In this definitive briefing on ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Change Actions, Lead Auditor Stuart Barker explains exactly what it is and the two approaches to being compliant. He shares insights on the common mistakes people make and how to future proof your information security management system (ISMS) against future changes.
Table of contents
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Change Actions
- Two Commons Mistakes and how to Avoid Them
- The road to compliance
- Option 2: Full Integration
- The role of the ISO 27001 Toolkit
- Conclusion
- ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Climate Action Changes Explained Simply | The Lead Auditor Podcast
- ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Strategic Implementation Briefing [Auditor Explained]
- ISO27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes FAQ
- Further Reading
- ISO27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes Strategic Briefing Slides
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Change Actions
ISO 27001:2022 was updated in February 2024 with Amendment 1 to include climate change considerations. This created an opportunity for consultants to generate billable hours and for organisations to over-engineer their response.
Let us explore the precise analysis of the change and the strategic, cost effective solution for compliance.
The amendment introduced two textual changes to two of the clauses.
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.1: Understanding the Organisation and Its Context Organisations are now required to formally determine whether climate change is a relevant internal or external issue impacting their information security management system.
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.2: Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Interested Parties A new mandatory note specifies that relevant interested parties may have specific requirements related to climate change that the organisation must consider.
These additions represent a mandate but are not a fundamental evolution of the information security management system.
The main driver is the introductions of climate change across all of the ISO standards, irrespective of their direct relevance.
The required action is actually minimal and there is no need to panic as no significant work has been introduced unless you want there to be.
Two Commons Mistakes and how to Avoid Them
There are three common mistakes that people make. They are based on the simplicity of the amendment and it’s vulnerability to misinterpretation.
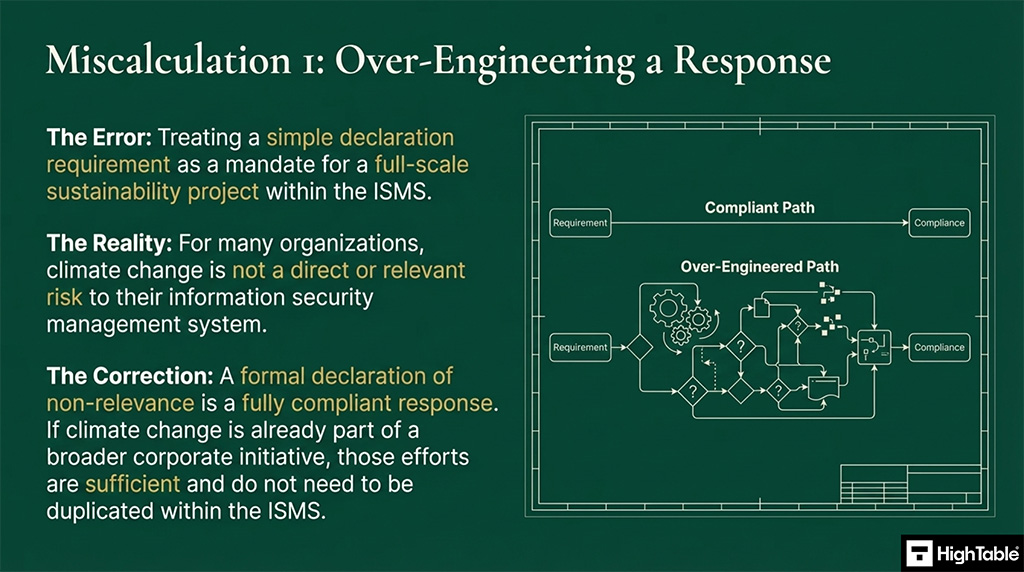
- Over-Engineering the Compliance Response Avoid treating this minor amendment as a full-scale sustainability project, as a formal declaration of non-relevance is a perfectly valid and compliant response for most organisations.
- Engaging Expensive External Consultants Steer clear of high-cost external help for these changes, as the requirements are purely procedural rather than technical and can typically be addressed internally in under one hour.
For many climate change is not a direct or relevant risk to the information security management system. For them, a formal declaration of non-relevance is a valid and compliant response.
The road to compliance
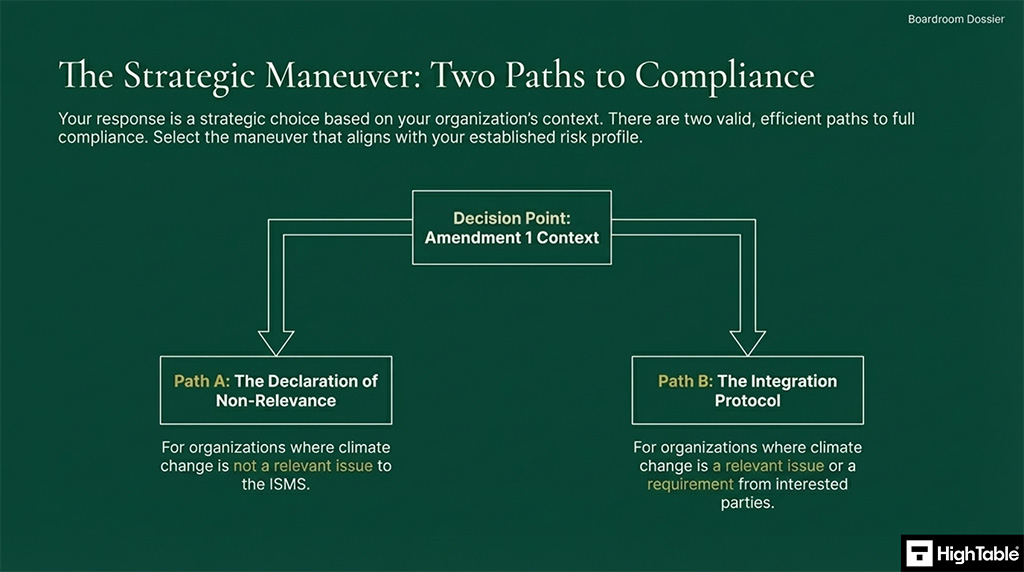
For compliance there are two paths and the response you take is dependent on the context of your organisation. Each path is valid and each path is compliant.
Option 1: Declaration of Non-Relevance
The first path is a declaration of non-relevance. This is the most efficient and clear approach to compliance. To implement this you
- Review: Formally evaluate the impact of climate change within your organisation to determine its relevance to the ISMS.
- Document: Update your Context of the Organisation document with a formal statement confirming that climate change was reviewed and deemed not a relevant issue.
- Confirm: Record that relevant interested parties were consulted and expressed no specific requirements related to climate change.
Option 2: Full Integration
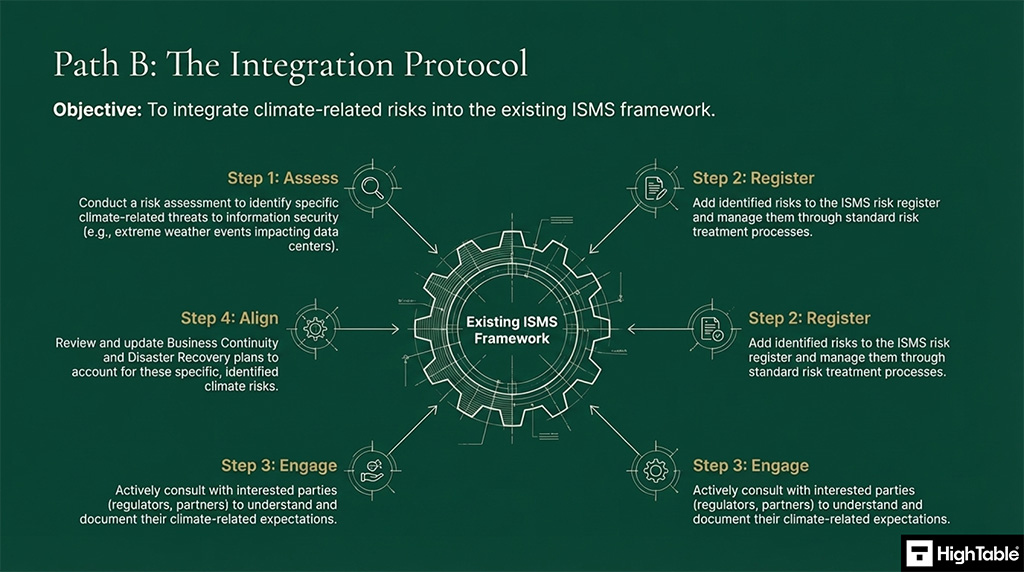
The second path is the full integration approach. This integrates climate-related risks into the existing ISMS framework. The process to implement this is:
- Assess: Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify specific climate-related threats that could impact information security.
- Register: Incorporate all identified climate risks into the formal ISMS risk register for management through your standard risk treatment process.
- Align: Review and update business continuity and disaster recovery plans to ensure they account for identified climate-related risks and scenarios.
- Engage: Consult with regulators, partners, and other interested parties to understand and document their specific climate-related requirements and risks.
Responding to this amendment is a minor task but maintaining a defensible and audit ready ISO 27001 posture is of strategic importance. By owning your compliance framework in-house you have greater control and reduced costs whilst eliminating dependence on external experts.
The role of the ISO 27001 Toolkit
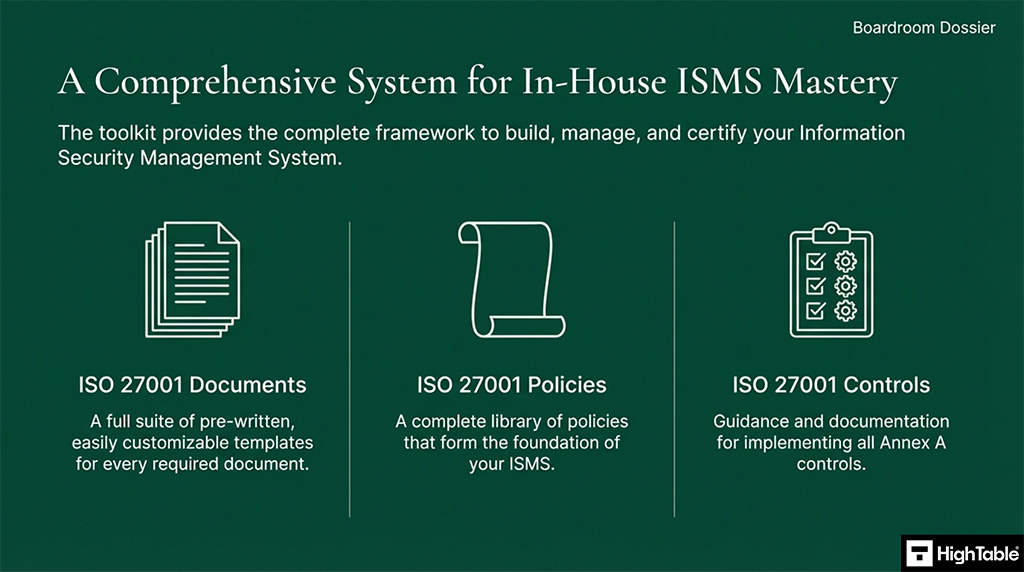
Having the ISO 27001 Toolkit from High Table provides the complete framework to build, manage and certify your information security management system whilst ensuring and guaranteeing you are up to date with the latest changes.
Replacing the leased model of platforms or the consultant model with an ownership model will equip your internal team with an audit verified management system at a fraction of the costs.
Conclusion
- Precision Over Panic Compliance should be approached with technical precision rather than urgency, acknowledging that the changes are manageable.
- Minor Procedural Update Recognise that ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 is a minor procedural change rather than a fundamental overhaul of your security framework.
- Resist Unnecessary Complexity Avoid consultant-driven complexity and associated expenses by focusing on the specific requirements of the amendment.
- Execute Defined Strategies Analyse your specific organisational context and implement one of the two compliant strategies provided in this briefing.
ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Climate Action Changes Explained Simply | The Lead Auditor Podcast
In this episode: Lead Auditor Stuart Barker and team do a deep dive into the ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Climate Action Changes. Technically referenced as ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Change Actions. The podcast explores what it is, why it is important and two paths to compliance. The most tactical taking less than 1 hour to implement.
ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Strategic Implementation Briefing [Auditor Explained]
In this strategic implementation briefing, Lead Auditor Stuart Barker and team do a deep dive into the introduction of ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Change Actions.
ISO27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes FAQ
What is the ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 regarding climate change?
ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 is a minor procedural update released in February 2024 that mandates organisations to determine if climate change is a relevant issue within their ISMS. It introduces two textual changes to Clauses 4.1 and 4.2, ensuring climate considerations are harmonised across all ISO management standards.
How do I comply with the ISO 27001 climate change requirements?
Compliance is achieved by executing a formal review of your organisational context, which typically takes less than 60 minutes. You must update your Context of the Organisation document to state whether climate change is a relevant issue and confirm that interested parties have no conflicting climate-related requirements.
Does ISO 27001 Amendment 1 require a full sustainability project?
No, Amendment 1 does not require a full-scale sustainability project or extensive technical changes. A common mistake is over-engineering the response; for the majority of organisations, a simple documented declaration of non-relevance within the ISMS framework is entirely sufficient to satisfy external audit requirements and maintain certification.
What are the two paths to ISO 27001 climate action compliance?
Organisations can choose between a Declaration of Non-Relevance or Full Integration. The first path involves documenting that climate change does not impact security, while the second path requires adding climate threats to the risk register and aligning business continuity plans to account for specific environmental risks.
Further Reading
ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1: – Absolutely Everything You Need to Know
ISO27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes Strategic Briefing Slides