The auditor-verified guide to calculating audit fees, implementation costs, and hidden expenses. Stop guessing and start budgeting with precision.
Table of contents
- What does ISO 27001 actually cost?
- Visual Blueprint: The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- Cost Masterclass: The Auditor’s Breakdown
- The Lead Auditor Podcast: Budgeting Strategy
- Decoding the Fee Structure: Where the money goes
- The ISO 27001 Cost Calculator
- Strategic Savings: How to Lower Your Cost
- Stop Overpaying: The Implementation Suite
- The Financial Briefing: ISO 27001 Cost Architecture
- Download the ISO 27001 Certification Cost Board Presentation Pack
- ISO 27001 Certification Cost Mind Map
What does ISO 27001 actually cost?
The cost of ISO 27001 certification varies significantly based on organization size and complexity, but typically falls into three buckets: Implementation Costs (£5k – £60k), Stage 1 & 2 Audit Fees (£6k – £12k), and Maintenance Costs (£3k+/year).
For a typical 50-person technology company, the total Year 1 investment ranges from £15,000 to £40,000. This guide deconstructs those figures so you can present a defensible budget to your Board.
Visual Blueprint: The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)

Cost Masterclass: The Auditor’s Breakdown
In this financial briefing, Lead Auditor Stuart Barker explains the “Audit Day” formula used by certification bodies and exposes the “Consultant Tax” that inflates most budgets.
The Lead Auditor Podcast: Budgeting Strategy
Listen to the briefing: Stuart interviews a Certification Body insider to reveal how “scoping” your ISMS correctly can reduce your audit fee by up to 30%.
Decoding the Fee Structure: Where the money goes
Your budget must account for three distinct phases. Failing to distinguish between these leads to budget overruns.
1. The Implementation (The Variable)
- This is where you have the most control. You can pay a consultant £15,000+ to do it for you, or use a verified framework like the High Table Implementation Suite (~£290) to manage it internally.
2. The Certification Audit (The Fixed Cost)
- Paid directly to the Certification Body (e.g., BSI, SGS).
- Calculated based on “Audit Days” mandated by ISO 27006 (e.g., 50 employees ≈ 6-8 audit days).
- Estimated Cost: £1,000 – £1,200 per audit day.
3. The Maintenance (The Hidden Cost)
- Surveillance audits (Year 2 & 3).
- Penetration testing (Annual).
- Staff training and awareness tools.
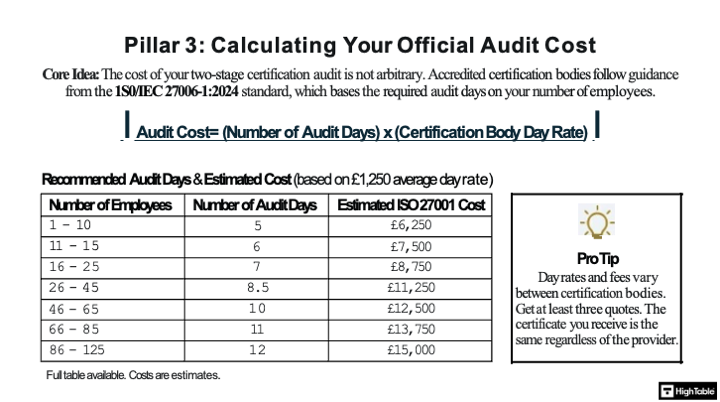
The ISO 27001 Cost Calculator
A simple table or video showing how to calculate audit days based on employee count.
| Number of employees | Number of Audit Days | Estimated ISO 27001 Cost |
|---|---|---|
| 1 -10 | 5 | £6250 |
| 11 – 15 | 6 | £7500 |
| 16 – 25 | 7 | £8750 |
| 26 – 45 | 8.5 | £11250 |
| 46 – 65 | 10 | £12500 |
| 66 – 85 | 11 | £13750 |
| 86 – 125 | 12 | £15000 |
| 126 – 175 | 13 | £16250 |
| 176 – 275 | 14 | £20625 |
| 276 – 425 | 15 | £21875 |
| 426 – 625 | 16.5 | £23125 |
| 626 – 875 | 17.5 | £24375 |
| 876 – 1175 | 18.5 | £25625 |
| 1176 – 1550 | 19.5 | £26875 |
| 1551 – 2025 | 21 | £28125 |
| 2026 – 2675 | 22 | £29375 |
| 2676 -3450 | 23 | £30625 |
| 3451 – 4350 | 24 | £31875 |
| 4351 – 5450 | 25 | £33125 |
| 5451 – 6800 | 26 | £34375 |
| 6801 – 8500 | 27 | £35625 |
| 8501 – 10700 | 28 | £36875 |
Strategic Savings: How to Lower Your Cost
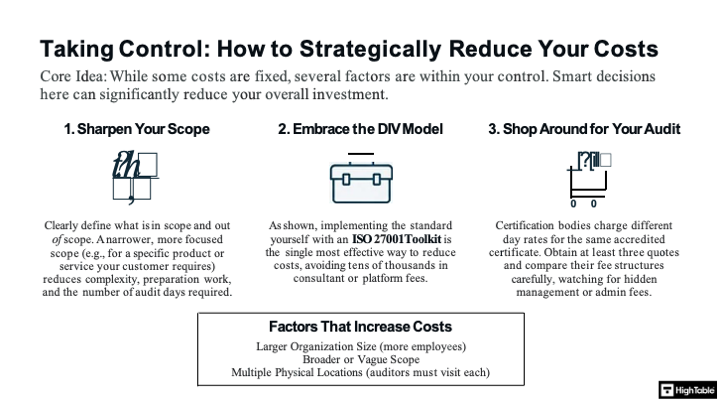
You cannot negotiate the Audit Fee (it is regulated). But you can reduce the number of days required.
- Reduce Complexity: Narrow your Scope (Clause 4.3).
- Eliminate Consultants: Use an Auditor-Verified Toolkit to replace 90% of the consultancy work.
- Pre-Audit Validation: Using our Internal Audit Service ensures you pass first time, avoiding costly “Special Audits” for failures.
Stop Overpaying: The Implementation Suite
Most of the cost of ISO 27001 is “Consultancy Time.” The ISO 27001:2022 Implementation Suite replaces £15,000 of consulting fees with a structured, auditor-verified framework for a fraction of the price.
Your Savings: ~£14,700 vs. Traditional Consultancy.
The Financial Briefing: ISO 27001 Cost Architecture
A strategic breakdown of the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) designed for your Board Deck presentation.
Understanding the price of certification requires looking beyond the quote from the certification body. The following briefing slides deconstruct the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for an ISO 27001 project, breaking down the mandatory audit fees, the variable implementation costs, and the hidden maintenance expenses.
Use these slides to build your business case and secure budget approval from your executive leadership team.

The Four Pillars of ISO 27001 Cost Analysis
Certification is not a single invoice; it is a three-year financial commitment. Most organizations budget for the Certification Audit (The Fixed Cost) but fail to account for the Implementation (The Variable Cost) and Maintenance (The Hidden Cost).
“If you only budget for the audit, you will run out of money before the auditor even arrives. Implementation is where 80% of the operational spend occurs.”

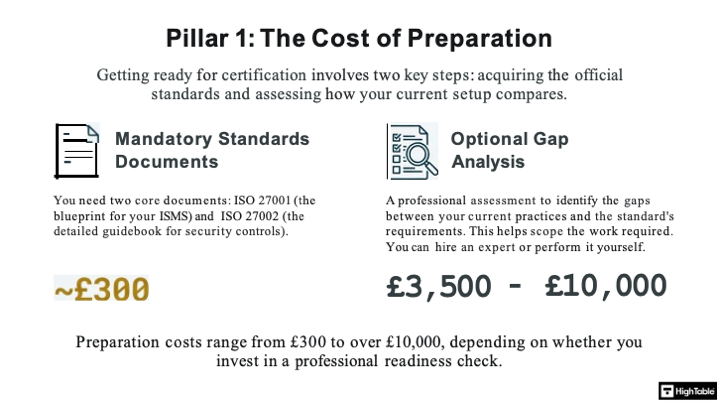
The Preparation Cost Analysis
Preparation costs go under the radar but are vital, especially in terms of purchasing the ISO 27001:2022 standard.
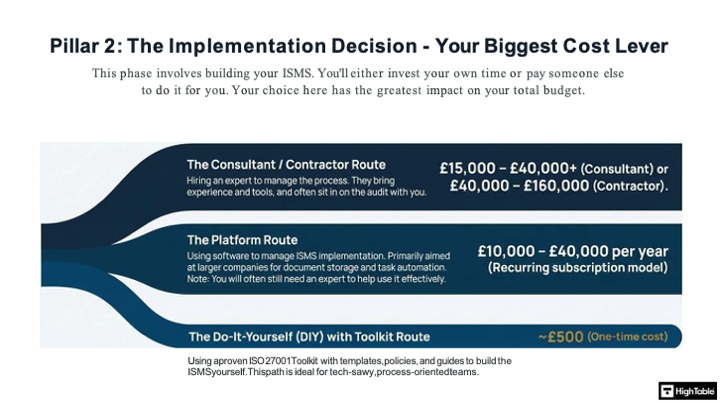
The Implementation Cost Analysis
This is the only line item entirely within your control. You effectively have three purchasing options:
- Full Consultancy (£15k+): High cost, low internal effort.
- Implementation Suite (£290): Low cost, guided effort. (The High Table Model).
- DIY (Unknown): Zero cash cost, but massive “Time Cost” and high risk of audit failure.
The ROI: Using a verified framework like the Implementation Suite typically yields a 50x ROI compared to hiring a full-time consultant.
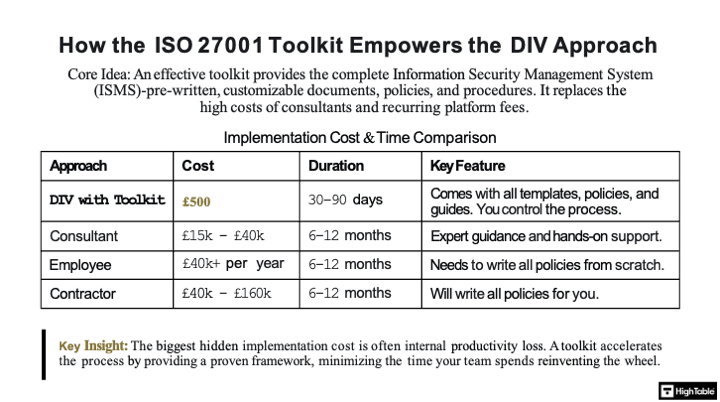
The ISO 27001 Toolkit Cost Comparision
It is easy to see that the cost of doing it with the ISO 27001 toolkit is the most affordable and strategic choice.
The Audit Fee Formula
Certification bodies (BSI, SGS, etc.) do not guess your price. They are legally mandated by ISO 27006 to calculate “Audit Days” based on your employee headcount and complexity.
The Math: A 50-person company typically requires 6–8 audit days. At an average rate of £1,100/day, your base fee is mathematically fixed.
Cost Control Strategy: You cannot negotiate the day rate, but you can reduce the complexity score by refining your Scope (Clause 4.3).
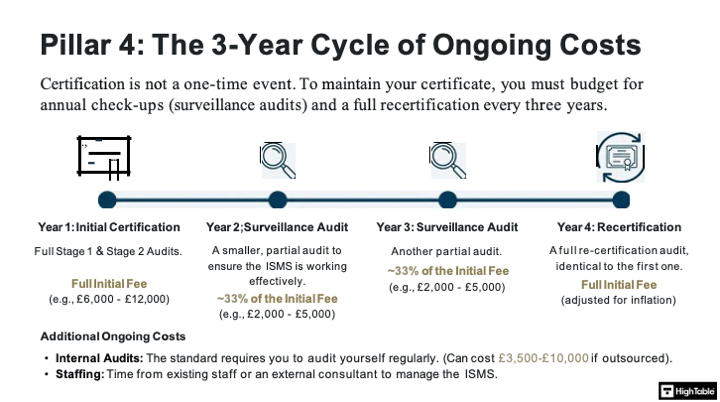
The Hidden Maintenance Costs Analysis
ISO 27001 is not a “one-and-done” achievement. You must budget for annual Surveillance Audits, which typically cost 33-50% of the initial certification fee. Additionally, you must factor in annual penetration testing and ongoing staff training tools.
Budget Warning: Ensure your OPEX budget covers Years 2 and 3, or you risk losing the certificate you just paid to get.
The Cost Reduction Strategy
There are simple steps you can take to drastically reduce your overall costs.
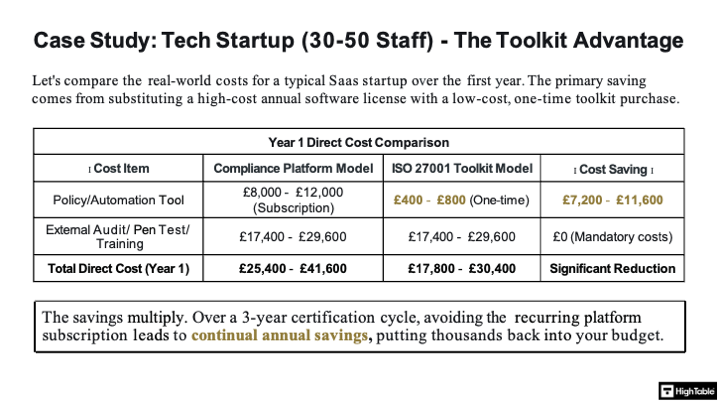
The ISO 27001 Certification Cost Case Study: Tech Startup
The ISO 27001 Certification Cost Case Study: AI Company
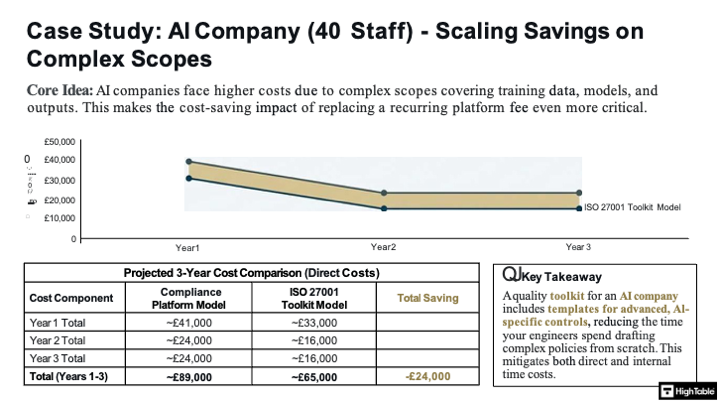
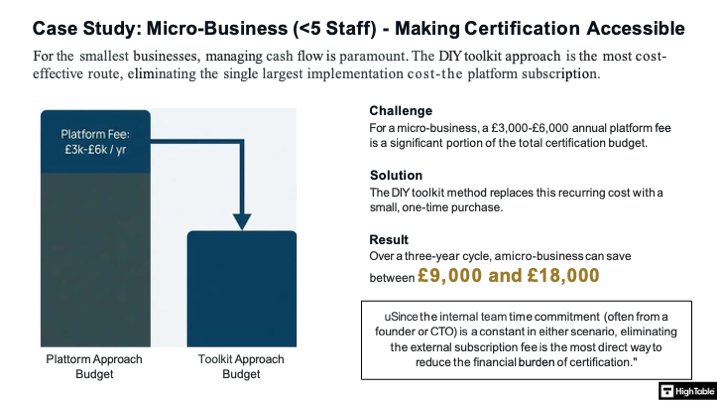
The ISO 27001 Certification Cost Case Study: Micro-Business
There are challenges with the ISO 27001 Cost for Individuals & Micro-Businesses. It is possible to make the certification accessible but it all comes down to having the right implementation strategy.
The ISO 27001 Certification Cost Strategy

Download the ISO 27001 Certification Cost Board Presentation Pack
Need to present these figures to your CFO or Board of Directors? Download the complete slide deck (PDF)
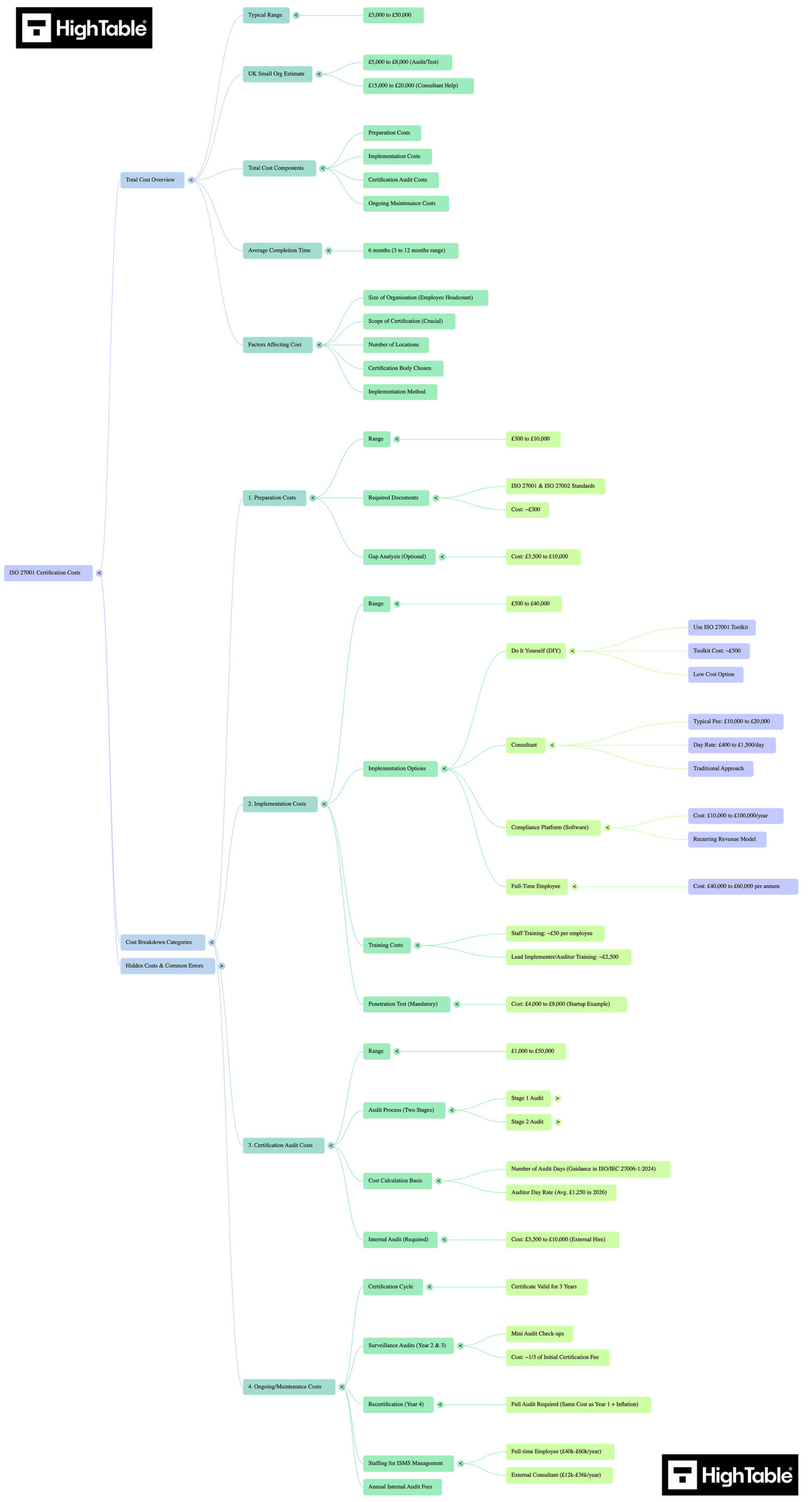
ISO 27001 Certification Cost Mind Map
Implementing this clause requires seeing the connections between disparate requirements. The following schematic distills the complex regulatory text into a clear, actionable workflow. Use this visual roadmap to navigate the critical critical path from initial assessment to final audit evidence.