ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 is a security control that mandates organizations to determine the necessary competence of personnel affecting information security performance. It requires companies to ensure staff possess appropriate education, training, or experience to manage risks effectively. By maintaining documented evidence of skills, this clause delivers the business benefit of reducing human error and ensuring audit readiness.
In this guide, I will show you exactly how to implement ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 and ensure you pass your audit. You will get a complete walkthrough of the control, practical implementation examples, and access to the ISO 27001 templates and toolkit that make compliance easy.
I am Stuart Barker, an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor with over 30 years of experience conducting hundreds of audits. I will cut through the jargon to show you exactly what changed in the 2022 update and provide you with plain-English advice to get you certified.
Key Takeaways
- Mandatory Requirement: The clause is a mandatory requirement that ensures personnel working on the information security management system (ISMS) have the necessary skills and experience.
- Implementation: You must engage with trained ISO 27001 resources, assign roles and responsibilities, and identify the required information security skills.
- Auditor’s Focus: Auditors will verify compliance by checking for documented roles, evidence of competence (e.g., a competency matrix), and training plans to address any gaps.
- Common Mistakes: The most frequent errors include not having anyone with ISO 27001 experience, failing to document roles, and neglecting to create training plans to maintain competence.
Table of contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 and Why is it Important?
- Applicability of ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 across different business models.
- Watch the ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Video Tutorial
- How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 7.2
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Implementation Checklist
- ISO 27001 Competency Matrix
- How to build your own competence matrix
- How to audit ISO 27001 clause 7.2
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Audit Checklist
- How to pass the ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 audit
- Top 3 ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Mistakes and How to Fix Them
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Top Non Conformities
- Fast track ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence for AI & Machine Learning Teams
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.2: Related Controls & Clauses
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 verses ISO 27001 Clause 7.1 and ISO 27001 Clause 7.3
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Mapped to other Standards
- Efficiency Hack: “Double Dipping” with ISO 9001/14001
- The SaaS Escape Hatch: Migrating Competence Data to Excel
- Troubleshooting: The “Legacy Staff” Problem
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.2: Competence FAQ
- Further Reading
- Glossary of Competence Terms
- Conclusion: Competence is a Process, Not a Destination
What is ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 and Why is it Important?
ISO 27001 competence is ensuring you have the skills and experience to run the information security management system.
What is does it mean? It means you have people on the team when we’re running your information security management system (ISMS) that know how to run the management system.
You cannot have ISO 27001 and go for certification if nobody knows any anything about ISO 27001, they’ve got no experience in ISO 27001 and they’ve got no knowledge in ISO 27001.
Purpose and Definition
The purpose of ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence is to make sure that the people you have working on the information security management system (ISMS) have the skills, knowledge and experience to do it.
The organisation shall: a) determine the necessary competence of person(s) doing work under its control that affects its information security performance; b) ensure that these persons are competent on the basis of appropriate education, training, or experience; c) where applicable, take actions to acquire the necessary competence, and evaluate the effectiveness of the actions taken; and d) retain appropriate documented information as evidence of competence.
ISO 27001:2022 Clause 7.2 Competence
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Requirement
Applicability of ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 across different business models.
| Business Type | Applicability of Clause 7.2 | Why it is Important | Examples of Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Businesses | Focuses on “jack-of-all-trades” roles and verifying the competence of external support (e.g., IT providers or consultants) rather than building large internal teams. | Ensures you don’t over-hire. Allows you to demonstrate compliance by outsourcing complex security roles (like Legal or Internal Audit) while retaining oversight. |
|
| Tech Startups | Requires specific technical competence in secure development (SDLC), cloud configuration, and incident response to meet rapid deployment cycles. | Critical for building trust with enterprise clients and investors. Proves your team isn’t just coding fast, but coding securely. |
|
| AI Companies | Demands niche expertise in data privacy, model robustness, AI ethics, and handling large-scale datasets securely. | Mitigates high risks associated with data poisoning and regulatory fines (e.g., EU AI Act). Competence here is a direct safeguard against existential business risk. |
|
Watch the ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Video Tutorial
In the ISO 27001 tutorial How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence I show you how to implement it and how to pass the audit.
How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 7.2
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 is a crucial part of an Information Security Management System (ISMS), focusing on the competence of people working under the organisation’s control. While Clause 7.1 deals with resources, Clause 7.2 specifically addresses the skills, knowledge, and experience needed to protect information assets. Implementing this clause is not just a box-ticking exercise; it’s about building a robust and knowledgeable security culture. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the essential actions to ensure all personnel are competent to perform their duties and contribute effectively to the ISMS.
To successfully implement ISO 27001 Clause 7.2, organisations must move beyond basic training logs to establish a defensible framework for human risk management. You must define, assess, and evidence the competence of every individual influencing your information security performance, including legal and technical roles. Follow these technical steps to build an audit-ready competence program.
Step 1: Formalise ISMS Roles and Accountability
- Action: Define specific information security duties for every role using a granular Accountability Matrix (RASCI). Assign ownership for Clause 7.1 resources and Annex A controls.
- Result: Ensures clear ownership of ISO 27001 controls and prevents ambiguity regarding who is responsible for critical tasks such as risk assessments or incident response.
- Technical Requirement: Update job descriptions to include specific ISMS responsibilities and map these to your Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) definitions to ensure segregation of duties.
Step 2: Define Technical and Legal Competency Requirements
- Action: Document the exact qualifications, experience, and skills required for each role. This includes internal technical skills (e.g., AWS security, firewall config) and external legal requirements (e.g., GDPR, Data Protection).
- Result: Creates a measurable standard for assessing staff. It also clarifies where external support, such as outsourced legal counsel or virtual DPOs, is necessary to meet competence obligations.
- Technical Requirement: Specify required certifications (e.g., CISSP, CISM, ISO 27001 Lead Auditor) and formalise contracts for outsourced legal competence where in-house expertise is absent.
Step 3: Conduct a Competency Gap Analysis
- Action: Audit your current workforce’s capabilities against your defined baselines using a Competency Matrix. Identify where incumbents lack necessary certifications or documented experience.
- Result: Generates a prioritised list of vulnerabilities where a lack of knowledge could lead to non-conformity.
- Technical Requirement: Utilise a structured Competency Matrix to visualise data, ensuring every person affecting the ISMS has a corresponding record of skill validation.
Step 4: Execute Targeted Training and Resourcing
- Action: Address identified gaps by implementing ISO 27001 Lead Implementer/Auditor training for internal staff or engaging specialist ISO 27001 consultants for complex phases like establishment and certification.
- Result: Mitigates human risk by ensuring the correct resource is used at the correct lifecycle phase, balancing internal development with external expertise.
- Technical Requirement: Create formal Training Plans within your Learning Management System (LMS) or engage High Table consultants to bridge high-risk competency gaps during the implementation phase.
Step 5: Centralise and Validate Audit Evidence
- Action: Archive all proofs of competence, including certificates, quizzes, and induction checklists, in a retrievable format.
- Result: Guarantees a smooth audit process by providing instant verification that competence is being actively managed and evolved.
- Technical Requirement: Maintain a digital register of Continuing Professional Development (CPD) logs and third-party competence contracts (e.g., legal/security operations) within your HR or GRC repository.
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Implementation Checklist
Effective implementation of ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 does not require expensive Learning Management Systems (LMS) or bloated GRC platforms. In fact, relying on SaaS tools often creates complexity and vendor lock-in. The most robust audit evidence is often the simplest: a signed document or a well-maintained spreadsheet. Use this checklist to implement competence controls using tools you already own.
| Step | Action | Common Challenge (The SaaS Trap) | The Solution (High Table Approach) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Define Requirements | Create a Competency Matrix in Excel or Google Sheets defining the skills required for each role. | Over-complicating the process by purchasing HR software modules that disconnect security requirements from actual job descriptions. | Use a simple spreadsheet. List roles on the Y-axis and required skills (e.g., “Firewall Config”, “GDPR Awareness”) on the X-axis. It is free, instant, and fully customisable. |
| 2. Assess Gaps | Manually compare current staff CVs and experience against your new Matrix. | Relying on automated “skills scraping” tools that miss context and create false positives, requiring manual review anyway. | Managerial Review. A human conversation between a manager and an employee is the most accurate way to validate actual competence versus theoretical knowledge. |
| 3. Plan Training | Update the “Training Plan” tab in your spreadsheet for any identified gaps. | Signing up for expensive “All-in-One” compliance training subscriptions where staff click through generic videos without learning. | Targeted Resourcing. Use free, high-quality resources (like YouTube or vendor documentation) or specific courses. Record the plan in your spreadsheet, not a third-party portal. |
| 4. Execute & Verify | Conduct the training and perform a post-training assessment (quiz or observation). | Trusting a SaaS platform’s “green tick” as evidence. Auditors know people skip through videos. | Demonstrable Competence. Have the employee perform the task under supervision or sign a policy reading receipt. A signed PDF is a permanent, immutable record you own. |
| 5. Retain Evidence | Save certificates, signed induction checklists, and training logs in a secure folder structure. | Storing evidence inside a proprietary GRC tool. If you stop paying the subscription, you lose your audit evidence. | Standard Folder Structure. Store files in SharePoint/Google Drive (e.g., /ISMS/7.2 Competence/Staff Name/). You retain full control and access to your data forever. |
The Role of External Consultants and Outsourcing
It can be useful to rely on the competence of third parties. If you engage with third parties and consultants then this is a fast track to the evidence of competence for the areas that they cover.
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Templates
For ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence the entire ISO 27001 toolkit is relevant but in particular the following templates directly support this ISO 27001 clause:
ISO 27001 Competency Matrix Template
The ISO 27001 competency matrix template is used to record the employees and the skills that they have, the skills they require and any training needs. It is directly supports clause 7.2 and is a key document to meeting it.

ISO 27001 Accountability Template
The ISO 27001 accountability template records which employees are accountable and responsible for the information security management system and all of the ISO 27001 Annex A controls. It is a key document in identifying and recording who is doing what and is used along with the competency matrix to record the skills and experience they have for the areas that they have been assigned.

ISO 27001 Training Policy Template
The ISO 27001 training policy template is a supporting document that sets out the organisations approach to training and commitment to ensuring employees have the skills and experience that they need to perform the roles that they have been assigned to.

ISO 27001 Competency Matrix
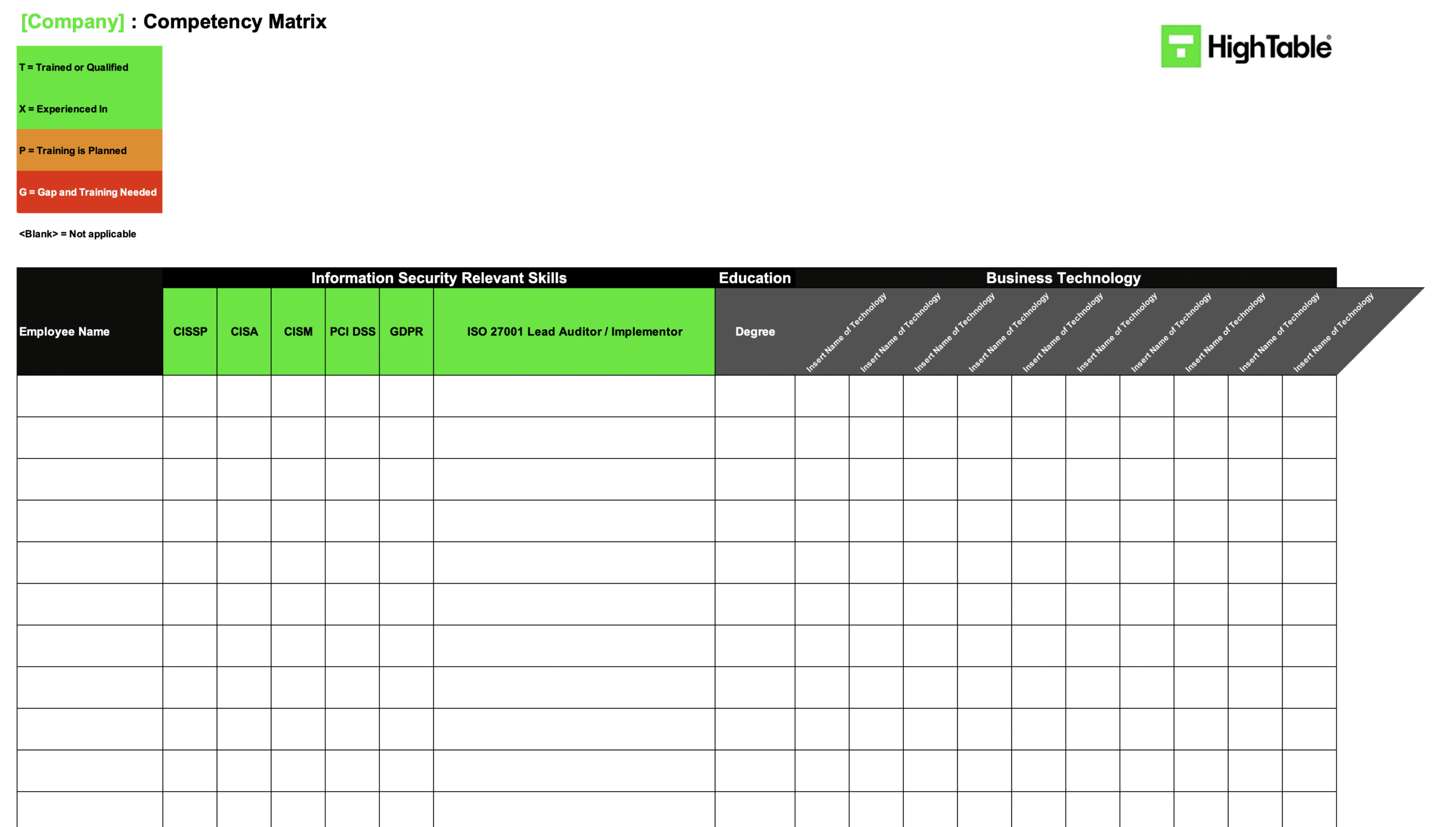
Sample Competency Matrix Entry (What “Good” Looks Like)
Don’t over-complicate your matrix. An auditor wants to see a clear link between the Role, the Skill, and the Evidence. Here is a practical example of a “Gold Standard” entry for a generic role.
| Role | Required Security Competence | Desired Level (1-5) | Current Level | Evidence Reference | Gap / Action? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Engineer | AWS Security Group Configuration | 4 (Expert) | 4 | AWS Certified Security – Specialty (Cert #12345) | No Action |
| HR Manager | ISO 27001 Screening (Clause 7.1.2) | 3 (Competent) | 2 | Internal Shadowing with Security Lead (In Progress) | Gap: Training booked for 15/09 |
| Receptionist | Physical Access Control (Annex 5.15) | 2 (Basic) | 2 | Signed SOP 004 + Clear Desk Check (12/08) | No Action |
How to Measure “Effectiveness” (The Clause 7.2(c) Trap)
Clause 7.2(c) requires you to evaluate the effectiveness of your training. Attendance is not effectiveness. Here are three metrics (KPIs) you can use to prove your training actually works:
- Phishing Failure Rate: If you run Phishing Competence training, measure the “Click Rate” before and after. A drop from 15% to 2% is hard evidence of competence.
- SLA Compliance: For technical roles, track the “Time to Patch” critical vulnerabilities. If competence increases, patch times should decrease.
- Error Rates: Track the number of “accidental data leaks” or “misdirected emails” reported to the DPO. A downward trend proves your Data Protection training is effective.
How to build your own competence matrix
How to audit ISO 27001 clause 7.2
This audit checklist is a guide on how to conduct an internal audit of ISO 27001clause 7.2 competence based on what the ISO 27001 certification auditor will audit. It gives practical audit tips including what to audit and how.
| Audit Step | Audit Objective | Audit Techniques & Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Review Competency Requirements | Verify the organisation has explicitly identified the necessary competencies for all ISMS-related roles. | Document review (Job Descriptions, Role Profiles, Competency Frameworks); Interviews with Management and HR; Analysis of ISMS activities. |
| 2. Assess Competence Levels | Ensure that specific competence levels (e.g., Basic, Advanced, Expert) are defined for each required competency. | Review of Skills Matrices; Interviews with Subject Matter Experts (SMEs); Analysis of competence level descriptions for measurability. |
| 3. Evaluate Assessment Methods | Verify that appropriate, evidence-based methods are used to assess the current competence of personnel. | Review of assessment procedures (Self-assessments, Peer reviews); Observation of assessment activities; Interviews with HR. |
| 4. Examine Training Plans | Ensure that formal Development Plans are in place to address any identified competency gaps. | Review of Training Plans and Development Programmes; Analysis of Training Needs Assessments (TNA); Interviews with Line Managers. |
| 5. Assess Training Effectiveness | Verify that the organisation evaluates whether training actually resulted in gained competence, not just attendance. | Review of post-training quizzes and on-the-job observations; Analysis of performance data; Interviews with trainees. |
| 6. Evaluate Competence Maintenance | Ensure that personnel maintain their competence over time through continuous professional development (CPD). | Examination of certification renewal logs; Review of CPD records; Interviews regarding continuous learning opportunities. |
| 7. Examine Competence Records | Verify that accurate, retrievable records of personnel competence and training are maintained. | Inspection of Learning Management Systems (LMS) or Training Databases; Review of physical training files; HR interviews. |
| 8. Assess Competence Review Process | Ensure that competence requirements are regularly reviewed and updated based on changing threats or technologies. | Review of competency review procedures; Analysis of changes in ISMS requirements; Management interviews. |
| 9. Evaluate Training Resources | Verify that adequate budget, time, and facilities are available to support required training activities. | Review of training budgets and resource allocation plans; Interviews with budget holders. |
| 10. Assess Learning Culture | Verify that the organisation actively promotes a culture of continuous security learning and development. | Analysis of employee engagement in learning activities; Review of internal communication materials; Staff interviews. |
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Audit Checklist
| Audit Step | Audit Action | Required Evidence (The ‘Owned’ Way) | Common Non-Conformity Flags (Red Flags) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Competency Definitions | Verify that specific security skills are defined for each role, not just generic “security awareness”. | Competency Matrix (Excel/PDF): A static document explicitly listing technical (e.g., “Firewall Config”) and soft skills (e.g., “Phishing Detection”) per role. | Generic “All Staff” Baselines: Using the same low-level competency requirement for a Receptionist and a Cloud Engineer. |
| 2. Role Assignment | Check that ISMS roles (e.g., Risk Owner, Document Controller) are formally assigned to named individuals. | Signed Job Descriptions: PDFs signed by the employee acknowledging their specific ISMS responsibilities. | “Implied” Responsibilities: Assuming the IT Manager is the Security Lead without formal documentation or acceptance. |
| 3. Skills Gap Analysis | Review how the organisation identified current skill deficiencies against their defined requirements. | Gap Analysis Report: A simple spreadsheet highlighting red/amber/green status for each employee against the Competency Matrix. | Zero Deficiencies: A matrix that shows 100% competence for everyone. This usually indicates a “tick-box” exercise rather than a genuine assessment. |
| 4. Training Effectiveness | Validate that training actually transferred knowledge, rather than just marking a video as “watched”. | Post-Training Assessments: Graded quizzes (Google/Microsoft Forms) or “Observation Records” signed by a line manager. | Completion Certificates Only: Relying solely on third-party LMS certificates without verifying if the staff member understood the content. |
| 5. Evidence Retention | Ensure evidence of competence is retrievable, immutable, and owned by the organisation. | Centralised Evidence Folder: A structured directory (SharePoint/Drive) containing certificates, CVs, and CPD logs. | Vendor Lock-in: Evidence stored exclusively inside a proprietary GRC platform that would be lost if the subscription ends. |
| 6. Continual Improvement | Verify that competence is maintained and updated as threats evolve (e.g., AI risks, new regulations). | 12-Month Training Plan: A forward-looking schedule including budget for external courses, conferences, or advanced certifications. | Reactive Training: Training only happens after an incident or non-conformity occurs, with no proactive planning. |
How to pass the ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 audit
To pass an audit of ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence you are going to
- Understand the requirements of ISO 27001 Competence
- Identify the roles you need
- Allocate people to roles
- Assess the competency of people to perform those roles
- Address competency gaps through training or bringing in specialist help
The “Auditor Interview” Cheat Sheet
Auditors will randomly interview staff to verify competence. They won’t ask “Tell me about Clause 7.2.” They will ask practical questions. Distribute this cheat sheet to your team before the audit:
| If the Auditor asks… | Do NOT say… | DO say… |
|---|---|---|
| “How do you know how to do your job securely?” | “I don’t know, I just do it.” | “I follow the Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) stored in SharePoint, and I completed my specific induction training last June.” |
| “What training have you had?” | “I watched a video once.” | “I completed the annual Information Security refresher last month, and I have regular 1-2-1s with my manager to discuss any new tools or risks.” |
| “Who is responsible for security here?” | “The IT Manager.” | “We all are. I am responsible for the security of the data I handle, but [Name] is the ultimate owner of the ISMS.” |
What an auditor looks for
The audit is going to check a number of areas for compliance with ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence. Lets go through them
| Audit Focus Area | What the Auditor Checks |
|---|---|
| 1. Roles are Documented and Assigned | The auditor verifies that specific ISMS roles are formally documented and clearly allocated to individuals. You must demonstrate that every required role has an assigned owner within the management system. |
| 2. Competence is Documented | The auditor looks for evidence (such as a Competency Matrix) proving that assigned personnel possess the necessary skills. If gaps exist, they check for a documented remediation plan to acquire that competence. |
Top 3 ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Mistakes and How to Fix Them
In my experience, the top 3 mistakes people make for ISO 27001 clause 7.2 are
| The Mistake | Why it Fails (The SaaS Trap) | How to Fix It (The Anti-SaaS Way) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Lack of ISO 27001 Experience | Many assume buying a GRC platform equates to “compliance in a box”. Software cannot replace the nuanced judgement required to run an ISMS or interpret auditor requirements. | Invest in People, Not Tools. Either hire a qualified ISO 27001 Lead Auditor/Implementer or train existing staff using standard courses. A human expert with a spreadsheet beats an ignorant team with a £20k tool every time. |
| 2. Undocumented or Vague Roles | Organisations often dump the ISMS on IT or assume that assigning “Admin” permissions in software counts as role assignment. This leads to gaps in legal, HR, and physical security responsibilities. | Create a RASCI Matrix. Use a simple Excel sheet to map every ISO 27001 clause to a specific job title (e.g., HR Manager for Clause 7.2). Formally communicate this via signed job descriptions, not software logins. |
| 3. Absence of Forward-Looking Training Plans | Relying on ad-hoc training or automated LMS “ticks” often fails the “continual improvement” test. Auditors need to see a plan for future competence, not just past completion. | 12-Month Training Schedule. Create a simple document outlining the training roadmap for the next year. Include budget for conferences, specific technical courses, and refresher sessions. Keep it in your shared drive for easy audit access. |
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Top Non Conformities
| Audit Non-Conformity | The SaaS Trap (Root Cause) | The Auditor’s Finding | The Ownership Fix (Toolkit) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. “Attendance” Mistaken for Competence | The “Content Library” Fallacy. SaaS platforms sell you 100+ generic videos. You assume that because staff clicked “Play”, they are competent. This conflates awareness with competence. | “Evidence of training attendance was presented, but there was no verification that the specific technical skills required for the role (e.g., Secure Coding) were actually acquired or tested.” | Competency Verification Records. Don’t just log attendance. Use a simple Post-Training Quiz (Microsoft Forms) or a signed Observation Record where a manager validates the skill was demonstrated in the real world. |
| 2. Failure to Address Identified Gaps | The “Dashboard” Illusion. The GRC tool highlights a skill gap in red, but because the tool is separate from the budget/HR process, it remains red for months with no action. | “Competency gaps identified in the Skills Matrix have remained open for >6 months with no documented plan, budget, or timeline for remediation.” | 12-Month Training Plan (Excel). A static, forward-looking document that commits specific budget and dates to fixing gaps. If it’s in a spreadsheet you own, it gets reviewed; if it’s in a dashboard, it gets ignored. |
| 3. Lack of Evidence for External Staff | The “User Licence” Limit. You didn’t buy SaaS licences for your contractors, MSPs, or cleaners, so they are excluded from the system. | “Third-party users with access to the ISMS (e.g., Cloud Administrators, Cleaners) were excluded from the competency framework and no evidence of their security competence was available.” | Third-Party Competence Agreements. Include competence requirements in the contract or Service Level Agreement (SLA). Store the signed contract in your Central Evidence Folder—no extra user licences required. |
Fast track ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
| Feature | High Table Toolkit (The ‘Owned’ Way) | Online SaaS Platform (The ‘Rent’ Way) |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Forever Access. Your Competency Matrix and Training Logs live on your servers (SharePoint, Google Drive). If you stop buying from us, you keep your compliance evidence forever. | Data Ransom. Your training records and certificates are stored behind a paywall. If you stop paying the monthly subscription, you lose access to your historical audit evidence. |
| Simplicity | Zero Learning Curve. HR managers and Team Leads already know how to use Microsoft Excel and Word. They can update the Competency Matrix immediately without training. | Complex Onboarding. Requires training your entire staff to use a proprietary interface just to upload a certificate or tick a “training complete” box, wasting valuable time. |
| Cost | One-Off Fee. You pay once for the ISO 27001 Toolkit and use it for 10 or 10,000 employees. There are no hidden “per-user” licence fees for expanding your team. | Per-User Tax. SaaS models often charge per seat. As you hire more staff to grow (or include contractors in Clause 7.2 scope), your compliance costs spiral out of control. |
| Freedom | No Vendor Lock-in. Auditors prefer seeing original files (PDFs, XLSX). You can easily migrate your data or change your process whenever you want because you hold the master files. | The “Walled Garden”. Exporting data is often difficult or produces unusable formats, deliberately making it hard for you to switch providers or show evidence to external auditors. |
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence for AI & Machine Learning Teams
Implementing ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 for AI and Machine Learning teams requires a specialised approach that goes beyond standard IT security. You must validate that your Data Scientists and MLOps Engineers possess the specific technical competence to secure training pipelines, prevent model inversion, and mitigate adversarial attacks. Follow these steps to build a competency framework capable of handling high-risk AI assets.
Step 1: Define Security Roles within MLOps Pipelines
- Action: Assign explicit information security responsibilities to Data Scientists, ML Engineers, and AI Ethicists within your Accountability Matrix.
- Result: Prevents “Shadow AI” by ensuring clear ownership of model security, training data privacy, and model weight protection.
- Technical Requirement: Map security duties to your MLOps workflow, specifically defining who is competent to authorise model deployment, access raw training data, and manage IAM roles within environments like AWS SageMaker or Hugging Face.
Step 2: Establish AI Security Competency Baselines
- Action: Document the specific security skills required for AI roles, moving beyond general coding to include secure model development and data sanitisation.
- Result: Creates a defensible standard for hiring and assessing staff handling proprietary algorithms and sensitive datasets.
- Technical Requirement: Mandate proficiency in specific frameworks such as the OWASP Top 10 for LLMs, NIST AI Risk Management Framework (RMF), and secure data handling techniques like k-anonymity or differential privacy.
Step 3: Conduct a Threat-Modelling Skill Gap Analysis
- Action: Assess your AI team’s ability to identify and neutralise AI-specific threats compared to your defined baselines.
- Result: Identifies critical vulnerabilities where developers may prioritise model accuracy over security, exposing the organisation to prompt injection or data poisoning attacks.
- Technical Requirement: Utilise an AI-specific Competency Matrix to flag gaps in knowledge regarding adversarial machine learning, supply chain attacks on pre-trained models, and secure API integration.
Step 4: Deploy Specialised AI Risk Training
- Action: Provision technical training focused on the intersection of cybersecurity and machine learning for all relevant staff.
- Result: Ensures personnel are competent in hardening models against extraction attacks and understanding the legal implications of data usage (e.g., GDPR in AI).
- Technical Requirement: Implement training modules covering Model Governance, secure usage of Open Source models, and specific counter-measures for Large Language Model (LLM) vulnerabilities.
Step 5: Evidence Competence via Model Governance Artifacts
- Action: Centralise evidence of competence not just through certificates, but through the practical application of security controls in model documentation.
- Result: Provides auditors with concrete proof that staff are applying their security training to daily MLOps activities.
- Technical Requirement: Use “Model Cards” or “System Cards” as dynamic evidence of competence, recording who performed security evaluations, bias testing, and red-teaming exercises before production release.
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2: Related Controls & Clauses
| Related Clause / Control | Description | Why it Matters (The Link) |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 27001 Clause 7.1 Resources | Requires the organisation to determine and provide the persons necessary for the effective implementation of the ISMS. | Prerequisite. You cannot assess competence if you have not identified and resourced the people required to run the system. Clause 7.2 is the quality check on the quantity defined in 7.1.2. |
| ISO 27001 Clause 7.3 Awareness | Ensures staff are aware of the Information Security Policy and the implications of not conforming to ISMS requirements. | Skill vs. Knowledge. Competence (7.2) is the ability to apply knowledge and skills. Awareness (7.3) is knowing why it matters. You can be competent but unaware of policy, or aware of policy but incompetent at execution. |
| ISO 27001 Annex A 6.3 | Information security awareness, education and training. Personnel and relevant interested parties must receive appropriate awareness, education and training. | The Evidence Engine. This is the operational control that satisfies Clause 7.2. While 7.2 sets the requirement (“staff must be competent”), Annex A 6.3 is the mechanism (“we run this specific training course”) used to achieve it. |
| ISO 27001 Annex A 5.4 | Management responsibilities. Management must require all personnel to apply information security in accordance with the established policies and procedures. | Accountability. It is management’s specific duty to ensure their teams are competent. If a breach occurs due to human error, the auditor will check if the manager fulfilled A 5.4 by verifying the staff member’s Clause 7.2 competence records. |
| ISO 27001 Annex A 8.29 | Security testing in development and acceptance. Acceptance testing programmes and related criteria shall be defined for new information systems, upgrades and new versions. | Technical Competence. For Tech Startups/AI, this is where Clause 7.2 bites. You must prove your testers and developers have the specific technical competence to perform valid security tests, not just general IT skills. |
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 verses ISO 27001 Clause 7.1 and ISO 27001 Clause 7.3
To pass the audit, you must understand the distinct interplay between these three clauses. Clause 7.1 provides the resources (the bodies), Clause 7.2 ensures their capability (the skills), and Clause 7.3 ensures their understanding (the mindset). Confusing “Awareness” with “Competence” is a guaranteed non-conformity.
| Relationship Flow | The Common Myth / Misconception | The Audit Reality (What We Check) |
|---|---|---|
| 7.1 Resources ↓ 7.2 Competence | Myth: “We hired a Senior Developer, so they are automatically competent.” Many assume that a high salary or a previous job title (Clause 7.1) satisfies the requirement for competence (Clause 7.2). | Reality: CVs are not ISMS Evidence. An auditor does not care what they did at their last company. We need to see that they are competent in your specific policies and your secure development standards. You must verify skills, not just employment history. |
| 7.2 Competence vs 7.3 Awareness | Myth: “They watched the security video, so they are competent.” Organisations frequently confuse passive Awareness (Clause 7.3) with active Competence (Clause 7.2). | Reality: Knowing vs. Doing. Awareness is knowing that phishing exists. Competence is the technical ability to analyse email headers and block the sender. A completion certificate proves Awareness; a practical test or manager observation proves Competence. |
| 7.1 + 7.2 + 7.3 (The Feedback Loop) | Myth: “The SaaS dashboard says we are 100% compliant.” Believing that because all green ticks are present in a GRC tool, the staff are actually resourced, competent, and aware. | Reality: The “Empty Chair” Test. If a “Competent” staff member leaves (7.1 failure), the Competence (7.2) of the team drops immediately. A dashboard doesn’t update itself when people resign. We audit the current reality, not the software’s history. |
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Mapped to other Standards
| Standard / Framework | Specific Reference | Relationship to ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 (Competence) |
|---|---|---|
| ISO/IEC 42001 (AI Management) | Clause 7.2 | The “Twin” Clause. It mirrors ISO 27001 exactly but shifts the focus to AI competence. You must evidence that staff understand data bias, model drift, and AI ethics. Clause 7.2 in 27001 provides the foundational framework to simply “add” these AI skills to your existing Competency Matrix. |
| EU AI Act | Article 4 (AI Literacy) | Mandatory Education. The Act requires providers and deployers to ensure staff have a sufficient level of “AI Literacy”. ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 is the audit mechanism to formally document that this literacy training has occurred and been understood. |
| EU NIS2 Directive | Article 20 (Governance) | Executive Liability. NIS2 mandates that management bodies must undergo training to identify risks. Clause 7.2 is your defence mechanism, providing the immutable evidence (training logs) that executives are competent, protecting them from personal liability. |
| EU DORA | Article 13(6) (ICT Training) | Resilience Skills. Financial entities must develop programmes to maintain ICT knowledge. Clause 7.2 provides the structure to map these specific regulatory training requirements (e.g., Threat-Led Penetration Testing awareness) to specific roles. |
| ISO 9001:2015 (Quality) | Clause 7.2 | Unified Onboarding. Because the clause text is identical, you can use a single “Competency Matrix” to track both Security (27001) and Quality (9001) skills. This eliminates duplication and reduces the “audit fatigue” of maintaining two separate HR systems. |
| ISO 22301:2019 (BCMS) | Clause 7.2 | Crisis Competence. Focuses on the ability to perform under pressure. While 27001 asks if you can configure the firewall, 22301 asks if you can do it during a disaster. Clause 7.2 records prove that recovery teams have practiced their roles, not just read the policy. |
| ISO 20000-1:2018 (ITSM) | Clause 7.2 | Service Delivery. Ensures the Service Desk is competent to handle incidents. This overlaps 100% with ISO 27001’s requirement for incident response competence. One training record for “Incident Management” satisfies both standards. |
| SOC 2 | Criteria CC1.4 (COSO Principle 4) | “Attract, Develop, Retain”. SOC 2 requires evidence of competence to prove you aren’t just hiring warm bodies. ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 provides the artifacts (Performance Reviews, Training Plans) that SOC 2 auditors demand to verify this criteria. |
| NIST SP 800-53 | AT-3 (Role-Based Training) | Granularity. NIST explicitly requires training based on the role (e.g., privileged user vs. standard user). This reinforces the ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 requirement that competence must be “appropriate” to the role, pushing you away from generic “one-size-fits-all” videos. |
| PCI DSS v4.0 | Requirement 6.2.2 | Technical Skills. Mandates that developers are trained in secure coding techniques (e.g., avoiding SQL injection). This is a specific technical competence requirement that slots directly into the Clause 7.2 record for your Software Engineering team. |
| ITIL 4 | Workforce & Talent Management | Structured Skills. ITIL provides the “skills definition” (e.g., SFIA framework) that you can populate into your ISO 27001 Competency Matrix. Using ITIL definitions makes your Clause 7.2 evidence look professional and standardised. |
| GDPR | Article 37(5) | Expert Knowledge. The DPO must be designated on the basis of “expert knowledge”. ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 is the mechanism to document this expertise (e.g., CIPP/E certification), proving compliance with the regulation’s specific hiring requirement. |
Efficiency Hack: “Double Dipping” with ISO 9001/14001
If your organisation already holds ISO 9001 (Quality) or ISO 14001 (Environmental), you do not need to build a separate competence framework. Clause 7.2 in ISO 27001 is structurally identical to Clause 7.2 in these other standards. You can “Double Dip” your existing HR and Quality processes to save money.
- Unified Competency Matrix: Do not create a separate “Security Skills” spreadsheet. Simply add a “Information Security” column to your existing ISO 9001 Competency Matrix. This allows you to track security skills (e.g., GDPR awareness, secure coding) alongside quality skills in a single, master document.
- Integrated Onboarding: “Piggyback” on your existing HR induction process. When new hires complete their ISO 9001 Quality induction, immediately transition them into the ISO 27001 Security awareness module. This turns two separate training events into a single “Compliance Bootcamp.”
- Centralised Evidence Repository: Use the exact same HR folders or LMS that house your Quality training records to store Security certificates. Auditors for both standards can review the same “Staff Training Log,” preventing the need to maintain duplicate evidence silos.
The SaaS Escape Hatch: Migrating Competence Data to Excel
If you are trapped in a GRC platform (like Vanta or Drata) and want to switch to the ISO 27001 Toolkit to save money, you might worry about losing your training records. Here is the 3-step “Escape Hatch” process to migrate your data without losing audit evidence:
- Export the Raw CSV: Log into your GRC dashboard and navigate to the “Personnel” or “Training” tab. Look for the “Export to CSV/Excel” button. Do not rely on the PDF summary; you need the raw data rows.
- Sanitise and Map: Open the CSV. Delete columns like “System ID” or “Vanta ID.” Map the remaining columns to the Competency Matrix Template:
- Source Column “User Email” → Toolkit Column “Employee Name/Role”
- Source Column “Task Completed Date” → Toolkit Column “Training Date”
- Source Column “Evidence URL” → (Download these files immediately)
- Archive the “Snapshot”: Save the original CSV export and all downloaded certificate files in a folder named
/ISMS/Archive/Legacy_GRC_Export_YYYY-MM-DD/. This “Snapshot” serves as your historical evidence for the auditor, allowing you to start fresh in your new Excel Matrix from today’s date.
Troubleshooting: The “Legacy Staff” Problem
The Scenario: You have a Senior Systems Administrator (“Bob”) who has been with the company for 20 years. He refuses to complete the basic ISO 27001 awareness training because he feels it is beneath him.
The Audit Risk: If the auditor picks Bob for an interview and he is hostile or unaware of the current policy (regardless of his technical skill), you will get a Non-Conformity.
The Fix (Grandfathering): Do not force Bob to watch the video. Instead, use the “Grandfathering” technique in your Competency Matrix:
- Step 1: Mark his competence level as “Expert” based on “Experience” (20 years tenure).
- Step 2: Conduct a 10-minute “Policy Briefing” interview with him.
- Step 3: Record this meeting as “Executive Briefing” in the training log.
This satisfies the standard (Clause 7.2b: “based on… experience”) without engaging in a political battle you might lose.
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2: Competence FAQ
What is ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence?
ISO 27001 Clause 7.2, also known as the competence clause, requires organizations to determine the necessary competence of people doing work under their control that affects information security performance. This means the organization must identify the skills, knowledge, and experience needed for each role that impacts the Information Security Management System (ISMS), ensure that people in those roles possess them, and keep documented evidence of their competence.
What are the ISO 27001:2022 Changes to Clause 7.2?
Great news. There are no changes to ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 in the 2022 update.
What’s the difference between “competence” and “awareness” in ISO 27001?
Competence (Clause 7.2) is about having the specific knowledge, skills, and experience to perform a job effectively, especially as it relates to information security. It’s a role-specific requirement. Awareness (Clause 7.3) is about ensuring all people under the organization’s control are aware of the information security policy, their contribution to the ISMS, and the implications of not conforming. Awareness is a universal requirement for all personnel, while competence is targeted to specific roles.
How do I evidence I meet the requirement of ISO 27001 Competence?
The best way is to record the skills of your resources in a Competency Matrix.
How do you demonstrate competence to an auditor?
You can demonstrate competence by providing documented evidence such as:
- Job descriptions that outline required skills.
- Resumes or CVs showing relevant experience.
- Training records, certificates, or qualifications.
- Records of on-the-job training or mentoring programs.
- Performance reviews that assess security-related tasks.
Auditors may also conduct interviews to verify that personnel understand their responsibilities.
Can you show me how to build an ISO 27001 competence matrix?
Yes, in this video we show you step by step how to build your own ISO 27001 competence matrix from scratch in around 15 minutes.
What is a competency matrix and is it required?
A competency matrix is a tool, usually a spreadsheet, that maps personnel roles and responsibilities to the required skills, knowledge, and experience for information security. While it’s not explicitly required by the standard, it’s considered best practice because it provides a clear, documented way to demonstrate compliance with Clause 7.2, identify skill gaps, and manage training needs.
What actions are needed to ensure competence?
If an organization identifies a competence gap, Clause 7.2 requires them to take action. This may include:
- Providing training, such as workshops, e-learning courses, or seminars.
- Offering mentoring or on-the-job guidance from experienced staff.
- Encouraging professional development and obtaining certifications.
- Reassigning roles or hiring new, competent personnel.
The organization must also evaluate the effectiveness of these actions.
Do all employees need to be information security experts?
No, the standard does not require everyone to be an information security expert. It only requires that personnel are competent for the work they do that affects the ISMS. For example, an IT administrator needs technical security skills, while a call centre agent needs training on how to handle customer data securely and validate identities.
How often should competence be assessed?
ISO 27001 doesn’t specify a frequency, but competence should be reviewed regularly to ensure it remains current with evolving threats and changes in roles or technologies. This can be done as part of annual performance reviews, during internal audits, or when new security risks are identified.
What happens if an auditor finds a non-conformity in Clause 7.2?
A non-conformity in Clause 7.2 means the organization hasn’t sufficiently demonstrated that its personnel are competent to manage information security risks. This could be due to a lack of documented evidence, skill gaps, or ineffective training. The organization would then be required to implement corrective actions to address the issue and show evidence of improvement to the auditor.
Does experience count as competence?
Yes, absolutely. The standard explicitly states that competence can be based on appropriate “education, training, or experience.” Experience is a crucial component, and organizations should document it through job descriptions, performance reviews, or other records that highlight the individual’s history and accomplishments related to information security.
Can I use external resource for ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence?
Yes. Many companies seek the help of qualified, experienced third party suppliers to help with ISO 27001.
Can I train my staff to meet the requirements of ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence?
Yes, there are many reputable training courses for ISO 27001 Lead Auditor and ISO 27001 Lead Implementor.
How can we make competence-building cost-effective?
To build competence without breaking the bank, consider these strategies:
- Internal training: Have experienced employees mentor or train their colleagues.
- Knowledge sharing: Create forums or sessions for team members to share insights on emerging threats and best practices.
- Free resources: Encourage self-study using free online resources, articles, and government-provided security guides.
- Cross-training: Allow employees to work on different security projects to broaden their experience.
Further Reading
Glossary of Competence Terms
Competency Matrix
A Competency Matrix is a grid-based tool used to map required skills (rows) against specific job roles (columns). It visually identifies skill gaps and is the primary evidence document for ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 compliance.
Training Needs Analysis (TNA)
Training Needs Analysis (TNA) is the process of comparing a staff member’s current competence level against the required level defined in the Competency Matrix. The difference between the two defines the “Training Gap” that must be addressed.
Continual Professional Development (CPD)
CPD refers to the tracking and documenting of skills, knowledge, and experience that employees gain both formally and informally as they work. Maintaining CPD logs is crucial for satisfying the “Continual Improvement” aspect of Clause 7.2.
Grandfathering (Competence)
Grandfathering is an audit-accepted technique where an employee is deemed competent based on significant historical experience (tenure) rather than recent formal training. This must be formally documented and signed off by management.
Conclusion: Competence is a Process, Not a Destination
Implementing ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 does not require you to turn every employee into a cybersecurity expert, nor does it require expensive monthly software subscriptions. It requires a logical, defensible structure to identify who needs to know what, and evidence that they know it.
By moving away from automated SaaS tick-boxes and towards owned, managerial verification using tools like the ISO 27001 Toolkit, you build a competence framework that withstands auditor scrutiny and actually reduces human risk.
Ready to start? Download the Competency Matrix Template now and map your first 5 roles today.


