In this guide you will earn everything you need to know about ISO 27001:2022 policies including all of the changes and the updates.

Table of contents
- ISO 27001 Policies are a strategic asset not an operational burden
- The Core Components of Policies
- The Policy Architecture
- Leadership Mandate
- ISO 27001 Policies – Strategic Implementation Briefing [Auditor Explained]
- ISO 27001:2022 Clause 5.2 Policies for Information Security
- Policy Lifecycle
- How to deploy and implement policies
- Policy vs Procedure
- From Compliance Burden to Competitive Advantage
ISO 27001 Policies are a strategic asset not an operational burden

An ISO 27001 policy framework is the foundation of your information security management system (ISMS) and it moves information security from a reactive cost centre to a proactive business enabler.
- There are three primary benefits to having information security policies:
- Commercial Advantage: Polices a the most requested documents in the sales cycle. Having a robust framework removes friction from the sales process an accelerates revenue by meeting the needs of client due diligence.
- Enhanced Reputation: Independent verification through ISO 27001 certification built on policies instills trust and is a competitive differentiator.
The Core Components of Policies

The ISO 27001 Framework is built on a hierarchy of policies. These are the statement of what do for information security and why we do it. They are not instructions on how we do it as this is covered in procedures. The modular approach allows for clarity, ownership and adaptability across multiple standards.
Information Security Policy
This is the keystone as the overarching policy sets the tone, objectives and commitment from leadership.
Risk Management Policy
This is the foundation and sets out the approach for how risk is identified, assessed and managed.
Topic Specific Policies
These are the modular policies that address the specific controls as mandated in ISO 27001:2022 Annex A.
The Policy Architecture
Policies are based in five key categories and grouped logically.
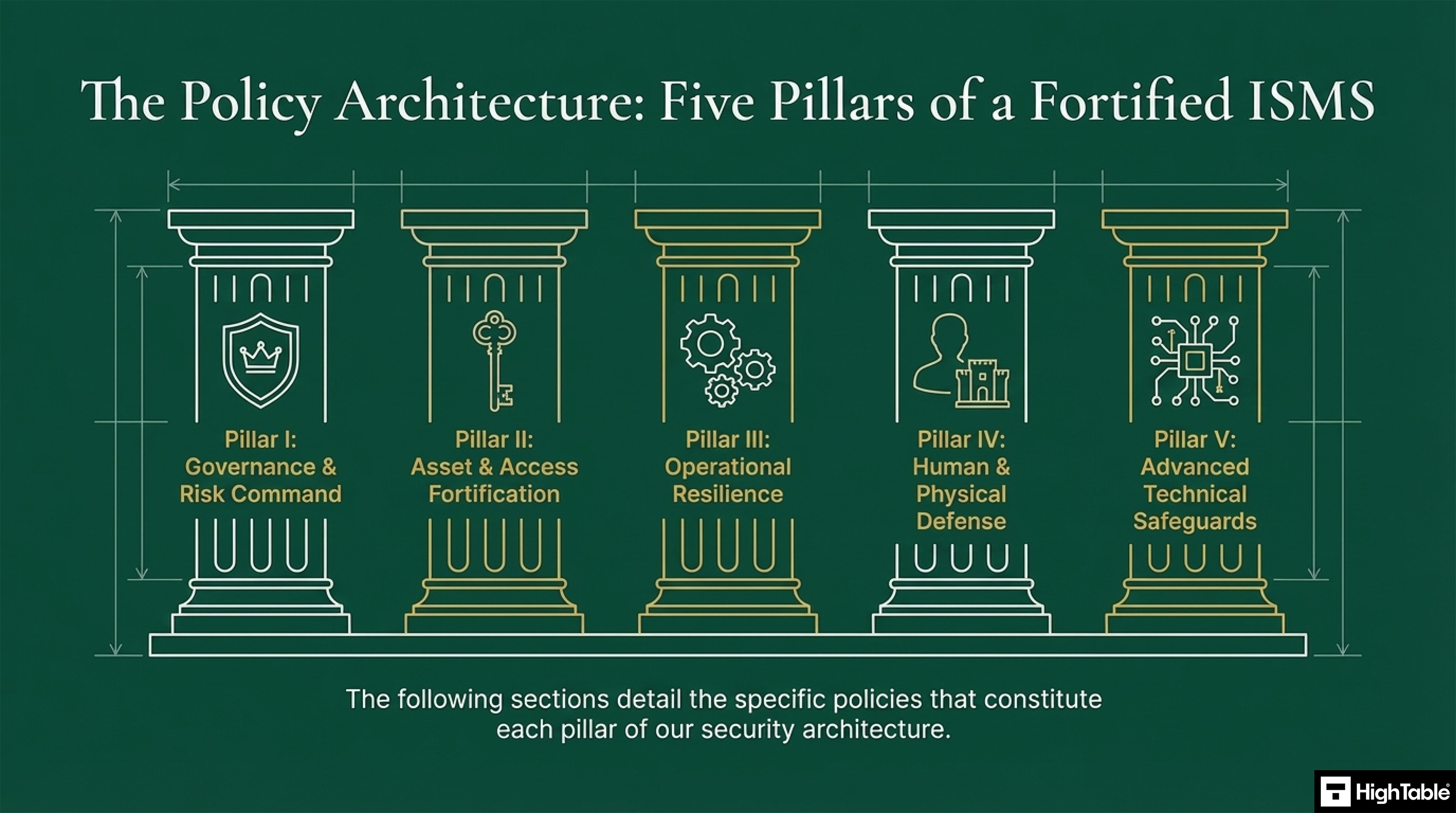
Governance Risk and Command
These policies establish the top down commitment and the principles that govern the entire information security management system (ISMS).

Operational Resilience
These policies ensure the ongoing integrity and availability of systems and data, protecting against loss, disruption and unauthorised modification.

Human and Physical
These policies address the risks of personnel and the physical environment.

Technical
These polices mandate security by design and by default securing development life cycle, suppliers and supply chain and advanced techniques such as cryptography.

Leadership Mandate
ISO 27001 is a top-down management system and requires demonstrable leadership commitment.
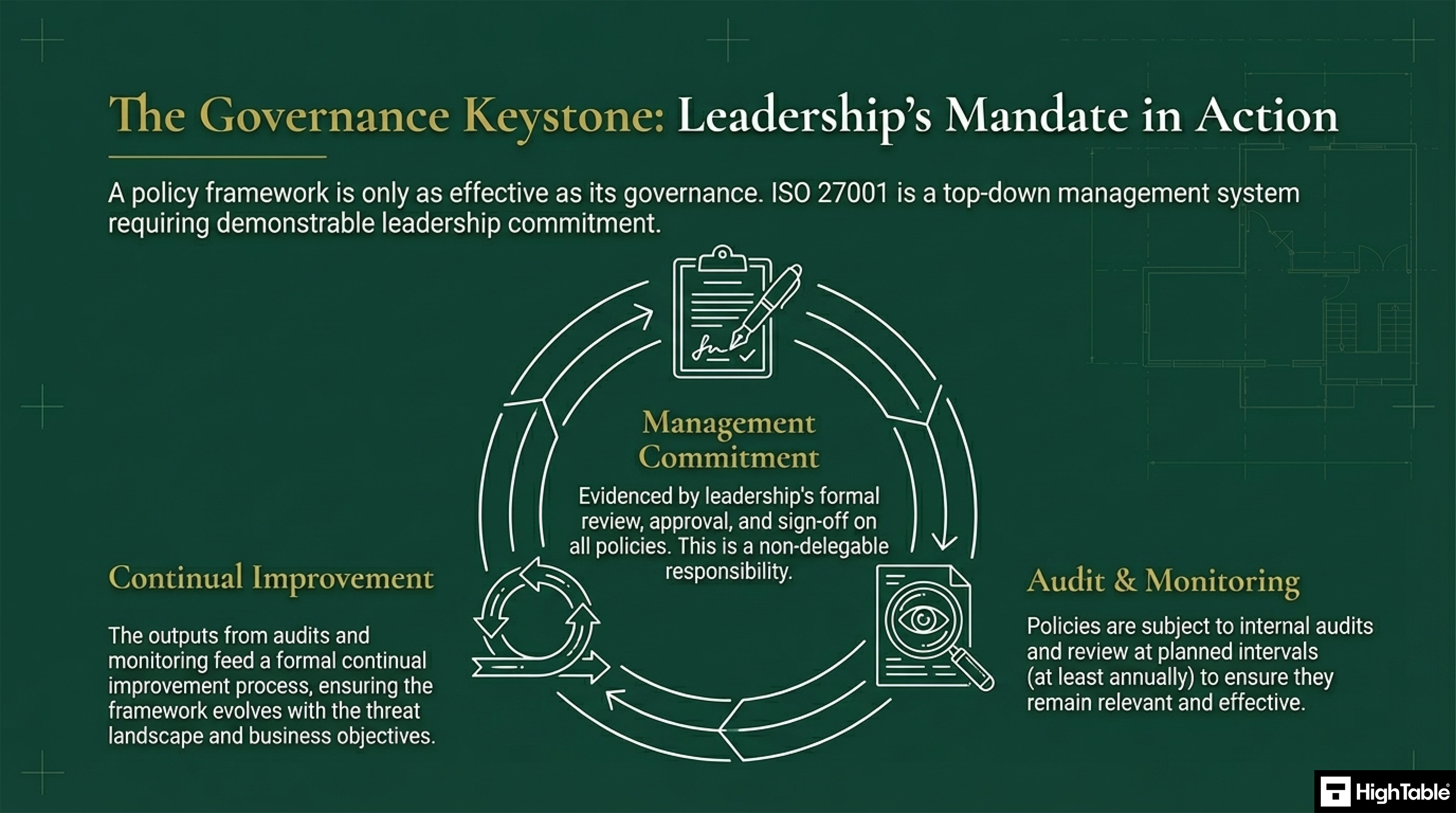
This forms part of a process of audit, monitoring and continual improvement. The management commitment is evidenced by the review, approval and sign off of all policies.
ISO 27001 Policies – Strategic Implementation Briefing [Auditor Explained]
In this strategic briefing video on ISO 27001 policies, ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Stuart Barker and his team talk you through what policies are, how to implement policies and how to pass the audit.
ISO 27001:2022 Clause 5.2 Policies for Information Security
The standard specifically address the need for policies in ISO 27001:2022 Clause 5.2 Policies for Information Security.

In this tutorial ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Stuart Barker shows you how to implement ISO 27001 Clause 5.2 Policy, and pass the audit.
Policy Lifecycle
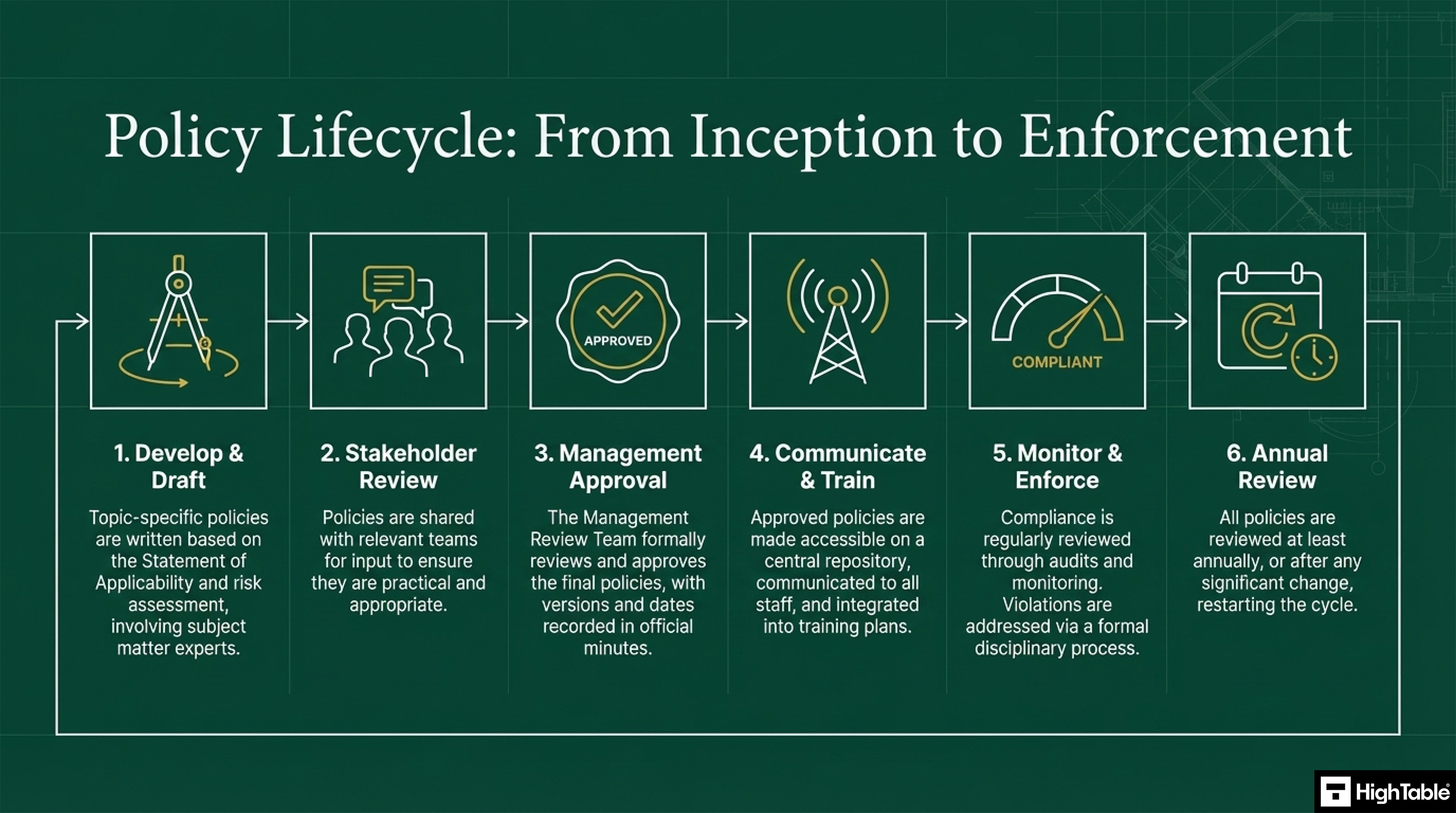
The lifecycle of policies is a 6 step process:
- Develop and Draft: topic specific polices are written based on the statement of applicability and risk assessment involving subject matter experts.
- Stakeholder Review: Policies are shared with relevant trams for input to ensure they are practical and appropriate.
- Management Approval: The Management Review Team formally reviews and approves the final polices, with versions and dates recorded in the official minutes.
- Communication and Training: Approve polices are made accessible on a central repository and communicated to all staff as well as integrated in to training plans.
- Monitor and Enforce: Compliance is reviewed on a regular basis through audits and monitoring and violations are address via the disciplinary process.
- Annual Review: All policies are reviewed at least annually or after significant change and the cycle starts again.
How to deploy and implement policies
In this tutorial video, ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Stuart Barker shows you how to implement ISO 27001 policies and deploy them into your organisation.
Policy vs Procedure
Policies and procedures are distinct, yet complimentary.

Policy
Details what must be done and why.
Procedure
Details how something is done.
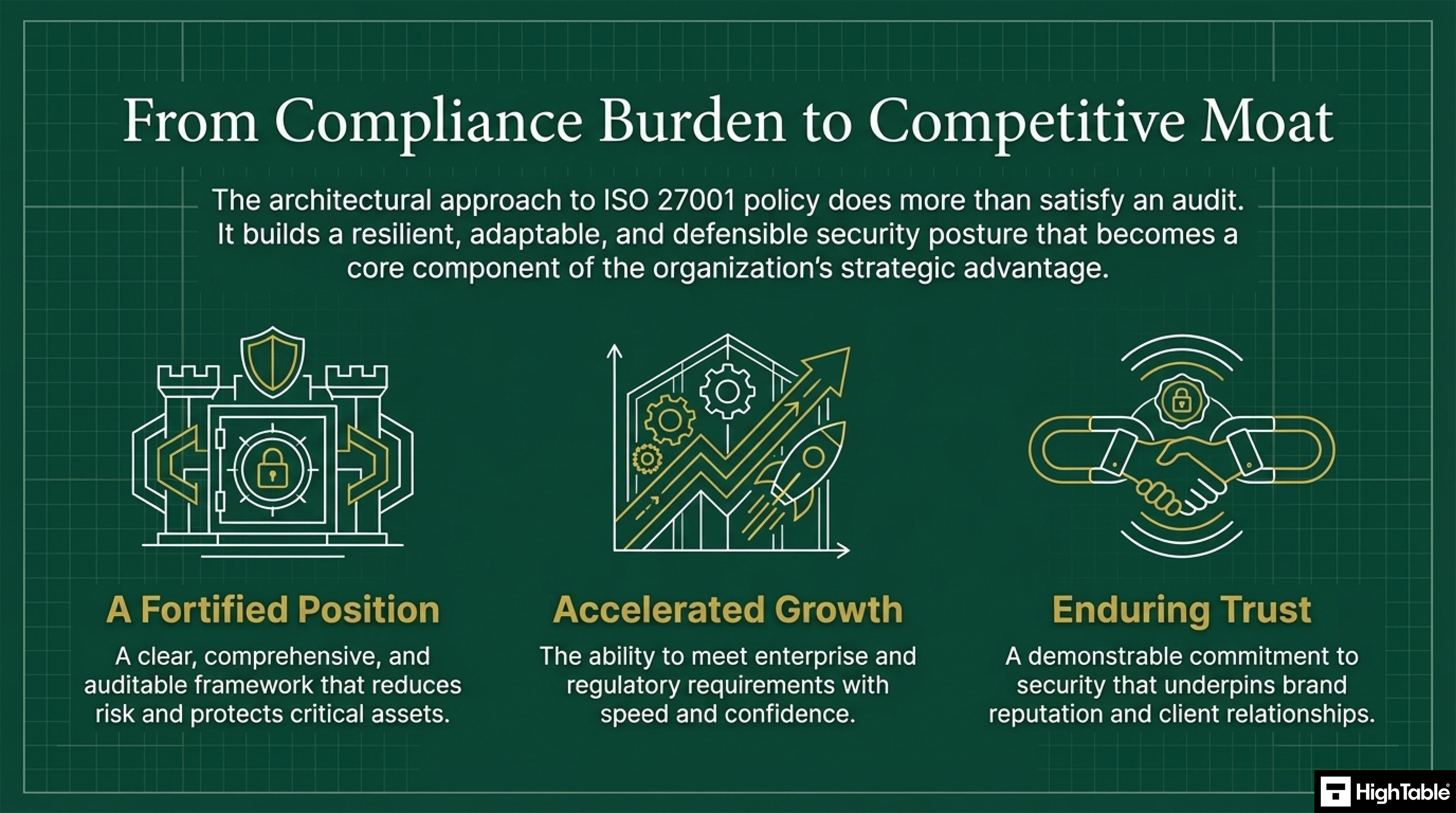
From Compliance Burden to Competitive Advantage
In conclusion, polices are no longer a compliance burden but a competitive advantage. They lead to
- A stronger more fortified poisiton
- Accelerated Growth
- Enduring Trust