How to implement ISO 27001:2022 Clause 4.1 is a detailed step-by-step guide to implementing ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 from an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor.
Table of contents
To implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 you will perform the following steps.
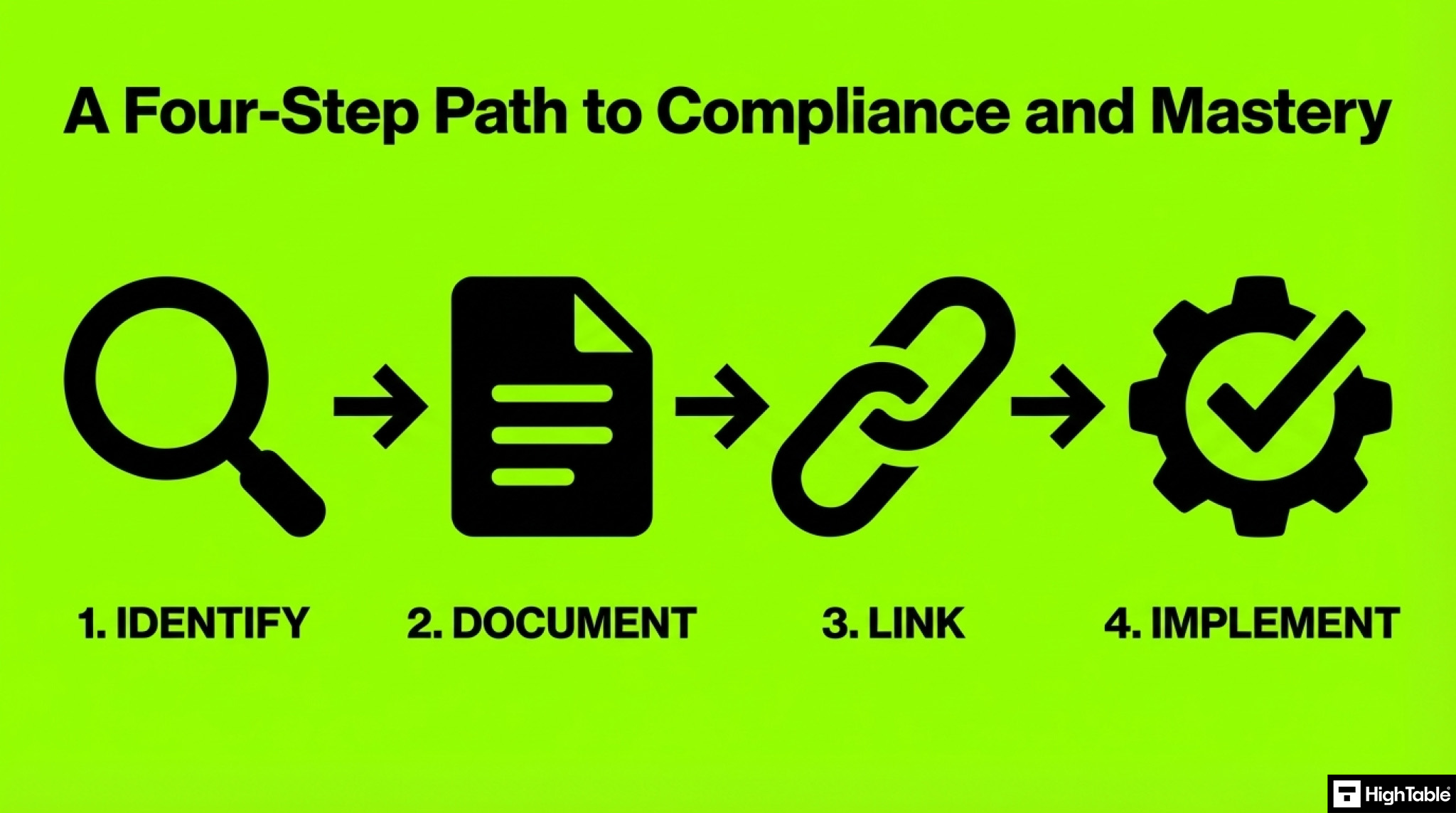
Step 1: Identify Your Issues

An internal issue is essentially synonymous with internal risk in the context of ISO 27001. Both refer to potential problems or threats originating within the organisation that could negatively impact the effectiveness of your Information Security Management System (ISMS).
External issue is synonymous with external risk in the context of ISO 27001. Both refer to potential problems or threats originating outside the organisation that could negatively impact the effectiveness of your Information Security Management System (ISMS).
In my experience, there are two approaches to identifying internal and external issues, the informal approach and the formal approach. Let’s take a look at each in turn:
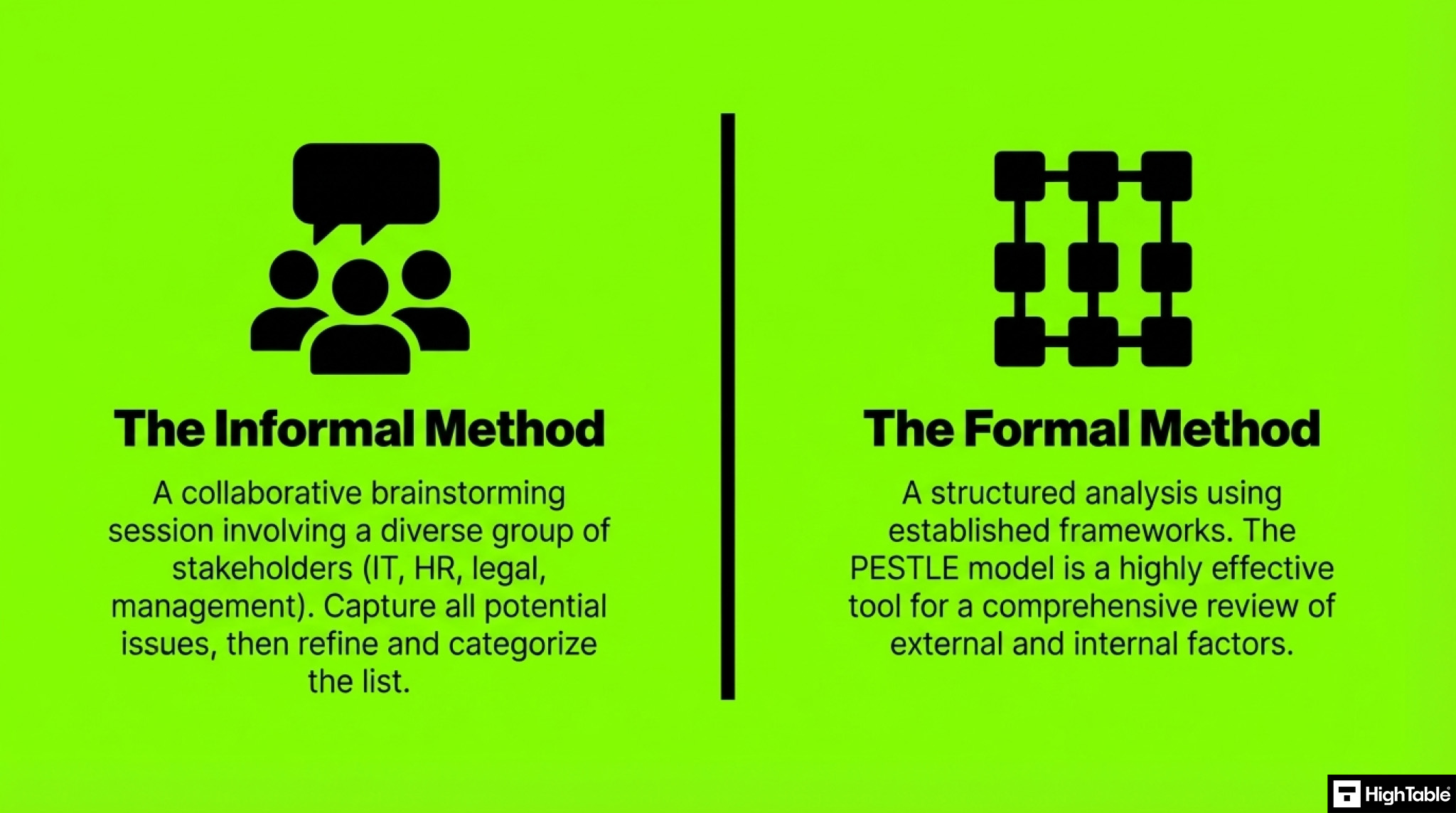
Informal Methods for Identifying Internal and External Issues
A key starting point is a collaborative brainstorming session. Involve a diverse group of stakeholders, including representatives from various departments, IT, HR, legal, and senior management. An optional facilitator can guide the discussion and ensure all perspectives are considered.
Begin by capturing all potential issues. This initial brainstorming phase should be inclusive, considering all potential concerns raised by participants.
Refine the list through discussion and analysis. Gradually narrow down the list, prioritizing the most significant and impactful issues based on their likelihood and potential consequences.
Categorise issues by department where possible. This can help identify departmental-specific vulnerabilities and facilitate targeted risk mitigation strategies.
Formal Methods for Identifying Internal and External Issues
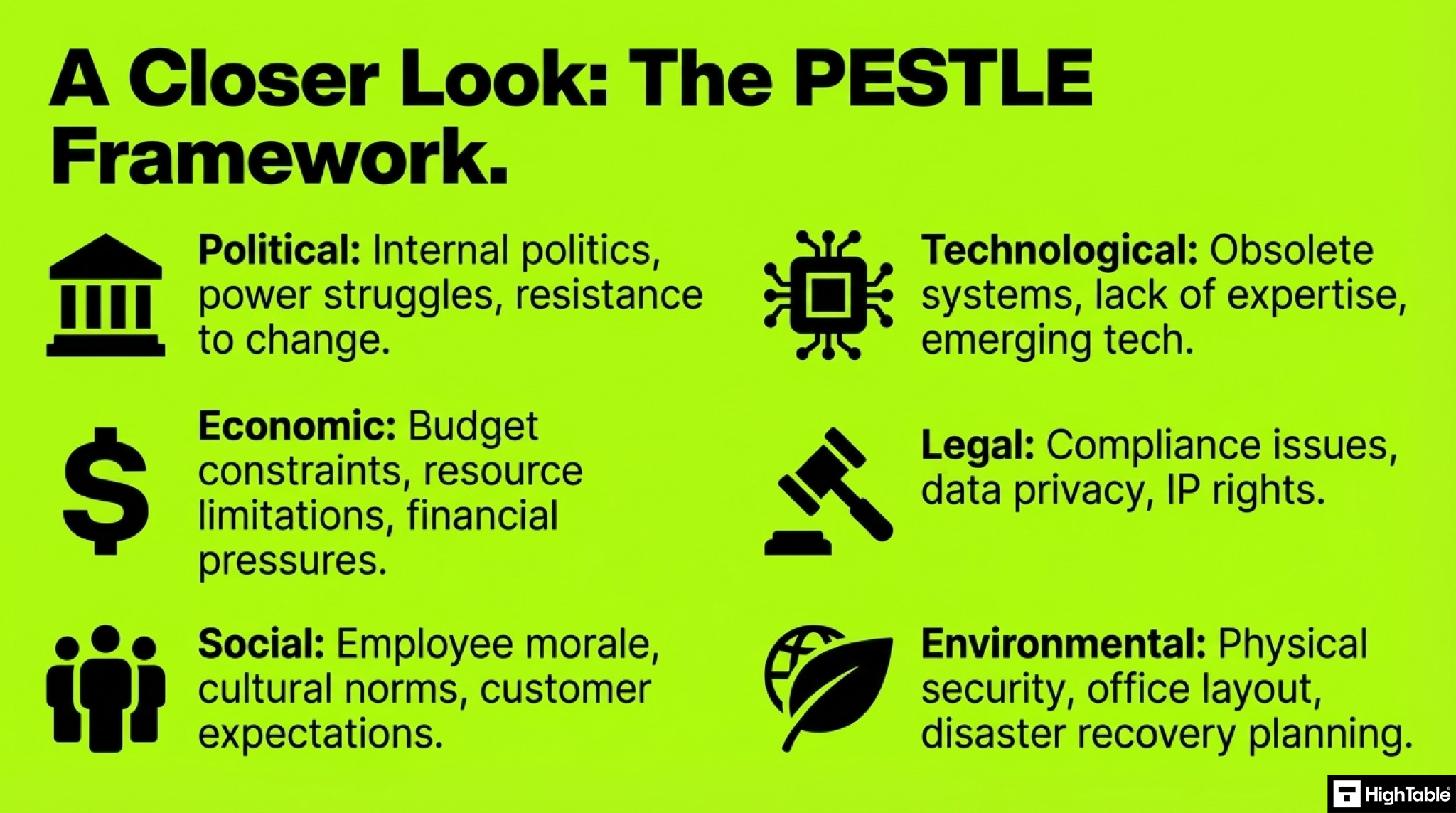
For a more structured approach, consider a PESTLE analysis. This framework can be adapted to identify internal issues by focusing on internal factors:
- Political: Internal politics, external politics, power struggles, and resistance to change within the organisation.
- Economic: Budget constraints, resource limitations, and internal financial pressures, external financial pressures.
- Social: Employee morale, cultural norms, internal communication challenges, customer expectations and requirements and external communication challenges.
- Technological: Obsolete technology, lack of technical expertise, inadequate IT infrastructure, new and emerging technology.
- Legal: Internal legal and regulatory compliance issues, data privacy concerns, intellectual property rights, external legal and regulatory compliance issues, and data privacy concerns.
- Environmental: Internal environmental factors such as office layout, physical security measures, and disaster recovery planning. External environmental factors such as climate or office and facility location specific concern
Things to consider when identifying internal issues
When considering ISO 27001 internal issues and what could impact information security, the following can be a great guide:
- The organisation’s culture.
- Organisational governance.
- Organisational structure.
- People’s roles and accountabilities.
- Policies.
- Company objectives and the strategies that are in place to achieve them.
- Organisational capabilities in terms of resources and knowledge.
- The relationships, perceptions and values of internal interested parties.
- Information systems.
- Information flows and decision-making processes.
- Standards, guidelines and models adopted by the organisation.
- Contractual relationships.
Things to consider when identifying external issues
When considering external issues and what could impact information security, the following can be a great guide:
- The social and cultural, political, legal, regulatory, financial, technological, economic, natural and competitive environment, whether international, national, regional or local.
- Key drivers and trends having impact on the objectives of the organisation; and
- Relationships with perceptions and values of external interested parties.
Step 2: Document Your Context

ISO 27001 requires organisations to document internal and external issues within the ISO 27001 Context of the Organisation Template. This helps establish the foundation for the Information Security Management System (ISMS) by understanding the internal and external factors that can influence its success. In this short video I give you some guidance on how write and document your internal and external issues.
Recommended document structure
A clear and concise way to document internal issues is through a table with two columns:
| The Issue Name | The Issue Description |
|---|---|
| [Issue 1 Name] | [Detailed description of the issue and its potential impact on the ISMS] |
| [Issue 2 Name] | [Detailed description of the issue and its potential impact on the ISMS] |
| [Issue 3 Name] | [Detailed description of the issue and its potential impact on the ISMS] |
Example document structure
Here is a real world example of that document structure in practice:
| The Issue Name | The Issue Description |
|---|---|
| Lack of Management Commitment | Top management may not consistently prioritise information security, leading to insufficient resource allocation, lack of clear direction, and inconsistent enforcement of policies. This can hinder the successful implementation and maintenance of the ISMS. |
| Inadequate Employee Awareness | Employees may not be adequately trained on security policies, procedures, and best practices, leading to human error, such as accidental data breaches or non-compliance with security measures. This can increase the risk of data breaches and system disruptions. |
| Resistance to Change | Employees may resist changes to security policies or procedures, fearing disruption to their daily work or perceiving the changes as unnecessary burdens. This can lead to non-compliance with security measures and hinder the effectiveness of the ISMS. |
Key documentation considerations
- Use clear and concise language to describe each issue.
- Clearly articulate the potential impact of each issue on the ISMS and the organisation as a whole.
- Regularly review and update the list of issues to reflect changes within the organisation and the evolving threat landscape.
When to update issues
You may be wondering how often you should update the internal issues. ISO 27001 internal issues should be updated regularly to ensure the effectiveness of your Information Security Management System (ISMS). Here’s a breakdown of when updates are crucial:
1. At regular intervals
At least annually, conduct a thorough review of internal issues. This allows you to assess changes within the organisation, such as:
- Organisational changes: Restructuring, mergers, acquisitions, or significant personnel changes.
- Technological advancements: New technologies, software updates, or changes in the threat landscape.
- Legal and regulatory changes: New laws, regulations, or industry standards impacting information security.
- Business changes: New products, services, or business processes that may introduce new security risks.
2. Based on trigger events
- Following any security incident, conduct a thorough review of internal issues to identify any contributing factors and implement necessary corrective actions.
- During internal audits, review and update internal issues based on the findings and recommendations of the audit team.
- As part of the regular management review process, discuss and update the list of internal issues to ensure they remain relevant and accurate.
- Whenever risk assessments are conducted or updated, review and update the list of internal issues to reflect any new or changed risks.
3. Best practices
- Maintain a record of all changes made to the list of internal issues, including the date of the change, the reason for the change, and the person responsible for the change.
- Ensure that all relevant stakeholders are aware of any changes to the list of internal issues.
- Involve key personnel from across the organisation in the review and update process to ensure a comprehensive and accurate assessment of internal issues.

Step 3: Link Issues to Your ISMS Risk Management

Follow your risk assessment process and apply it to the internal and external issues that you have identified.
Internal and external issues can represents risk and ISO 27001 is a risk based management system, so you will follow the risk process to identify and mitigate risks.
Determine whether the identified issues and risks require risk management by utilising the ISO 27001 risk register template and ISO 27001 risk management process template.
Step 4: Implement ISO 27001 Amendment 1

It is quick and simple to implement ISO 27001 amendment 1 and in this short video I show you how.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1: A Pro Tip for Implementers

When recording the ISO 27001 Internal and External Issues, the standard does not stipulate that you should only record the negative. In other words, do not go out of your way to find and report the negative.
It’s possible that you have considered internal issues or external issues and, in fact, it is not an issue for you.
By writing down the issues and then providing an explanation, either positive or negative, you are demonstrating that you considered it. If the explanation is positive, it shows that you considered it, and a clever auditor won’t raise it as a problem thinking they’ve got one over on you.
You can confidently say, “Yes, we considered it, we documented it, and for us, it is not an issue.”
If the explanation is negative, indicating that you do have an issue, then describe the issue and indicate whether or not you have raised a risk in the risk register to address it.
It is expected and considered good practice for each issue that is an issue to be included in the risk register and managed via risk management.
Based on experience and real world implementations my pro tip would be to record positive as well as negative internal and external issues. Watch the short video to see why.
Lead Implementer Detailed Step-by-Step Guide
Time needed: 1 hour and 30 minutes
How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.1
- Conduct a Brainstorm Session
Challenge
Identifying internal and external issues can be challenging.
Solution
Create cross-functional teams: Create teams with members from different departments to encourage knowledge sharing and collaboration.
Manage stakeholders: With key interested parties from across the business and organisational units perform a brainstorming session to record the potential issues that you may face.
Leverage Best Practice: Consider using the example internal issues and external issues later in this article as your starting point. - Compliance and Security Requirements
Challenge
Maintaining compliance while adapting to constantly evolving regulations presents a significant challenge.
Solution
Utilise compliance management tools: Employ specialised tools to track and monitor regulatory changes and ensure compliance adherence.
Integrate compliance into the ISMS: Incorporate compliance requirements directly into the Information Security Management System (ISMS) framework.
Provide continuous training: Regularly train security teams on the latest regulatory requirements and best practices for maintaining compliance in test environments.
Create a legal register: Use an ISO 27001 legal register template to record all relevant laws. - Align with the Organisation
Challenge
Internal and external issues to the management system do not exist in isolation of the organisation and it can be challenging to align with organisation goals.
Solution
Understand the organisation: Read and understand the organisation mission and goals and ensure these are referenced when identifying issues.
Integrate business goals into the ISMS: Incorporate the business goals into the information security management system and align them with the goals of the ISMS.
Document the organisation: Create a documented overview of the organisation utilising the ISO 27001 Organisation Overview Template. - Assess the organisation’s infrastructure
Challenge
Having a comprehensive understanding and record of the organisations technical infrastructure and human resources presents a significant challenge.
Solution
Create organisation charts: Work with HR to create organisation charts. Using the roles and responsibilities aligned with ISO 27001:2022 Clause 5.3 (Organisational Roles, Responsibilities and Authorities) identify gaps and internal resource issues.
Map roles and responsibilities: Understand the roles that are required for the information security management system as referenced in ISO 27001:2022 Clause 5.3 (Organisational Roles, Responsibilities and Authorities) and document them in the ISO 27001 Information Security Roles and Responsibilities Template identify gaps and internal resource issues.
Create technical documentation: Working with the technical teams and domain experts create accurate technical documentation including server and network diagrams and identify and internal technological issues. - Risk Management
Challenge
Identifying and mitigating all potential risks, especially within complex IT environments, presents a significant challenge.
Solution
Comprehensive Risk Assessments: Conduct thorough risk assessments tailored to identifying ISO 27001 internal Issues and ISO 27001 external issues to the ISMS. This process should adhere to ISO 27001 Clause 6.1 (Planning), focusing on identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities and threats.
Conduct a Risk Assessment: Determine whether the identified issues and risks require risk management by utilising the ISO 27001 risk register template and ISO 27001 risk management process template. - Document Internal and External Issues
Challenge
Maintaining a record of internal and external issues can be confusing and present a challenge.
Solution
Create an ISO 27001 Context of Organisation document: Record the issues using the ISO 27001 Context of Organisation template.
Further Reading
How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.1
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Implementation Checklist
How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 4.1
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Audit Checklist
ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Absolutely Everything You Need to Know
ISO27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes – Definitive Briefing
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Understanding the Organisation and Its Context Explained
About the author