ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 is a security control that mandates an organisation must establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This foundational requirement integrates people, policies, and technology, providing the holistic governance framework necessary to systematically manage information risks and achieve operational resilience.
In this guide, I will show you exactly how to implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 and ensure you pass your audit. You will get a complete walkthrough of the control, practical implementation examples, and access to the ISO 27001 templates and toolkit that make compliance easy.
I am Stuart Barker, an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor with over 30 years of experience conducting hundreds of audits. I will cut through the jargon to show you exactly what changed in the 2022 update and provide you with plain-English advice to get you certified.
Key Takeaways
- Foundation of the ISMS: Clause 4.4 is the foundational requirement of the ISO 27001 standard. It mandates that an organisation must establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve its Information Security Management System (ISMS).
- A Living System: The ISMS is not a one-time project. The standard emphasises that it is a dynamic and ongoing process that requires constant proactive management, monitoring, and updating to remain effective against evolving threats.
- Management Commitment is Crucial: The success of the ISMS depends heavily on senior management buy-in and commitment. Without their support and allocation of resources, the system is likely to fail.
- Holistic Approach: The clause requires a holistic approach to information security. This involves defining the ISMS scope, conducting comprehensive risk assessments, implementing appropriate security controls, and ensuring the ISMS is regularly monitored and reviewed for continual improvement.
Table of contents
- What Is an ISMS? Understanding the Core Concept
- Key Components of an Information Security Management System
- What is ISO 27001 Clause 4.4?
- Applicability of ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 across different business models.
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Explainer Video
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Podcast
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Implementation Video Tutorial
- 3 approaches to implementing an ISMS
- How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.4
- ISO 27001 ISMS Templates
- How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 4.4
- How to pass the ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 audit
- Top 3 ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Mistakes and How to Fix Them
- Fast track ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
- ISMS Relevant Standards
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 FAQ
- ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Executive Briefing Slides
What Is an ISMS? Understanding the Core Concept
An information security management system (ISMS) is a combination of policies, processes, systems and people that ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data.
ISO 27001 is a risk-based system. It’s a system based on understanding what the risks are to you and your organisation and then implementing controls to mitigate those risks.
The management system element itself is about how you organise yourself, how you manage and how you deliver the information security management.
Key Components of an Information Security Management System
The Information Security Management System (ISMS) includes
- ISO 27001 Mandatory Documents
- ISO 27001 Policies
- ISO 27001 Controls
- ISO 27001 Processes and Procedures
What is ISO 27001 Clause 4.4?
ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 is the Information Security Management System. It requires an organisation to have an information security management system that is established, implemented and continually improved.
An ISO 27001 ISMS is made up of the ISO 27001 documents, ISO 27001 policies and processes that deliver your information security controls and keeps you safe.
Part of ISO 27001 Clause 4 Context of Organisation this is the fourth requirement. It builds upon
- ISO 27001 Understanding the Organisation and its Context where we define internal issues and external issues that could impact the information security management system.
- ISO 27001 Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Interested Parties where we captured and addressed the needs of stakeholders in our information security management system.
- ISO 27001 Determining the Scope of the Information Security Management System where we defined what aspects of our organisation were to be covered.
So we know what could impact it, what people want from it, what it will be applied to and now we look at the actual information security management system itself.
Stop Guessing. Start Passing.
AI-generated policies are generic and fail audits. Our Lead-Auditor templates have a 100% success rate. Don’t risk your certification on a prompt

Purpose and Definition
The purpose of the ISO 27001 ISMS is to make sure you have an actual information security management system in place and that it is established, implemented and continually improved.
The ISO 27001 standard defines the ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Information Security Management System as:
The organisation shall establish, implement, maintain and continually improve an information security management system, including the processes needed and their interactions, in accordance with the requirements of this document.
ISO 27001:2022 Clause 4.4 Information Security Management System
Applicability of ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 across different business models.
| Business Type | Applicability | Why it is Important | Clause 4.4 ISMS Implementation Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Businesses | Mandatory / Critical | Clause 4.4 is the “engine” of your security. For small firms, it ensures that security isn’t just a list of rules, but a repeatable process that survives staff turnover. | Developing a simple, document-based management system that integrates with existing office workflows (e.g., using a centralised Toolkit). |
| Tech Startups | Operational / Scalable | Ensures that the fast-paced “move fast and break things” culture is balanced with a structured system for maintaining and improving security as the product evolves. | Embedding security processes into the DevOps pipeline and automated CI/CD environments to satisfy “continual improvement” requirements. |
| AI Companies | Advanced / Governance-led | With high-risk data processing, AI firms need a management system that specifically addresses the complex interactions between data ingestion, model training, and deployment. | Mapping the interactions between standard IT processes and specialised AI governance frameworks (like ISO 42001) within the core ISMS. |
ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Explainer Video
In this strategic implementation briefing for ISO 27001:2022 Clause 4.4 Information Security Management System, ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Stuart Barker and his team talk you through what it is, how to implement in and how to pass the audit.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Podcast
In this episode: Lead Auditor Stuart Barker and team do a deep dive into the ISO 27001:2022 Clause 4.4 Information Security Management System. The podcast explores what it is, why it is important and the path to compliance.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Implementation Video Tutorial
Being so broad brush what this clause is actually saying is – implement the ISO 27001 standard. In reality that is the information security management system. So if you go through all of the requirements of ISO 27001 and satisfy them, you will have an information security management system and you will satisfy this clause.
In the ISO 27001 tutorial How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 The Information Security Management System I show you how to implement it and how to pass the audit.
3 approaches to implementing an ISMS
| Implementation Approach | Process and Requirements | Key Benefits and Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Write it yourself | Requires purchasing the standard, reviewing all ISO 27001 clauses, determining necessary documentation, and creating all content manually. | Demands significant internal knowledge and experience. High resource commitment. |
| 2. Buy a Toolkit | Utilise a proven management system that includes mandatory documents, training, support, and expert knowledge. | Fast-tracks implementation based on best practice. Cost-effective and provides a solid framework for certification. |
| 3. Engage a consultant | Hire an external expert to create a bespoke management system tailored specifically to your organisation. | Excellent option for bespoke systems where cost is not a primary constraint. |
How to implement ISO 27001 Clause 4.4
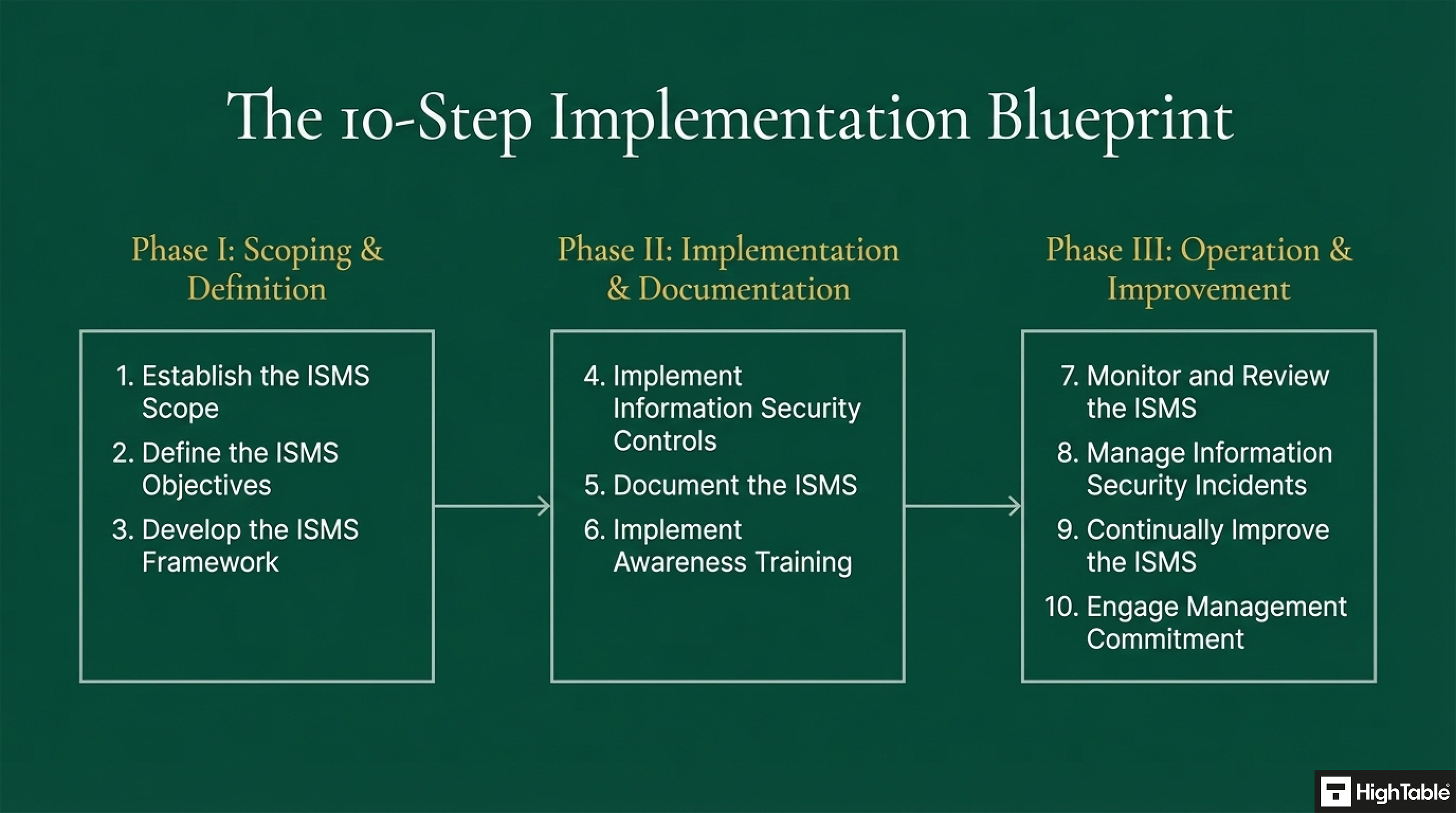
In this step by step implementation checklist to ISO 27001 interested parties I show you, based on real world experience and best practice, the best way to implement Clause 4.4.
1. Gain Management Buy In
The whole process is doomed to fail without management buy in and support. Using stakeholder management technqiues and other influencing techniques appropriate to the culture of your organisation get buy in and adequate resources to support the management system.
2. Establish the ISMS Scope
Define clear boundaries for the ISMS, specifying what assets, processes, and locations are included.
It can be difficult to set clear boundaries, especially in complex organisations. We explored this in detail in our practical guide, how to establish ISO 27001 scope.
3. Define the ISMS Objectives
Set measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives for information security. Setting Information Security objectives was covered in detail in our previous post, how to set ISO 27001 objectives.
4. Build the ISMS Framework
The ISMS framework is the structure, roles, responsibilities, policies and processes of the information security management system. We have delved into the specific steps in our comprehensive guide How To Implement ISO 27001: A Step By Step Guide.
5. Document the Information Security Management System
The information security management system is primarily a set of documentation that covers information security policies and processes. We explored documentation for the ISMS in the ISO 27001 Toolkit: Business Edition.
6. Implement Information Security Controls
Based on scope and risk you will choose the ISO 27001 Annex A controls that are appropriate to you, follow the implementation guidance and implement them. The comprehensive ISO27001 Annex A Controls Reference Guide provides practical, step-by-step implementation guidance.
7. Train People
Training is the bedrock of any ISMS and a culture of information security awareness. Once the framework is in place and management system is documented it is important to communicate it and train people in how to use it. There are practical training tips in our previous blog ISO 27001 Annex A 6.3 Information Security Awareness, Education And Training.
8. Monitor and Review the ISMS
To ensure the continued effectiveness of the ISMS and to ensure that it continues to meet it’s stated objectives you should regularly monitor and review it’s performance. With a combination or automated monitoring and internal audits, oversight will be provided to the management review team and fed into both the risk assessment process and the continual improvement process.
9. Manage Information Security Incidents
As incidents will occur you will establish a process for incident management, which we have covered in our previous guide ISO 27001 Annex A 5.24 Information Security Incident Management Planning and Preparation
10. Continually improve the ISMS
Continual improvement is a key concept in ISO 27001, as it acknowledges that things are not perfect and can always be better. Whether that is in response to changes in the business or to incidents the practical guide, ISO 27001 Clause 10.1 Continual Improvement, covers how.
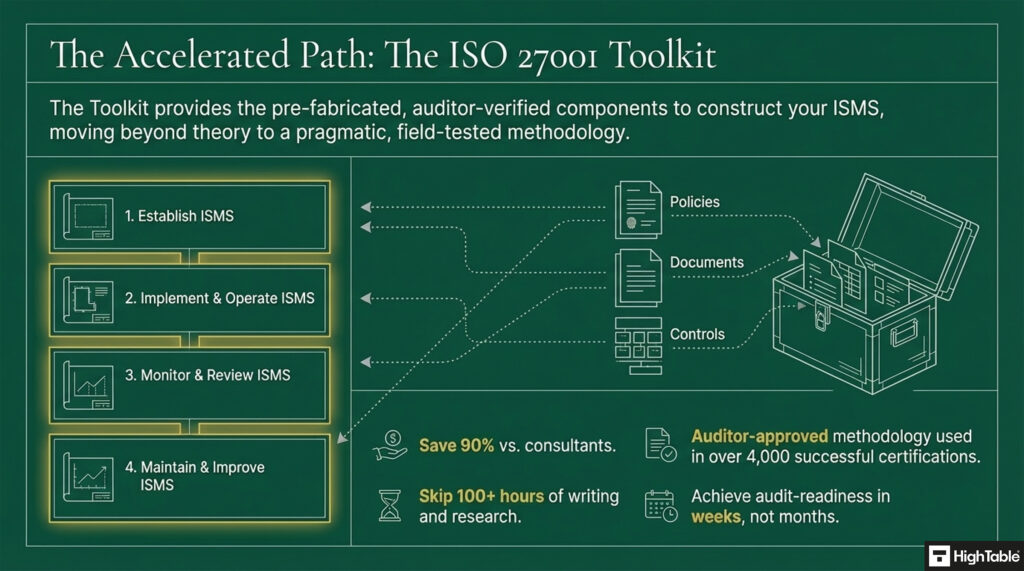
ISO 27001 ISMS Templates
ISO 27001 clause 4.4 ISMS is actually a series of ISO 27001 templates that we have collated into the ISO 27001 Toolkit. Designed specifically for those wanting to do it themselves and save both time and money in the process.
ISO 27001 templates have the advantage of being a massive boost that can save time and money so before we get into the implementation guide we consider these pre written templates that will sky rocket your implementation.
I created the Ultimate ISO 27001 Toolkit to fully meet clause 4.4 and it has been used thousands of times, globally, to get clients ISO 27001 certified.
I’ve sat in the Auditor’s chair for 20 years. These are the exact tools I use to guarantee a pass.

How to audit ISO 27001 Clause 4.4
To conduct an internal audit of ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Scope use the following audit checklist which sets out what to audit and how to audit it.
1. Check that the ISMS is established
The first step is to make sure the management system is in place. You are checking that there is a documented ISMS scope and objectives, policies, and procedures are all in place. In addition that the the boundaries of the ISMS and its interaction with other business processes are documented.
It can be challenging ensuring the scope is appropriate and doesn’t exclude necessary areas, that objectives are measurable and aligned with business goals, and that policies and procedures are comprehensive and up-to-date. In addition, sometimes, documentation exists but isn’t implemented.
- Review documented scope, objectives, policies, and procedures.
- Interview personnel to confirm understanding and application.
- Examine records of management review and internal audits.
2. Verify the ISMS is operating as intented
Once you have confirmed that the ISMS is established you will then check that is operating as intended by verifying that controls are implemented and working.
There is no doubt that determining the effectiveness of controls in practice, especially where they are complex or rely on human behaviour is challenging and that maintaining consistent implementation across the organisation can also be difficult.
- Observe processes, conduct walkthroughs, and examine records of control implementation (e.g., access logs, change management records).
- Perform penetration testing or vulnerability scanning where appropriate.
3. Assess if the ISMS is continually improving
Confirm that the ISMS is regularly monitored, reviewed, and improved. This includes addressing internal audit findings, management review outputs, and feedback from interested parties.
Ensuring continual improvement is more than just maintaining the status quo. Identifying and implementing effective improvements can be difficult, especially when resources are limited.
- Review records of management review, internal audits, corrective actions, and preventive actions.
- Interview personnel about their involvement in the improvement process.
4. Review the ISMS monitoring and measurement
Verify that the organisation has established processes for monitoring and measuring the effectiveness of the ISMS and its controls.
Defining appropriate metrics and ensuring they are consistently measured and reported can present a challenge as can using the data effectively to drive improvement.
- Examine records of monitoring and measurement activities (e.g., performance reports, incident logs).
- Interview personnel about how they use the data.
5. Assess internal audits
Check that internal audits of the ISMS are conducted regularly to assess its conformity to ISO 27001 and its effectiveness.
Ensuring internal audits are conducted objectively and by competent auditors represents a challenge. Following up on audit findings and implementing corrective actions can also be difficult.
- Review internal audit plans, reports, and follow-up actions.
- Interview internal auditors and auditees.
6. Ensure management reviews have happened
Verify that top management reviews the ISMS at planned intervals to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness.
Ensuring management review is more than a formality and that it addresses the key issues affecting the ISMS can be difficult for organisations.
- Review minutes of management review meetings.
- Interview top management about their involvement in the ISMS.
7. Get evidence of continual improvement
Confirm that the organisation is continually improving the effectiveness of the ISMS, demonstrating that improvements are actually leading to better outcomes.
- Examine records of improvement initiatives and their impact on the ISMS.
- Interview personnel about their involvement in the improvement process.
8. Verify that corrective action takes place
Verify that the organisation has a process for taking corrective action to address nonconformities.
Identifying the root cause of nonconformities and implementing effective corrective actions can be overlooked.
- Review records of corrective actions, including root cause analysis and effectiveness checks.
9. Review the existence of interested parties
Check that the organisation considers the needs and expectations of interested parties relevant to information security.
- Review records of interested party analysis and how their requirements are incorporated into the ISMS.
- Interview personnel about their interactions with interested parties.
10. Ensure there is documented information
Confirm that the ISMS has appropriate documented information to support its operation.
Maintaining documented information that is up-to-date and accessible is the biggest challenge.
- Review a sample of documented information (e.g., policies, procedures, records) to ensure it is controlled and up-to-date.
How to pass the ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 audit
To pass an audit of ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 ISMS you are going to establish, implement and continually improve your information security management system and to do that you would be best placed to get a copy of the ISO 27001 toolkit.
What an auditor looks for
The auditor is going to check a number of areas for compliance with Clause 4.4 ISMS. Lets go through them
- That you have a documented information security management system: The simplest way to do this is to download the ISO 27001 Toolkit.
- That you can evidence the effective operation of the information security management system: Once you have your information security management system in place the audit is going to look for evidence of the effective operation. This means having records of activity. Examples are having meeting minutes for the management review team, the risk register, risk reviews, continual improvement, incident management. What you say you do, you should be able to evidence.
- That you are continually improving: Not everything will be perfect and not everything will work 100% of the time. When things go wrong you will have incident management that may lead to continual improvement. When you conduct internal audits you may find things not working as expected that may lead to continual improvements. External audits may find things that require continual improvement. Risk management may also lead to continual improvement. Be prepared to evidence your continual improvement and the associated records.
Top 3 ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Mistakes and How to Fix Them
These are the top 3 mistakes that organisations makes for ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 ISMS that will costs you thousands:
- Buying a portal or web based tool: A portal may well be a great investment in time to help the information security manager to do their job but there is a lot of cost involved in going this route and the work that is required, still needs doing. This is a cost on top of the cost of ISO 27001 implementation. Extra cost. When the time is right, consider it but it is our experience for the novice or beginner these tools will only complicate matters and increase your costs exponentially.
- Doing it yourself with no help at all: It is not complicated but there is a lot to cover. Even if you just watch our ISO 27001 YouTube how to’s or follow this free how to implement ISO 27001 guide you will be better placed for the journey ahead. Assuming you can do it with zero knowledge will lead to expensive mistakes and expensive rework.
- Giving it to IT to sort out: ISO 27001 is a management system that covers the entire business. Whilst there are elements of IT, this is NOT an IT standard or IT solution. It requires business leadership and business buy-in. Give it to IT, and you are doomed to fail.
Fast track ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
| Feature | High Table ISO 27001 Toolkit | Online SaaS / GRC Platforms |
| Ownership | Permanent Assets: You download the entire ISMS framework. These files are yours to keep, archive, and use forever. Your compliance history is stored on your terms. | Rented Infrastructure: Your ISMS “lives” on someone else’s server. If you stop paying the subscription, you effectively lose the “system” you worked so hard to build. |
| Simplicity | Zero Training Required: Clause 4.4 is about processes and interactions. Documenting these in Word and Excel is intuitive. There is no need to put your team through “SaaS University” just to update a process. | Steep Learning Curve: Most SaaS tools are over-engineered. Your team will spend more time learning how to navigate the software than actually improving your security posture. |
| Cost | One-Off Fee: You make a single investment. As your business grows and you add more employees, your costs remain exactly £0.00. | Scalable “Compliance Tax”: SaaS platforms usually charge per user or per module. As your company scales, your annual subscription becomes a significant financial burden. |
| Freedom | No Vendor Lock-In: You have total portability. You can host your ISMS on SharePoint, Google Drive, or a local server. You aren’t beholden to a single software provider’s roadmap. | Proprietary Trap: Exporting your data from a SaaS platform into a format an auditor can use offline is often a nightmare, making it incredibly difficult to switch providers. |
The Tools We Use.
100% Audit Success. Zero AI Guesswork.

ISMS Relevant Standards
There are many standards that are relevant to the ISMS.
| Standard / Framework | Description and Purpose | Core Contribution to the ISMS |
|---|---|---|
| ISO/IEC 27000 Family | The primary global standards governing information security management based on international best practice. | Lays out specific requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving the ISMS framework. |
| ITIL Framework | A collection of policies and concepts focused on the effective management of IT infrastructure and services. | Provides best practices for service management and technical security operations within the IT infrastructure. |
| COBIT Framework | A governance framework developed by ISACA for information management strategy. | Assists security personnel in developing governance strategies while minimising risk and controlling security impacts. |
ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 FAQ
What are the ISO 27001:2022 Changes to Clause 4.4?
In essence, nothing has changed; it is a clarification of wording. They now refer through the standard to this ‘document’ rather than this ‘international standard’, so you should replace the words ‘international standard’ with the word ‘document’. They have also added the term ‘including the processes needed and their interactions’ to be absolutely crystal clear that processes are included, rather than implying it.
What do you need when building your Information Security Management System (ISMS)?
When building your Information Security Management System (ISMS) you are going to need:
- An Information Security Management System: You can implement ISO 27001 yourself without spending £10,000s on consulting fees in less than 30 days. Get the ISO 27001 Toolkit and implement it yourself.
- Free Training on How to Implement the ISMS: Training comes built into the ISMS and is also free to follow here: How to Build and Implement an ISMS.
- A Free Strategy Call to Answer Questions: Booking a free 30 minute strategy call where an expert can show you exactly what needs to be done to do it 10x Faster and 30x cheaper than alternatives.
What is the purpose of an ISMS?
The purpose of an Information Security Management System (ISMS) is to minimise risk to the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data. Ultimately it wants to prevent a data breach and ensure your business can operate uninterrupted.
- Confidentiality: making sure data can only be accessed by authorised people.
- Integrity: keeping data accurate and complete.
- Availability: making sure data can be accessed when it’s required.
Who is responsible for the ISMS?
The responsibility for the operation of the information security management system is usually the information security professional. It takes someone with knowledge and experience to run, though it can be learnt and done yourself with the ISO 27001 toolkit.
What is an ISMS based on?
The Information Security Management System (ISMS) is based on risk and business need. The level of controls chosen and implemented are directly related to that business risk, and influenced by the organisation’s needs, objectives, security requirements, size, and processes. To be effective, it includes processes for continual improvement, incident management, and ongoing internal audit.
What are the benefits of an Information Security Management System (ISMS)?
Beyond being required for certification, the top 5 benefits of an ISMS are:
- Certification: You cannot get ISO 27001 certification without it.
- Improved security: Effectively addresses common information security risks.
- Reduced risk: Identifies and addresses risks systematically.
- Improved compliance: Meets standard and regulatory requirements for an effective system.
- Reputation Protection: Reduces the potential for fines and PR impact in the event of a breach.
Why do you need an Information Security Management System (ISMS)?
You need it because you cannot get ISO 27001 certification without it. The ISMS brings consistency and maturity, where outcomes are determined by process rather than who did it on the day. Documenting processes future-proofs your organisation and removes reliance on individuals, eliminating the single point of knowledge failure.
What is the goal of an Information Security Management System (ISMS)?
The goal of an Information Security Management System (ISMS) isn’t necessarily to maximise information security, but rather to reach an organisation’s desired level of information security based on need and risk. These levels of control vary from one organisation to the next.
What controls should an Information Security Management System (ISMS) include?
The standard doesn’t mandate specific controls but provides a list (ISO 27001 Annex A) for consideration. You will create a Statement of Applicability showing which controls you have implemented based on risk and need. An ISMS must identify assets and provide a risk assessment, steps taken to protect assets, an action plan for breaches, and identified responsible individuals.
How do I monitor and review an ISMS?
The ISMS should be monitored and reviewed on a regular basis to ensure effective operation. This includes:
- Measures and Monitoring of the security controls.
- Conducting and reviewing the risk assessment.
- Conducting internal audits.
- Getting feedback from interested parties.
What are the implementation challenges for an ISMS?
Challenges vary based on size and complexity, but common hurdles include a lack of resources, lack of time, lack of expertise, cost, and change management.
ISO 27001 Clause 4.4 Executive Briefing Slides