ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Information Access Restriction is a security control that limits access to assets based on established policies. It enforces the Primary Implementation Requirement of technical restrictions to ensure users only access data necessary for their roles. This approach secures the Business Benefit of confidentiality and prevents unauthorised exposure.
In this guide, I will show you exactly how to implement ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 and ensure you pass your audit. You will get a complete walkthrough of the control, practical implementation examples, and access to the ISO 27001 templates and toolkit that make compliance easy.
I am Stuart Barker, an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor with over 30 years of experience conducting hundreds of audits. I will cut through the jargon to show you exactly what changed in the 2022 update and provide you with plain-English advice to get you certified.
Key Takeaways: ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Information Access Restriction
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 requires organizations to restrict access to information and other associated assets in accordance with their established access control policy. Unlike general user management, this control focuses on the restriction, ensuring that users only see the data they are authorized to see. It is the primary technical defense for maintaining Confidentiality and preventing unauthorised data exposure.
Core requirements for compliance include:
- Least Privilege: Users should only be granted the minimum level of access necessary to perform their job functions. If a user doesn’t need to “Delete” or “Export” data, those permissions must be restricted.
- Need-to-Know: Access should be restricted based on specific business tasks. Just because someone is a “Manager” doesn’t mean they need access to the entire HR or Finance database.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): You must define “Roles” (e.g., Admin, Manager, View-Only) and assign permissions to those roles rather than to individual users. This makes access management scalable and auditable.
- Technical Enforcement: Restrictions must be enforced within the application, database, or operating system. You cannot rely on “honor systems” or verbal instructions.
- Dynamic Access: You must account for special circumstances, such as restricting access during a disciplinary investigation or providing temporary “break-glass” access for emergencies.
Audit Focus: Auditors will look for “The Access Matrix”:
- The Blueprint: “Show me your Role-Based Access Matrix. What can a ‘Standard User’ see vs. a ‘Super Admin’?”
- Verification: They will perform a “live check” on a random user profile: “Show me that this Sales Rep cannot access the payroll folder.”
- Governance: “How often do you review these restrictions to ensure ‘Privilege Creep’ hasn’t happened?”
Role-Based Access Matrix (Audit Example):
| Feature / Data | Admin | Manager | Standard User | Guest / Read-Only |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| View Client Records | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Edit Billing Info | ✓ | ✓ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Delete Records | ✓ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Export Full Database | ✓ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways: ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Information Access Restriction
- What is ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3?
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Free Training Video
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Explainer Video
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Podcast
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Implementation Guide
- How to implement ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3
- Role Based Access Matrix Example
- How to pass an ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 audit
- Top 3 ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 mistakes and how to avoid them
- Applicability of ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 across different business models.
- Fast Track ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 FAQ
- Related ISO 27001 Controls
- Further Reading
- ISO 27001 Controls and Attribute Values
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Strategic Briefing Slides
What is ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3?
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Information Access Restriction is an ISO 27001 control that looks to make sure you have controls in place to restrict access to information based on risk and organisation need.
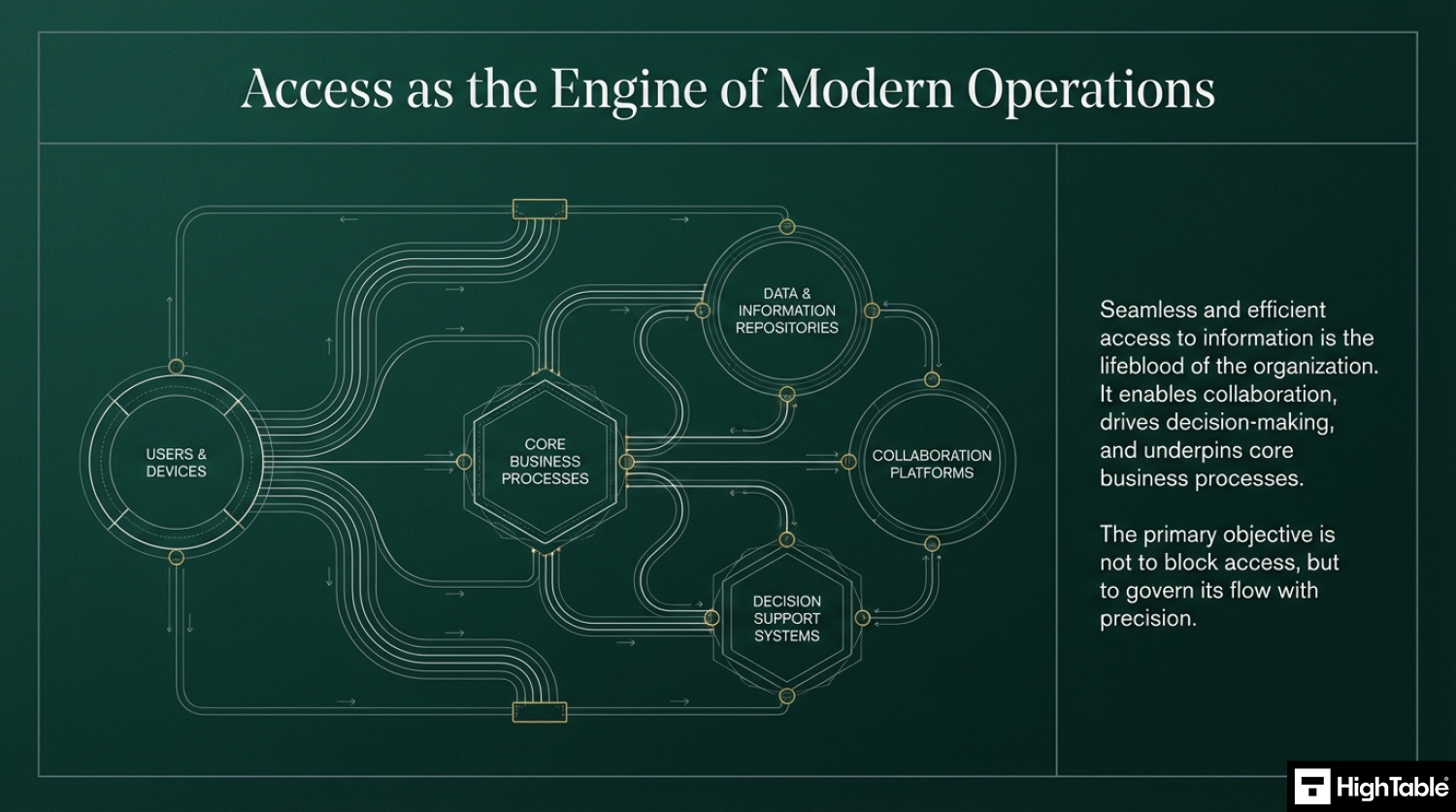
The best way to protect information security is with access control and information access restrictions. It’s primary function is to ensure the confidentiality of information and is a technique that you use every day to access websites and services.
This ISO 27001 annex a control sets out the requirement to restrict access to information and services and to properly implement and manage access control.
In ISO 27001 this is known as ISO 27001:2022 Annex A 8.3 Information Access Restriction.
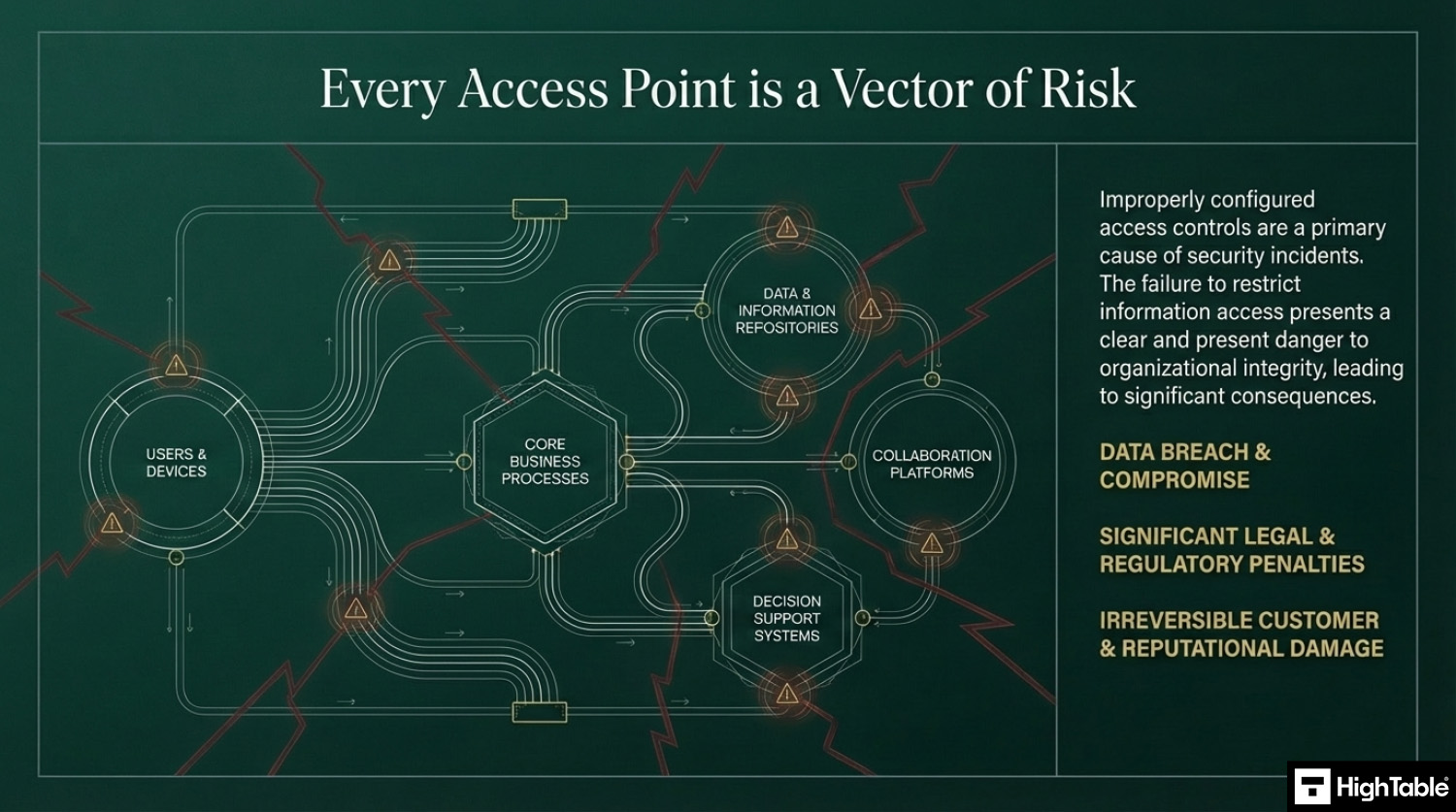
It is important because people with the wrong access controls in place could access information that was not intended for them and this presents a risk of data breach and data compromise which can have significant legal, regulatory and customer consequences.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Purpose
The purpose of ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Information Access Restriction is to ensure only authorised access and to prevent unauthorised access to information and other associated assets.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Definition
The ISO 27001 standard defines ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Information Access Restriction as:
Access to information and other associated assets should be restricted in accordance with the established topic-specific policy on access control.
ISO27001:2022 Annex A 8.3 Information Access Restriction
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Free Training Video
In the video ISO 27001 Information Access Restriction Explained – ISO27001:2022 Annex A 8.3 I show you how to implement it and how to pass the audit.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Explainer Video
In this beginner’s guide to ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Information Access Restriction, ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Stuart Barker and his team talk you through what it is, how to implement in and how to pass the audit.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Podcast
In this episode: Lead Auditor Stuart Barker and team do a deep dive into the ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Information Access Restriction. The podcast explores what it is, why it is important and the path to compliance.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Implementation Guide
This is not the Wild West so we do not allow everyone to have access to everything. A basic premise of information security is access. We protect what is important to us and only allow those that we want to have access to it, to have access to it.
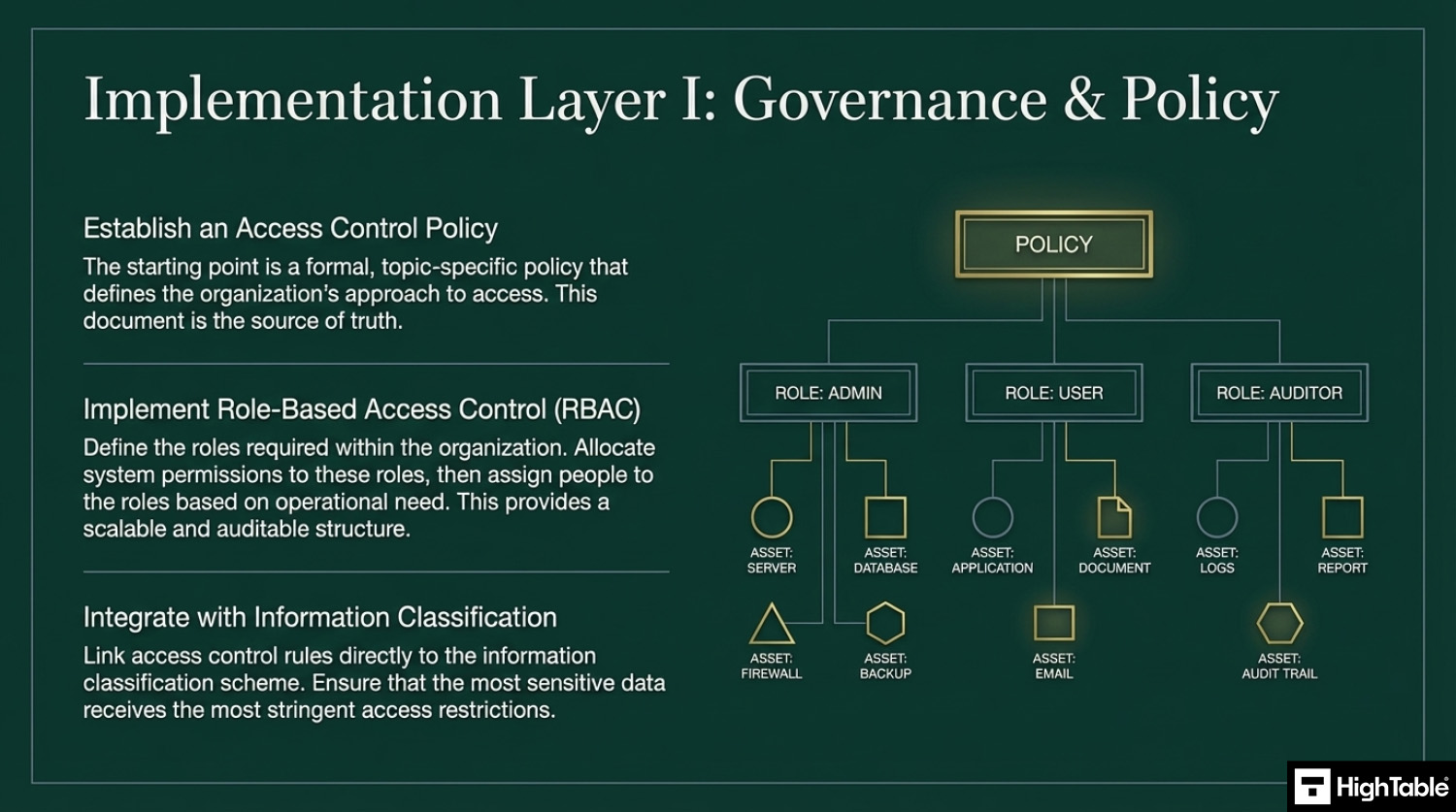
Implement an Access Control Policy
Your starting point for this control is to implement a topic specific policy on access control and include in that policy your approach to access. The ISO 27001 Access Control Policy Template is already written for you and ready to go and includes a great free Access Control Policy Example PDF. There is a lot more information on the Access Control Policy including how to write your own is covered in ISO 27001 Access Control Policy Ultimate Guide.
We are not talking here about privilege access which we covered in 8.2 Privilege Access but we are looking more general.
Implement Role Based Access
I find the use of role based access as a technique is a great tool here. Understanding what roles you need, defining them and then allocating people to roles based on need.
Adopt the principle of Least Privilege
Access should be granted based on the principle of least privilege, meaning users only get the minimum access necessary for their role.
Adopt the principle of Need-to-Know
Users should only have access to information they need to perform their duties.
Enforce access control
Learning from previous tutorials and in particular ISO 27001 Annex A 5.18 Access Rights you will ensure proper access control proportionate to the risk posed by the access that is required.
Account for dynamic access
The control is not particularly hard. It is mainly common sense. The standard talks a lot about dynamic access management techniques, which I think is phrase they are hoping catches on. It is mainly about second guessing dynamic changes that require access control considerations. Situations like sharing externally, or when investigations occur.
Base access on information classification
Link access control to information classification to ensure sensitive data is appropriately protected. You can take into account the information classification scheme when you are working out what your access requirements are.
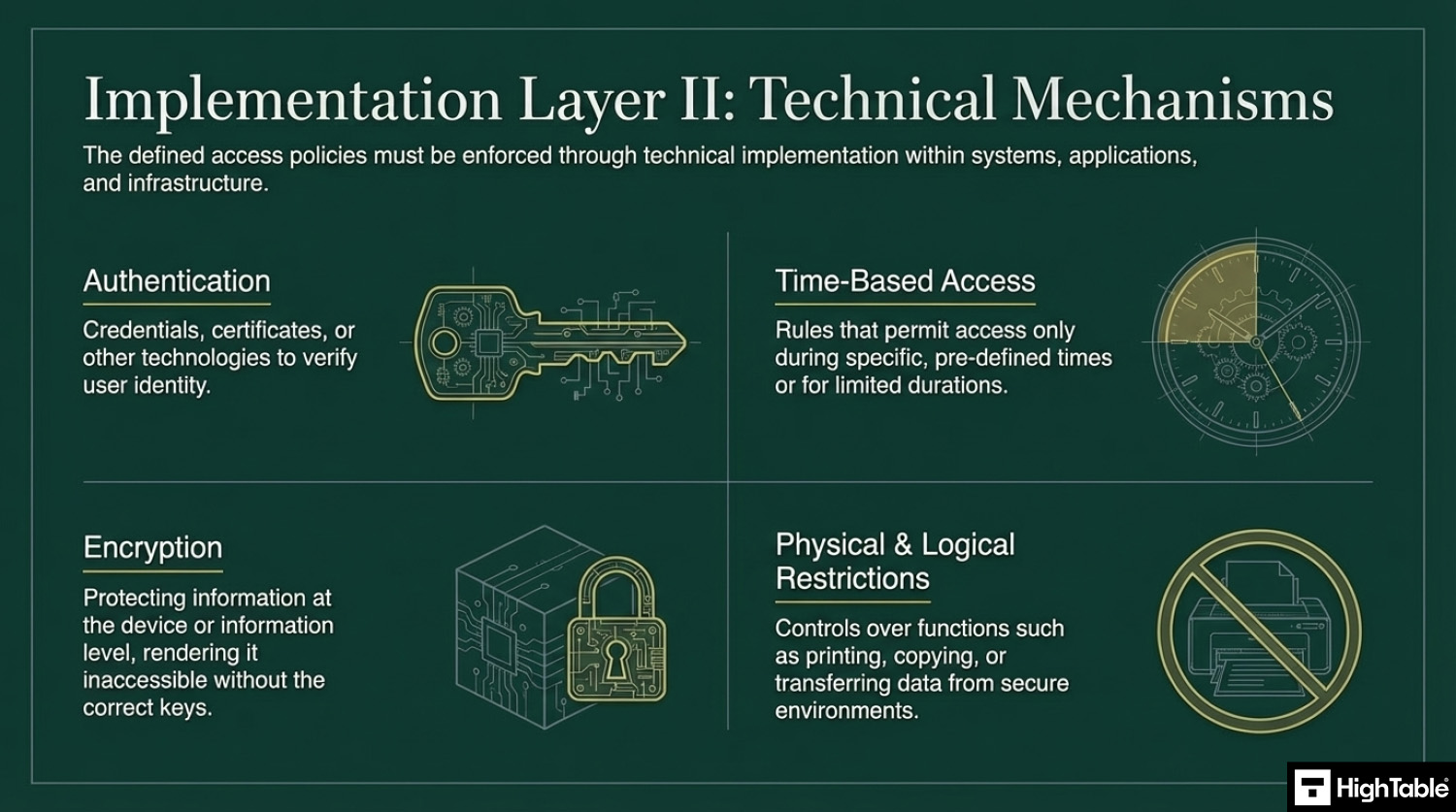
Implement technical controls
Ensure that the defined access policies are technically implemented in systems, applications, and services. The controls are mainly technical once you have the policy and the requirements. Examples of appropriate technical controls include:
- Authentication technology: credentials, or certificates to access information.
- Time based access: that allows access for or in set times.
- Encryption: for protecting information either at the device or information level.
- Printing permissions: Setting out what the printing permissions are if appropriate.
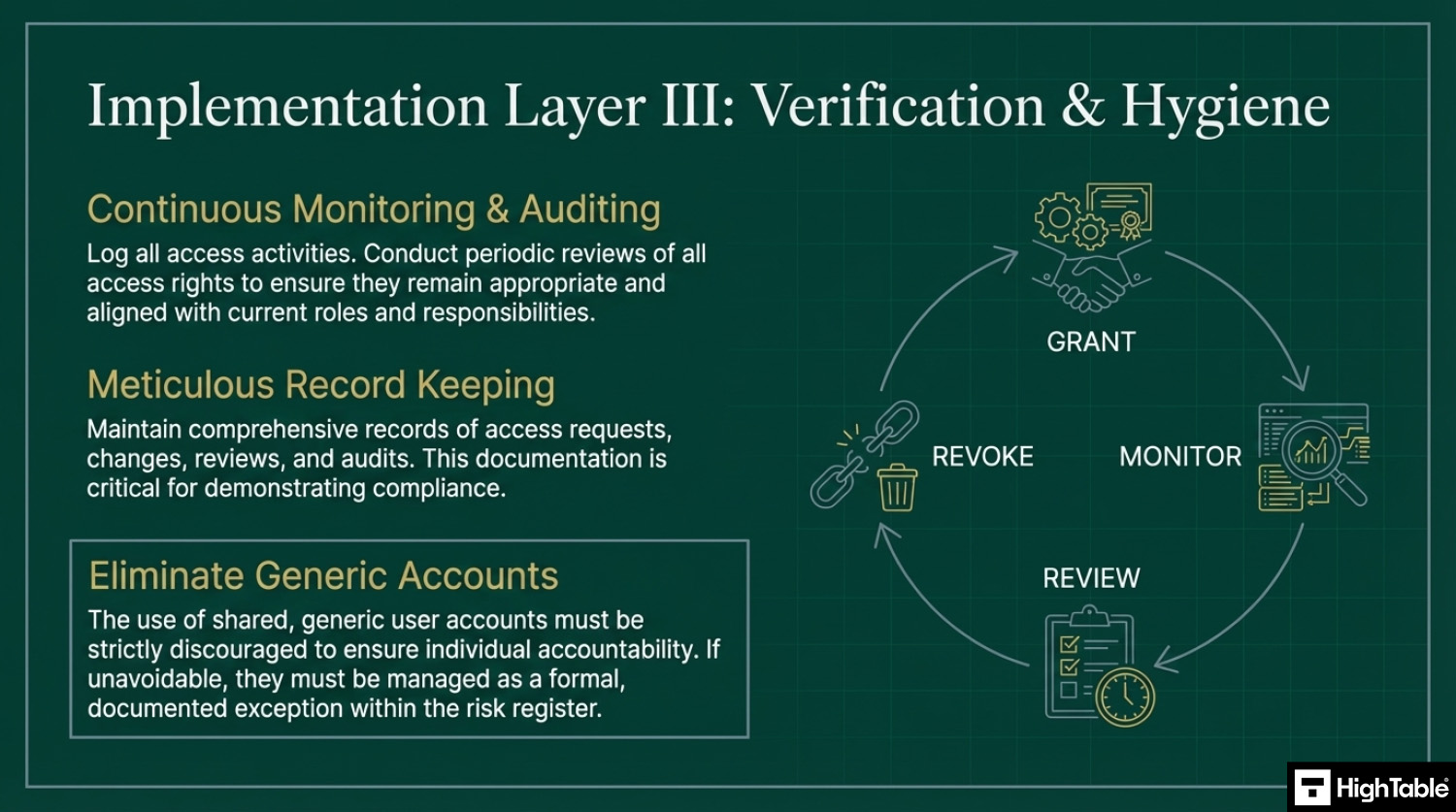
Implement Monitoring & Auditing
Log access activities and conduct periodic reviews of access rights to ensure they remain appropriate.
Keep records
There will be consideration for recording access, monitoring, reporting and alerting.
Information access restrictions have been around a long time and there is nothing to worry about here.
Remove generic accounts
You should really discourage the use of generic accounts. We want to be able to tie actions back to an individual. If you simple have to have a generic account then my recommendation is to manage it as an exception and record it in the risk register. Mange it via risk management, even if that is accepting the risk.
How to implement ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3
Restricting access to information is a fundamental security control designed to prevent unauthorised disclosure and ensure that personnel only interact with data necessary for their specific job functions. By following these technical implementation steps, your organisation can establish a robust access management framework that satisfies ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 requirements and mitigates the risk of internal and external data breaches.
1. Formalise Information Access Policies and Rules of Engagement
- Draft a topic specific Access Control Policy that defines the criteria for granting, limiting, and revoking access to various information classifications.
- Establish a Rules of Engagement (ROE) document for system administrators that outlines the technical boundaries for managing high sensitivity data repositories.
- Result: A documented governance framework that ensures all access decisions are consistent, authorised, and based on business requirements.
2. Provision Role Based Access Control (RBAC) via IAM
- Implement granular Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles to enforce the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) across all cloud and on premises systems.
- Group users into functional roles rather than assigning individual permissions to simplify the management of complex access structures.
- Result: Technical enforcement of the “need to know” principle, ensuring users only possess the minimum level of access required to perform their duties.
3. Enforce Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) and Conditional Access
- Mandate the use of phishing resistant Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) for all users accessing organisational applications and data sets.
- Configure Conditional Access policies to evaluate login context, such as geographic location and device health, before granting entry to sensitive environments.
- Result: A hardened authentication layer that prevents unauthorised access even in the event of primary credential compromise.
4. Restrict Privileged Access through PAM and JIT Workflows
- Deploy a Privileged Access Management (PAM) solution to isolate and monitor administrative accounts, which are prime targets for attackers.
- Utilise Just In Time (JIT) access workflows to provide temporary elevation of privileges for specific tasks, revoking these rights automatically upon completion.
- Result: Reduction of the “standing privilege” risk and a significantly smaller blast radius in the event of a privileged account compromise.
5. Execute Regular Access Reviews and Technical Audits
- Schedule quarterly access reviews where department heads must revalidate the permissions held by their team members.
- Utilise automated logging to track all access events and export these to a SIEM for real time monitoring of anomalous behaviour or unauthorised access attempts.
- Result: Continuous alignment between current user permissions and actual business needs, identifying and correcting “permission creep” before it becomes a vulnerability.
6. Revoke Access immediately upon Role Change or Termination
- Integrate the Human Resources Information System (HRIS) with the IAM platform to automate the suspension of access rights during employee offboarding.
- Formalise a workflow for role changes to ensure that old permissions are revoked before new rights are provisioned, preventing the accumulation of unnecessary access.
- Result: Elimination of “orphan accounts” and ensuring that former employees or transferred staff cannot access sensitive information from their previous roles.
Role Based Access Matrix Example
| Feature / Data | Admin | Manager | User | Guest |
| View Customer List | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Edit Customer Address | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Delete Customer | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Export Data | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
How to pass an ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 audit
Time needed: 1 day.
How to comply with ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3
- Have policies and procedures in place
Write, approve, implement and communicate the documentation required for information access restriction.
- Assess your access requirements and perform a risk assessment
Have an asset management process that includes an asset register. For each asset type perform a risk assessment and access requirements review.
- Implement controls proportionate to the risk posed
Based on the risk assessment implement the appropriate controls to mitigate the risk.
- Keep records
For audit purposes you will keep records. Examples of the records to keep include changes, updates, monitoring, review and audits.
- Test the controls that you have to make sure they are working
Perform internal audits that include the testing of the controls to ensure that they are working.
Top 3 ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 mistakes and how to avoid them
The top 3 mistakes people make for ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 are
- Not restricting access when people leave: Having a robust starter, leaver, mover process that accounts for leavers and considers the access restrictions during the notice period as well as when the person leaves is key. This is often overlooked with people having full access during notice and often the access still being in place when they leave.
- Not matching your classification policy: The access policy and the classification policy set out what you do, not how you do it. Often there is an mis match with what actually happens. Consider approaches like role based access that allow you to define the access restriction requirements and then monitor, report and audit against it.
- Your document and version control is wrong: Keeping your document version control up to date, making sure that version numbers match where used, having a review evidenced in the last 12 months, having documents that have no comments in are all good practices.
Applicability of ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 across different business models.
| Business Type | Applicability | Examples of Control Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Small Businesses | Focuses on basic folder-level and application-level restrictions to ensure staff only see what they need for their daily tasks. The goal is to prevent accidental data exposure across a small team. |
|
| Tech Startups | Critical for protecting the production environment and customer databases. Compliance requires a formal Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) model to manage permissions as the team scales rapidly. |
|
| AI Companies | Vital for ensuring the confidentiality of proprietary model weights and sensitive training datasets. Restrictions focus on isolating research data from standard corporate access. |
|
Fast Track ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
For ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 (Information access restriction), the requirement is to ensure only authorized access and prevent unauthorised access to information and assets. This is primarily a governance and organizational control focused on “Need-to-Know” and “Least Privilege” principles.
| Compliance Factor | SaaS Compliance Dashboards | High Table ISO 27001 Toolkit | Audit Evidence Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policy Ownership | Rents access to your RBAC rules; losing the subscription means losing your documented “Need-to-Know” standards. | Permanent Assets: Fully editable Word/Excel Access Control Policies that you own forever. | A localized Access Control Policy stored on your internal server defining departmental “Least Privilege” rules. |
| Implementation | Attempts to “automate” human decisions with complex dashboards that cannot define your office culture. | Governance-First: Formalizes your existing team structure into a professional Role-Based Access Matrix. | A completed RBAC Matrix showing that “Guest” accounts are restricted from “Finance” folders. |
| Cost Structure | Charges a “Per-Seat Tax” based on the number of users or roles managed, scaling aggressively as you grow. | One-Off Fee: A single payment covers your governance for 10 employees or 1,000 across the entire estate. | Allocating budget to secure ID management (like Okta or Entra) rather than a monthly compliance “paperwork” fee. |
| Organizational Freedom | Mandates rigid role documentation that may clash with lean startups or complex matrix management. | 100% Flexible: Standards adapt to any structure, from flat hierarchies to multi-national departments. | An Access Control Policy tailored to your specific agile workflow without being constrained by SaaS software logic. |
Summary: For Annex A 8.3, an auditor wants to see that you have a formal policy for access restriction and proof that you follow it (e.g., an RBAC matrix). The High Table ISO 27001 Toolkit provides the governance framework to satisfy this requirement immediately. It is the most direct, cost-effective way to achieve compliance using permanent documentation that you own and control.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 FAQ
What is the primary objective of ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3?
The objective is to strictly limit access to information and assets based on established access control policies. It is a preventive technological control designed to ensure that users, systems, and applications can only access the specific data they are authorized to see, thereby maintaining confidentiality and integrity.
- **Prevents unauthorized access** to sensitive business information.
- **Enforces the “Need-to-Know” principle** across the organization.
- **Aligns technical restrictions** with the organization’s broader Access Control Policy.
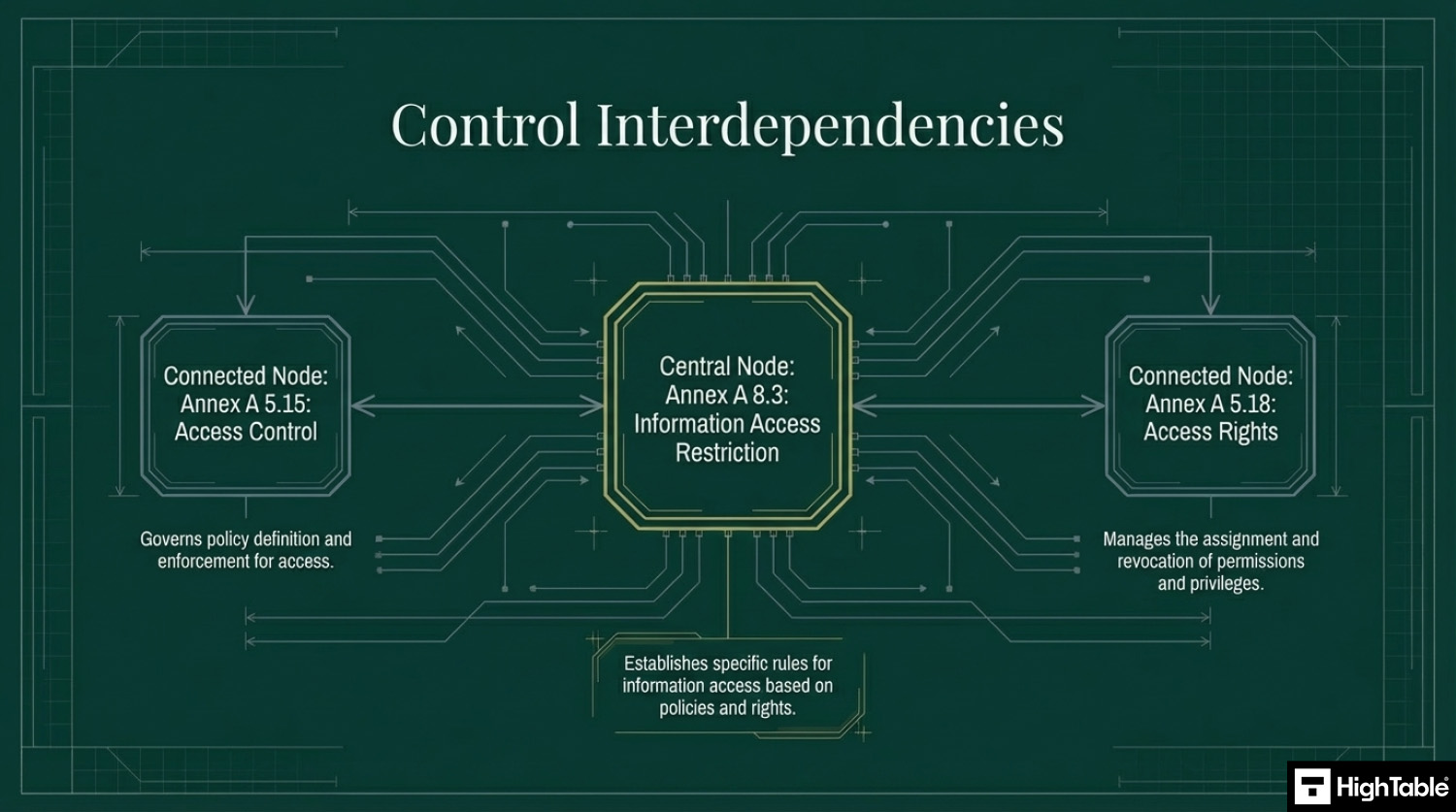
How does Annex A 8.3 differ from Annex A 5.15 (Access Control)?
Annex A 5.15 is the “Rule Book,” while Annex A 8.3 is the “Enforcement.” While they are closely related, 5.15 is an organizational control that focuses on defining the rules, policies, and management of logical and physical access. Annex A 8.3 is a technological control focused on the specific technical mechanisms used to restrict that access.
- Annex A 5.15 (Organisational): Defines who should have access and how users are managed.
- Annex A 8.3 (Technological): Applies the actual restrictions (e.g., file permissions, database views) to ensure the policy is technically active.
What is “Dynamic Access Management” in the context of ISO 27001?
Dynamic Access Management adjusts permissions in real-time based on context, rather than relying solely on static roles. The 2022 update to ISO 27001 places greater emphasis on this modern approach, acknowledging that access needs can change based on location, time, or threat levels.
- Time-Based Access: Restricting login capabilities to business hours only.
- Location-Based Access: Blocking access to sensitive financial data from non-corporate IP addresses.
- Action-Based Triggers: Temporarily elevating privileges for a specific task and revoking them immediately after.
How should we implement the “Principle of Least Privilege” for this control?
You must grant users the absolute minimum access required to perform their job functions—and nothing more. This is the golden rule of Information Access Restriction. Default settings should always be “Deny All,” with permissions explicitly added only when necessary.
- Default Deny: Start with zero access and add permissions incrementally.
- Granular Control: Avoid broad “Read/Write” permissions; separate them into “View,” “Edit,” “Delete,” and “Export.”
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign privileges to defined roles (e.g., “HR Manager”) rather than individual users to prevent privilege creep.
What evidence will an ISO 27001 auditor look for regarding Annex A 8.3?
Auditors will primarily look for a Topic-Specific Access Control Policy and evidence of technical enforcement (The Access Matrix). They will want to see that your written rules match the reality of your IT systems.
- Access Matrix: A document or system configuration showing which roles can access which data.
- Live System Checks: The auditor may ask you to log in as a standard user and attempt to access a restricted folder (e.g., Payroll).
- Access Logs: Records showing that access restrictions are being monitored and reviewed.
- Review Records: Proof that access rights are audited regularly (e.g., every 6 months).
What are the most common mistakes with Information Access Restriction?
The most frequent failure is “Privilege Creep” and failing to revoke access for leavers. Organizations often add new permissions as employees change roles but fail to remove old ones, leading to excessive access accumulation.
- Generic Accounts: Using shared logins (e.g., “admin@company.com”) which destroys accountability.
- Mismatched Policies: Having a strict policy on paper but lax settings in the actual software (e.g., everyone is a Local Admin).
- Inconsistent Offboarding: Leaving accounts active during notice periods without increased monitoring or restriction.
Related ISO 27001 Controls
Relevant ISO 27001 Annex A controls here include:
Further Reading
ISO 27001 Controls and Attribute Values
| Control type | Information security properties | Cybersecurity concepts | Operational capabilities | Security domains |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preventive | Confidentiality | Protect | Identity and access management | Protection |
| Integrity | ||||
| Availability |
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.3 Strategic Briefing Slides