ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 is the requirement to define the scope of the information security management system.
Table of contents
- What is ISO 27001 Clause 4.3?
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Infographic
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Mind Map
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Implementation Video Tutorial
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Podcast
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Strategic Implementation Briefing
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Auditor Requirements
- How to Implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.3
- How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 4.3
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Audit Checklist
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Templates
What is ISO 27001 Clause 4.3?
ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 (Determining The Scope Of The Information Security Management System) requires you to determine what is covered and protected by your Information Security Management System (ISMS).
In plain English, with limited resources you cannot protect everything as if it was confidential. You must identify what is most important to you, what you want to get certified for and explicitly document.
To satisfy this clause, you must document:
- What is in scope
- What is out of scope
- Your ISO 27001 Scope Statement
ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Infographic

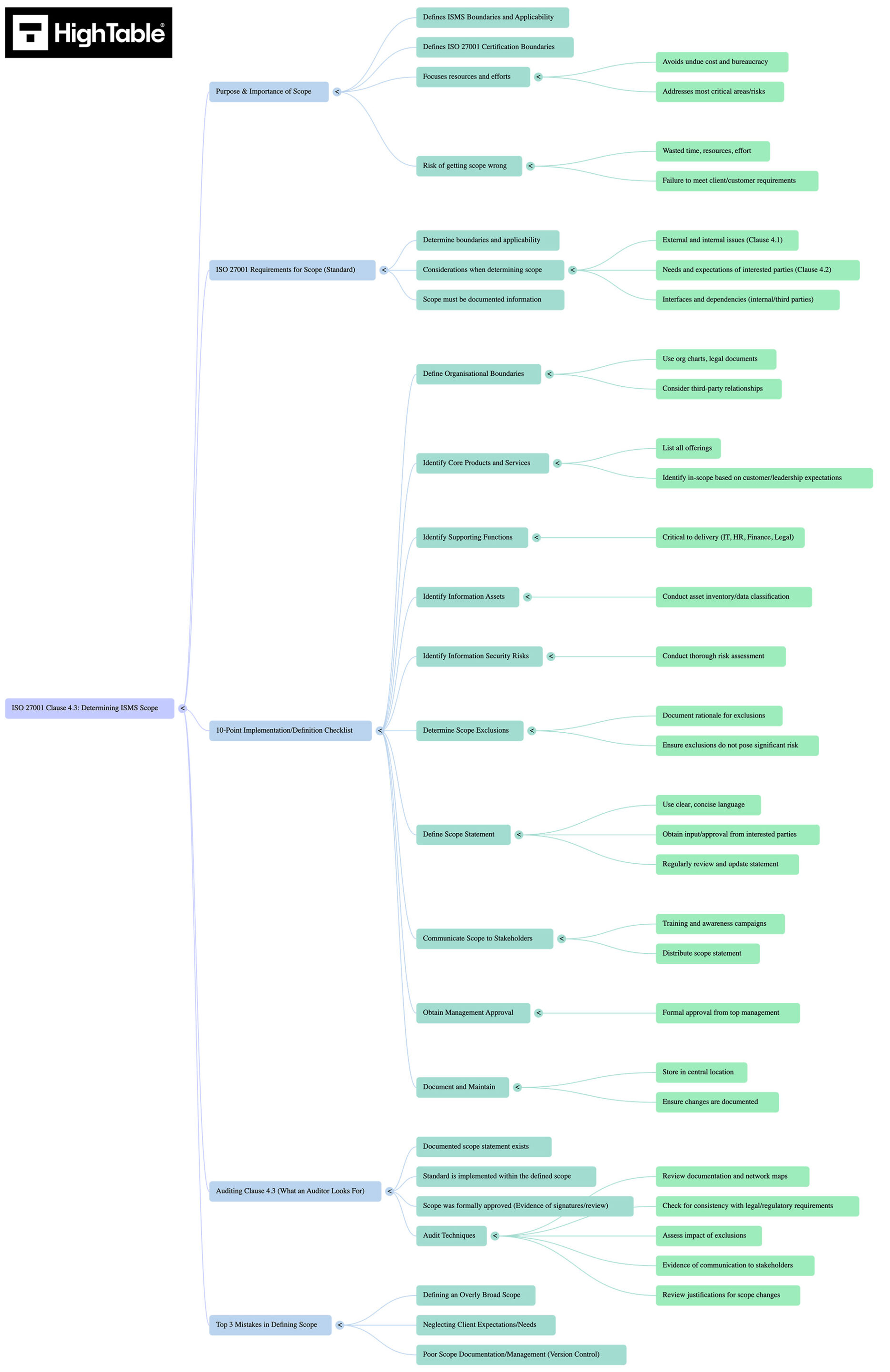
ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Mind Map
Identifying scope is not a box-ticking exercise; it is a filtering process. You are distinguishing between what you are protecting for good business practice and what you are protecting for certification and that must be audited.
This blueprint visualises the five vectors of influence that define your scope compliance obligations. Use this blueprint to audit your own understanding or to facilitate brainstorming sessions with your ISMS steering committee.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Implementation Video Tutorial
In this briefing, Lead Auditor Stuart Barker deconstructs the specific evidence requirements for Clause 4.3. Watch to learn how to distinguish between a “wish” and a “requirement” to avoid over-engineering your compliance scope.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Podcast
Listen to the briefing: In this episode, we move beyond the textbook definition. Stuart discusses how to handle determine a practical scope for your information security management system.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Strategic Implementation Briefing
In the strategic blueprint we give you the strategic blueprint for ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 including what it is, how to implement it, what an auditor wants to see and common mistakes people make from the perspective of an ISO 27001 lead auditor.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Auditor Requirements
The ISO 27001 standard states that the organization shall determine the boundaries and applicability of the information security management system (ISMS) to establish its scope. To satisfy a UKAS-accredited auditor, you must demonstrate:
- Integration of Inputs: You must provide evidence that your scope definition was not created in a vacuum. You must explicitly demonstrate how the Internal & External Issues (Clause 4.1) and the Interested Party Requirements (Clause 4.2) were considered when drawing the boundary lines. If a client contract (4.2) requires cloud security, your scope cannot exclude your cloud infrastructure.
- Interfaces & Dependencies: You must clearly define the physical and logical boundaries. An auditor will look for specific descriptions of interfaces with third parties (e.g., where your responsibility ends and a managed service provider’s begins) and dependencies between in-scope and out-of-scope processes.
The Trap: Do not attempt “Gaming the Scope.” You cannot exclude part of your business solely to avoid difficult controls or audit scrutiny if that part processes information relevant to the scope. If the “Marketing Department” is excluded but they share the same network and office as the “in-scope” Finance team, an auditor will likely reject the scope as invalid due to lack of network segmentation.
How to Implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.3
Follow the ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Guidance on How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.3
How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 4.3
Follow the ISO 27001 Leader Auditor Guidance on How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 4.3

ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Audit Checklist
The ISO 27001 Lead Auditor ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Audit Checklist

ISO 27001 Clause 4.3 Templates
We have already built the pre-configured templates for Clause 4.3. The ISO 27001 Implementation Suite includes:
- ISO 27001 Scope document
Fully formatted, auditor-verified, and ready for your logo.