ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 is the requirement to identify Internal and External Issues that could impact the information security management system.
Table of contents
- What is ISO 27001 Clause 4.1?
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Infographic
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Mind Map
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Implementation Video Tutorial
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Podcast
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Strategic Implementation Briefing
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Auditor Requirements
- How to Implement Clause 4.1
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Implementation Checklist
- How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 4.1
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Audit Checklist
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Templates
- Further Reading
What is ISO 27001 Clause 4.1?
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 (Understanding the organisation and its context) requires you to identify the internal and external issues that are relevant to your organisation’s purpose and affect its ability to achieve the intended outcomes of its Information Security Management System (ISMS). In plain English, you must determine the “macro” and “micro” factors that could help or hinder your security strategy.
To satisfy this clause, you must document:
- Internal Issues: Factors within your control, such as organisational culture, available resources, internal governance, and existing technology infrastructure.
- External Issues: Factors outside your control, such as legal and regulatory requirements, competitive landscape, political climate, and supply chain dependencies.
- This analysis forms the strategic foundation of your ISMS, ensuring your security posture is driven by operational reality, not theoretical compliance.
Reference: ISO 27001:2022 Clause 4.1: Understanding the Organization and Its Context
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Infographic

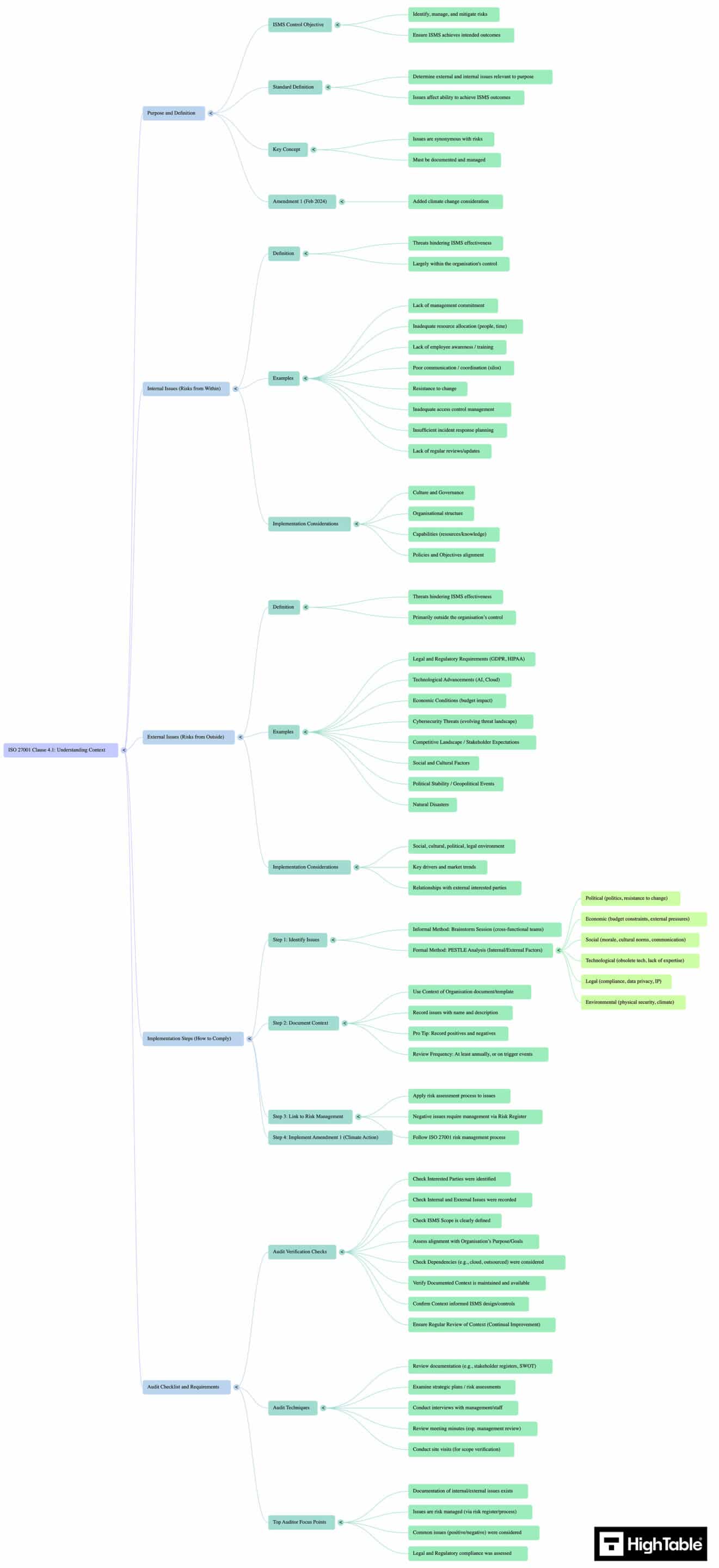
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Mind Map
Understanding Clause 4.1 requires moving beyond linear lists. The relationship between internal drivers, external forces, and their downstream impact on your ISMS is dynamic and interconnected.
We have developed the Contextual Architecture Map to visualise these dependencies. This schematic deconstructs the abstract requirements of the standard into four strategic quadrants, providing a “bird’s-eye view” of how your organisational context directly dictates your risk management and control selection.
Use this blueprint to audit your own understanding or to facilitate brainstorming sessions with your ISMS steering committee.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Implementation Video Tutorial
In this briefing, Lead Auditor Stuart Barker explains the intent of Clause 4.1 and why it is the most common point of failure in Stage 1 audits. He covers how to implement it and how to pass the audit.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Podcast
Listen to the briefing: In this episode, we move beyond the textbook definition. Stuart discusses how to use Clause 4.1 to secure budget from the board, and shares horror stories of organisations that failed their Stage 1 audit because they treated this clause as a “box-ticking” exercise.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Strategic Implementation Briefing
In the strategic blueprint we give you the strategic blueprint for ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 including what it is, how to implement it, what an auditor wants to see and common mistakes people make from the perspective of an ISO 27001 lead auditor.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Auditor Requirements
The ISO 27001 standard states that the organisation shall determine external and internal issues that are relevant to its purpose. To satisfy a UKAS-accredited auditor, you must demonstrate:
- Strategic Relevance: Your context isn’t just a list; it connects directly to your risk assessment.
- Regular Review: Evidence that these issues are reviewed at planned intervals (e.g., Management Review meetings).
- The Trap: Don’t just list “Cyber Attacks” as an external issue. Be specific about which attacks threaten your specific industry.
How to Implement Clause 4.1
Follow the ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Guidance on How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.1
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Implementation Checklist
Follow the ISO 27001 Lead Auditor ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Implementation Checklist
How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 4.1
Follow the ISO 27001 Leader Auditor Guidance on How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 4.

ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Audit Checklist
The ISO 27001 Lead Auditor ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Audit Checklist

ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Templates
ISO 27001 Internal and External Issues Template
The ISO 27001:2022 Context Of Organisation template is designed to fast track your implementation and give you an exclusive, industry best practice policy template that is pre written and ready to go. It is included in the ISO 27001 toolkit.

Stop Guessing. Start Passing.
AI-generated policies are generic and fail audits. Our Lead-Auditor templates have a 100% success rate. Don’t risk your certification on a prompt

Further Reading
How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.1
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Implementation Checklist
How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 4.1
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Audit Checklist
ISO 27001:2022 Amendment 1 – Absolutely Everything You Need to Know
ISO27001:2022 Amendment 1 Climate Action Changes – Definitive Briefing
ISO 27001 Clause 4.1 Understanding the Organisation and Its Context Explained