Introduction
In this article I lay bare the changes to the ISO 27001 standard that happened in 2024 in the ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes.
You will learn
- What is ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1
- How to implement ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes
- What is new in ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes
Table of contents
- Introduction
- What is ISO/IEC 27001:2022?
- What is ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment 1?
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Release Date
- What has changed in the new ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment?
- Everything you need to know – 60 second video
- What do I need to know about the new version amendment to ISO 27001
- How to implement ISO 27001 Amendment 1
- How to implement ISO 27001 Amendment 1 – 60 second video
- The top 3 Mistakes People make with the new ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1
- ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Climate Action Changes Explained Simply | The Lead Auditor Podcast
- ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Strategic Implementation Briefing [Auditor Explained]
What is ISO/IEC 27001:2022?
ISO 27001 is the international standard for information security. It is an Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) and the output is an ISO 27001 Certification. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 was the much anticipated 2022 update to the standard released in 2022.
Officially it is called: ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection — Information Security Management Systems Requirements
What is ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment 1?
ISO 27001 Amendment 1 is a change to the ISO 27001 standard that introduces requirements on climate change to the information security management system. It officially known as ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes

ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Release Date
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Change Actions was released in February 2024.
What has changed in the new ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment?
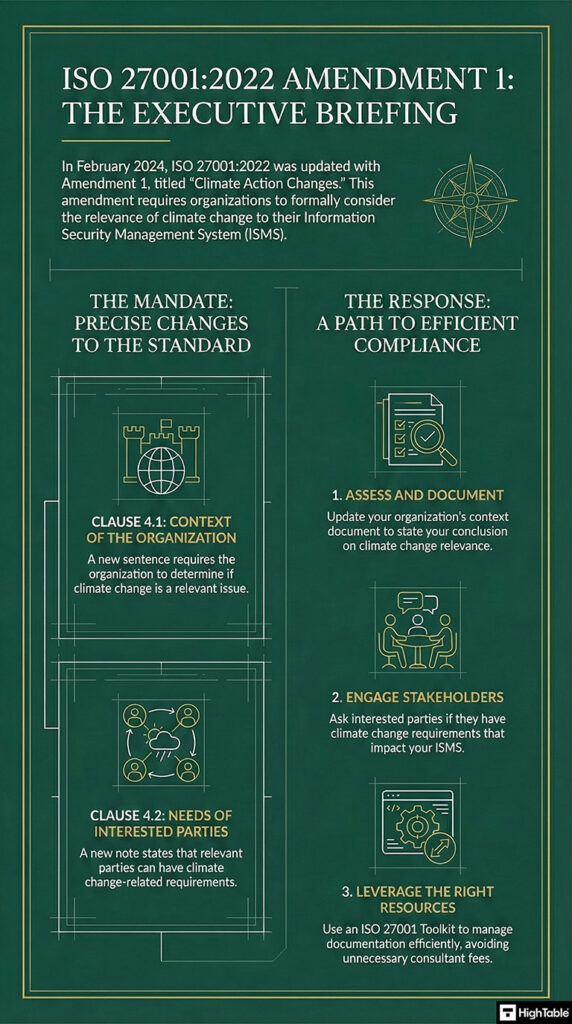
The change is the addition of requirements on climate change to the ISO 27001 standard. The following is a summary of the ISO 27001:2022 changes:
Added the following sentence at the end of the sub-clause:
The organisation shall determine whether climate change is a relevant issue.
Added the following note at the end of the sub-clause:
NOTE 2 Relevant interested parties can have requirements related to climate change.
Everything you need to know – 60 second video
Learn everything you need to know about ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes in this 60 second YouTube Short.
What do I need to know about the new version amendment to ISO 27001
You need to know that there is no need to panic and no significant work has been introduced, unless you want there to be. This is not an actual evolution of the information security management system (ISMS). The main focus is on introducing the climate change agenda to standards. Whether they are relevant to those standards or not.
How to implement ISO 27001 Amendment 1
To align with this ISO 27001 amendment 1, you should take proactive steps:
- Conduct a risk assessment to consider climate-related threats to information security. Work with risk management teams to evaluate environmental and climate threats and the impact of your information security management system on them.
- Engage with interested parties and stakeholders to understand their climate impact expectations. Regulatory bodies, industry groups, and business partners can help define climate requirements that could impact your information security implementation.
- Review your business continuity and disaster recovery plans to account for climate risks. Your continuity plans should consider potential disruptions caused by extreme weather, which could affect key infrastructure.
- Businesses can align security practices with environmental responsibility by incorporating sustainability considerations into their security policies. This can include exploring initiatives such as:
- Using green data centres that rely on renewable energy and efficient cooling systems.
- Opting for energy-efficient hardware to reduce power consumption.
- Implementing digital waste reduction initiatives to minimise the environmental impact of data storage and disposal.
- To maintain compliance with new industry standards, it’s essential to stay informed about evolving climate-related regulations. Taking a proactive approach to these changes will help your organisation adapt more smoothly.
If climate change is on your agenda then you are already covering this and there is nothing additional to do. If it is not then the following is the suggest approach.
You should update to the context of organisation document to include a line that sets out that climate change was reviewed and it was concluded that climate change is not a relevant risk to you or the information security management system. This is the easiest and quickest way to meet the requirement.
If it is a relevant risk to you then you should add it to the risk register and manage it via risk management.
In addition you should take note to ask interested parties if climate change is relevant to them and if so in what way so that you can include the requirement in your information security management system implementation. Be prepared when speaking to external ISO 27001 certification auditors to say that you asked them and it was not ( ideally ) or was relevant and what you did about it.
How to implement ISO 27001 Amendment 1 – 60 second video
Learn how to implement ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes in this 60 second YouTube Short.
The top 3 Mistakes People make with the new ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1
1. Overthinking it
You can do as much or as little as you need to do and should not overthink it. Stating that it is not a relevant risk and that you asked interested parties and they were not interested is enough. If climate change is on your agenda then you are already handling and implementing this through other standards and initiatives.
2. Paying consultants to work out the impact
Paying consultants to tell you that nothing has fundamentally changed is a big mistake. It is literally a couple of lines long and I have told you what it says.
3. Thinking climate change relates to an information security management system.
Parking any politics or agenda I leave it for you to work out if climate change has impact in risk terms to an information security management system (ISMS).
ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Climate Action Changes Explained Simply | The Lead Auditor Podcast
In this episode: Lead Auditor Stuart Barker and team do a deep dive into the ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Climate Action Changes. Technically referenced as ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Change Actions. The podcast explores what it is, why it is important and two paths to compliance. The most tactical taking less than 1 hour to implement.
ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Strategic Implementation Briefing [Auditor Explained]
In this strategic implementation briefing, Lead Auditor Stuart Barker and team do a deep dive into the introduction of ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Change Actions.
About the author



