPO is tasked with “raising awareness” of data protection. Clause 7.3 is the mechanism the DPO uses to deliver GDPR training and verify that staff understand the risks to data subjects. |
Awareness Triggers: Integrating Threat Intelligence
| Trigger Event | Source of Intelligence | Awareness Action (The Fix) |
| New Zero-Day Vulnerability | Vendor Advisories / CISA Alerts | Provision an urgent technical brief to developers and system admins regarding the specific “Rules of Engagement” for emergency patching. |
| Industry Phishing Trend | ISAC Reports / Peer Networks | Distribute a “Security Spotlight” alert to all staff with screenshots of the specific phishing lure (e.g., a fake “HR Payroll” update). |
| Social Engineering Surge | Internal Incident Logs / Near-Misses | Execute a targeted micro-learning session for high-risk departments (e.g., Finance or HR) on verifying identity before processing payments. |
| Cloud Configuration Leak | Security News / OSINT | Audit and refresh the awareness for DevOps teams regarding the “Implications of Non-Conformity” when handling public-facing S3 buckets or APIs. |
Navigating the “Auditor’s Evidence Trap”
| Evidence Type | The “Shadow” Action | Why it Wins the Audit |
| Messaging Logs | Take a screenshot when you post a security reminder or an alert about a new phishing trend in Slack, Teams, or WhatsApp. | Proves real-time, responsive communication beyond scheduled sessions. |
| Physical Context | Take a photo of the Office TV displaying a “Security Tip of the Week” or a security poster in the breakroom. | Demonstrates that security is integrated into the physical work environment. |
| Management Tone | Save the minutes or a recording of a Town Hall meeting where the CEO mentions the importance of ISO 27001. | Direct evidence of Clause 5.1 (Leadership) and Clause 7.3 (Awareness) alignment. |
| Peer-to-Peer | Bookmark a thread where one employee corrects another’s security practice (e.g., “Don’t forget to lock your screen!”). | This is the “Holy Grail” for auditors; it proves the culture has moved from “enforced” to “self-sustaining.” |
Closing the “Interested Parties” Gap (Clause 4.2 Alignment)
| Interested Party | Potential Risk | Required Evidence (The Solution) |
| Cleaning Staff | Unauthorised access to sensitive documents or unlocked screens during out-of-hours shifts. | Provision a simplified, translated “Security Essentials” flyer. Log their signature on a simplified Acceptable Use Policy (AUP). |
| Security Guards | Improper handling of visitors or failure to identify tailgating attempts at entry points. | Formalise specific “Rules of Engagement” (ROE) and conduct a mock “Unauthorized Entry” test to record their response. |
| MSPs / IT Contractors | Mismanagement of administrative credentials or failure to follow the Change Management process. | Audit the contract or SLA to ensure awareness training is mandated. Request copies of their internal training logs for your evidence folder. |
| Facilities / Maintenance | Accidental damage to infrastructure or unauthorised entry to the server room. | Execute a site induction briefing before access is granted. Record the date and topics covered in your visitor log. |
The Role-Based Awareness Matrix
| Department | Specific Security Focus | Mandatory Awareness Topics |
| Finance & Procurement | Financial Fraud & Social Engineering | Business Email Compromise (BEC), payment verification procedures, and secondary authorisation for bank detail changes. |
| Engineering / DevOps | System Integrity & Technical Debt | Secure Coding (Annex A 8.28), OWASP Top 10, Model Poisoning (for AI firms), and API key management. |
| Human Resources | Privacy & Asset Lifecycle | PII Protection (GDPR), secure offboarding procedures, and identifying social engineering in recruitment (fake candidates). |
| Sales & Marketing | Data Leakage & Brand Protection | Secure handling of CRM data, public-facing communication rules, and the risks of using unauthorised third-party SaaS tools (Shadow IT). |
| Senior Leadership | Governance & Liability | Executive Phishing (Whaling), legal implications of non-conformity, and resourcing for the ISMS (Clause 7.1). |
The Remote & Hybrid Awareness Nuance
| Remote Risk Area | The “Work from Anywhere” Threat | Awareness Fix (The Briefing) |
| Environmental Privacy | Smart speakers (Alexa/Siri) or family members overhearing sensitive client calls. | Provision guidance on “Audio Privacy.” Remind staff to mute smart devices and use headsets for confidential discussions in shared spaces. |
| Public Infrastructure | Use of unsecured “Coffee Shop” Wi-Fi leading to Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks. | Distribute a technical brief on mandatory VPN usage and the dangers of “Evil Twin” hotspots in transport hubs. |
| Device Integrity | Family members, specifically children, using work laptops for gaming or schoolwork. | Formalise the “Sole Use” rule. Ensure staff are aware that work assets are strictly for their use only, with no exceptions for household members. |
| Visual Hacking | Shoulder surfing in co-working spaces or on trains. | Execute awareness on physical privacy filters and the “Screen Lock” habit, even when just stepping away for a coffee at home. |
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3: Awareness FAQ
What is ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Awareness?
ISO 27001 Clause 7.3, titled “Awareness,” requires an organisation to ensure that all persons doing work under its control are aware of specific information security aspects. This isn’t just about providing training; it’s about embedding a security-conscious culture within the organisation.
What are the ISO 27001:2022 Changes to Clause 7.3 Awareness?
Great news. There are no changes to ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 in the 2022 update. The requirements for awareness remain consistent with the previous version of the standard.
Who needs to be aware according to Clause 7.3?
The standard states that “persons doing work under the organisation’s control” must be aware. This includes more than just full-time employees. It extends to contractors, temporary staff, and volunteers who have access to the organisation’s information and assets within the ISMS scope.
What specific topics must people be aware of?
According to the standard, individuals must be aware of: The information security policy of the organisation. Their contribution to the effectiveness of the ISMS, including the benefits of improved security performance. The implications of not conforming with the ISMS requirements.
How can an organisation demonstrate compliance with Clause 7.3?
Compliance is demonstrated through documented evidence of awareness activities. This isn’t about creating a single document, but rather showing a structured, ongoing programme. Examples include: Training attendance records (e.g., sign-in sheets, e-learning completion logs). Records of communications like emails, newsletters, and posters. Results from awareness quizzes or assessments. Minutes from meetings where security topics were discussed.
Who is responsible for ISO 27001 Awareness?
While the Information Security Officer (ISO) or a similar role is typically responsible for planning and overseeing the awareness programme, implementing it is a shared responsibility. The standard emphasises that it’s everyone’s duty to contribute to the effectiveness of the ISMS. Top management must also show commitment to the programme.
Is one-time training enough to meet the requirements of Clause 7.3?
No, one-time training is generally not sufficient. The standard implies an ongoing process. Threats and risks evolve, and so must awareness. An effective programme includes initial training for new hires, periodic refresher training for all staff, and continuous communication to keep security top-of-mind.
What’s the difference between “competence” (Clause 7.2) and “awareness” (Clause 7.3)?
Competence (Clause 7.2) is about having the necessary knowledge and skills to perform a specific job function. Awareness (Clause 7.3) is a more general requirement for everyone to understand their role in protecting information, regardless of their specific technical competence. You can think of competence as specialised knowledge, while awareness is universal knowledge.
Can ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 be met through simple emails or posters?
While emails, newsletters, and posters can be excellent tools for continuous communication, they are generally not enough on their own. Auditors look for a structured programme that demonstrates that the organisation is actively trying to make people aware. A combination of formal training, documented communication, and interactive methods is a more robust approach.
How do you measure the effectiveness of an awareness programme?
Measuring effectiveness goes beyond simply checking a box. It involves assessing whether the awareness programme actually changes behaviour. Methods include: Conducting mock phishing exercises to test if employees can spot and report suspicious emails. Analysing IT help desk tickets to see if the number of reported security incidents changes over time. Using surveys or quizzes to gauge understanding of key security policies.
Why is ISO 27001 Awareness important?
It’s a fundamental part of a successful Information Security Management System (ISMS), requiring an organisation to ensure that everyone under its control is aware of the information security policy, their contribution to the ISMS, and the consequences of not conforming. This clause is a key differentiator, as a strong security posture isn’t just about technology, but also about the people using it.
What are the consequences of not meeting the requirements of Clause 7.3?
Failing to meet Clause 7.3 can lead to a nonconformity during an ISO 27001 audit, which could prevent the organisation from achieving or maintaining its certification. More importantly, it creates a significant security risk. A workforce that isn’t aware of its security responsibilities is more likely to fall victim to social engineering attacks, phishing scams, or accidental data breaches.
Related ISO 27001 Controls
ISO 27001 Annex A 6.3: Information Security Awareness Education and Training
ISO 27001 Clause 7.4: Communication
Further Reading
ISO 27001 Security Awareness Training Policy Beginner’s Guide
ISO 27001 Awareness Beginner’s Guide
ISO 27001 Objectives | Beginner’s Guide
