ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Capacity Management is a security control that ensures organizations monitor and adjust resource usage to prevent system failures. It requires the monitoring of information processing facilities to maintain availability. The primary benefit is transforming reactive “fire-fighting” into proactive planning for future capacity requirements, ensuring business continuity.
In this guide, I will show you exactly how to implement ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 and ensure you pass your audit. You will get a complete walkthrough of the control, practical implementation examples, and access to the ISO 27001 templates and toolkit that make compliance easy.
I am Stuart Barker, an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor with over 30 years of experience conducting hundreds of audits. I will cut through the jargon to show you exactly what changed in the 2022 update and provide you with plain-English advice to get you certified.
Key Takeaways: ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Capacity Management
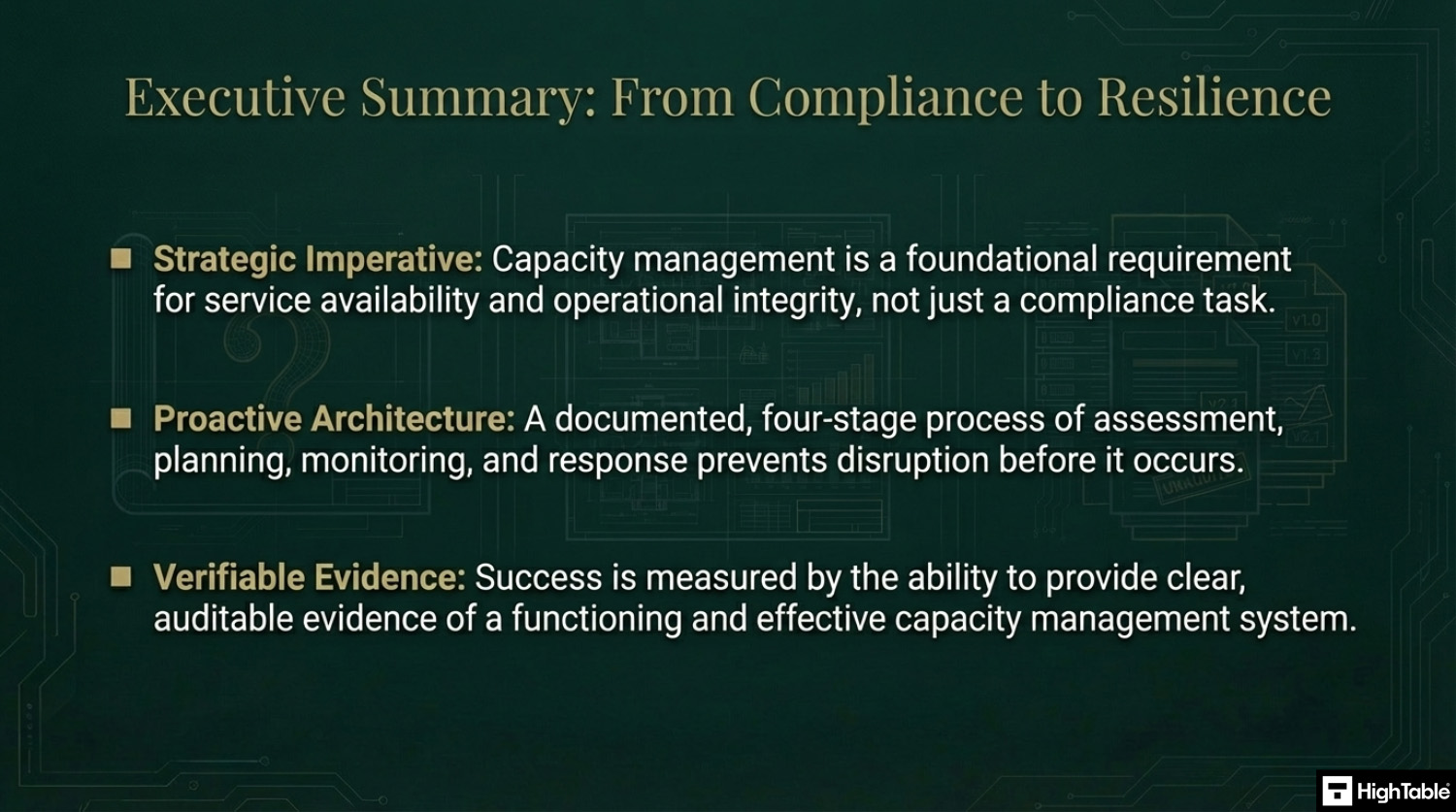
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 requires organizations to monitor and adjust the use of resources to ensure they meet current and future capacity requirements. Often mistaken for a simple “IT performance” task, this control is actually about Availability, ensuring your systems don’t crash because they ran out of disk space, memory, or even human staff. It moves the organization from being reactive (“The system is down!”) to being proactive (“We need to upgrade in three months”).
Core requirements for compliance include:
- Identify Critical Resources: You must define what “capacity” means for your business. This typically includes technical resources (CPU, disk space, bandwidth), human resources (staff levels), and physical facilities (office space, power).
- Monitoring & Thresholds: You shouldn’t wait for a failure. You must implement tools to monitor usage and set “triggers” or alerts (e.g., an alert when a database is 80% full).
- Trend Analysis: Compliance requires looking forward. You should analyze usage patterns to predict when you will run out of resources, allowing time for procurement and implementation.
- Tuning and Adjustment: When a threshold is hit, you must have a plan to respond, whether that’s deleting old data, auto-scaling in the cloud, or hiring additional contractors.
Audit Focus: Auditors will look for “The Alerting Trail”:
- Proof of Monitoring: “Show me the dashboard where you track server CPU or cloud storage usage.”
- The Trigger: “Show me an example of an alert that fired recently. How did you respond to it?”
- Future Planning: “Show me your last capacity review meeting notes or report. How are you planning for growth next year?”
Capacity Monitoring Strategy (Reactive vs. Proactive):
| Resource | Reactive (Audit Fail) | Proactive (Audit Pass) |
|---|---|---|
| Disk Space | “The server crashed because the disk is full.” | “Alerts notify us when the disk reaches 80% capacity.” |
| Cloud Hosting | “Why is our AWS bill so high this month?” | “Auto-scaling limits and cost alerts are configured.” |
| Staffing | “Everyone is burnt out and making mistakes.” | “Utilisation reports show we need a new hire next quarter.” |
| Bandwidth | “The internet is lagging during Zoom calls.” | “Traffic shaping prioritizes video calls over large downloads.” |
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways: ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Capacity Management
- What is ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6?
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Free Training Video
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Explainer Video
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Podcast
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Implementation Guide
- How to implement ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6
- Capacity Monitoring Strategy Example
- How to pass an ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 audit
- Top 3 ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 mistakes and how to avoid them
- Applicability of ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 across different business models.
- Fast Track ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 FAQ
- Related ISO 27001 Controls
- Further Reading
- ISO 27001 Controls and Attribute Values
- ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Strategic Briefing Slides
What is ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6?
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 is about capacity management which means you must identify your capacity requirements and ensure you meet them.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Capacity Management is an ISO 27001 control that looks to make sure you have the resources you need to the things that you need to do.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Purpose
The purpose of ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Capacity Management is to ensure the required capacity of information processing facilities, human resources, offices and other facilities.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Definition
The ISO 27001 standard defines ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 as:
The use of resources should be monitored and adjusted in line with current and expected capacity requirements.
ISO 27001:2022 Annex A 8.6 Capacity Management
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Free Training Video
In the video ISO 27001 Capacity Management Explained – ISO27001:2022 Annex A 8.6 I show you how to implement it and how to pass the audit.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Explainer Video
In this beginner’s guide to ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Capacity Management, ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Stuart Barker and his team talk you through what it is, how to implement in and how to pass the audit. Free ISO 27001 training.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Podcast
In this episode: Lead Auditor Stuart Barker and team do a deep dive into the ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Capacity Management. The podcast explores what it is, why it is important and the path to compliance.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Implementation Guide
With capacity management we are looking to make sure that we have enough resources to perform and deliver our products and services. There are varying degrees and levels of management depending on how complex you are, how complex your setup is, the organisation and your risk.
Resources to manage
The kinds of traditional capacity management and resources we would consider are things like storage space, disk space, CPU usage, memory usage, network bandwidth. You also have capacity in your staffing and also in your connected utilities.
Basically anything you use will have a capacity and a limit.
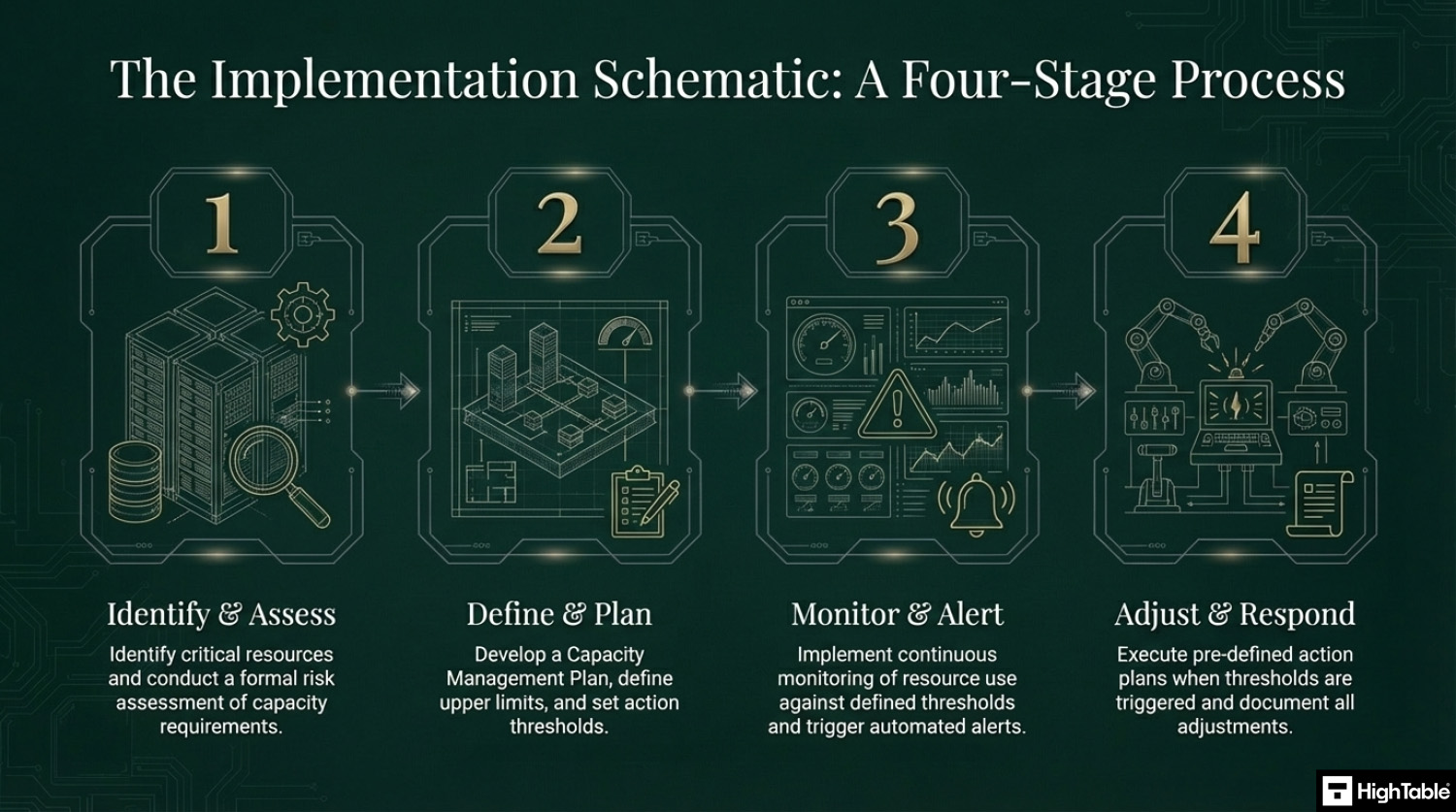
The 4 Stage Implementation Process
You are going to identify the resources that you need and use and are important to you. For those you perform a risk assessment and build controls based on risk. Upper limits need to be defined and thresholds set that trigger alerts with action plans that are activated when the threshold is triggered.
The four stages of implementation are:
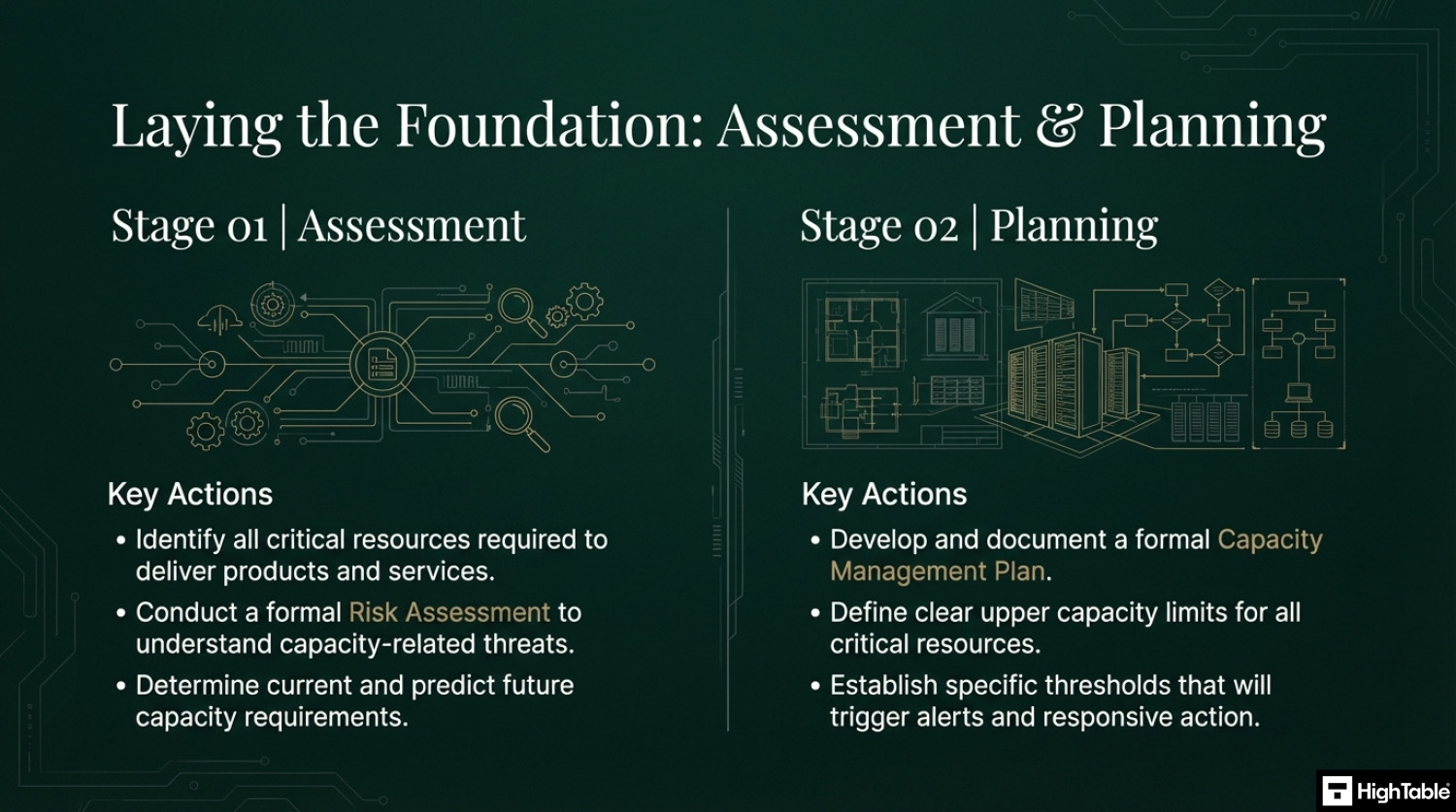
- Identify and Assess: identify critical resources and conduct a risk assessment of capacity requirements
- Define and Plan: Develop a capacity management plan and define upper limits and action thresholds
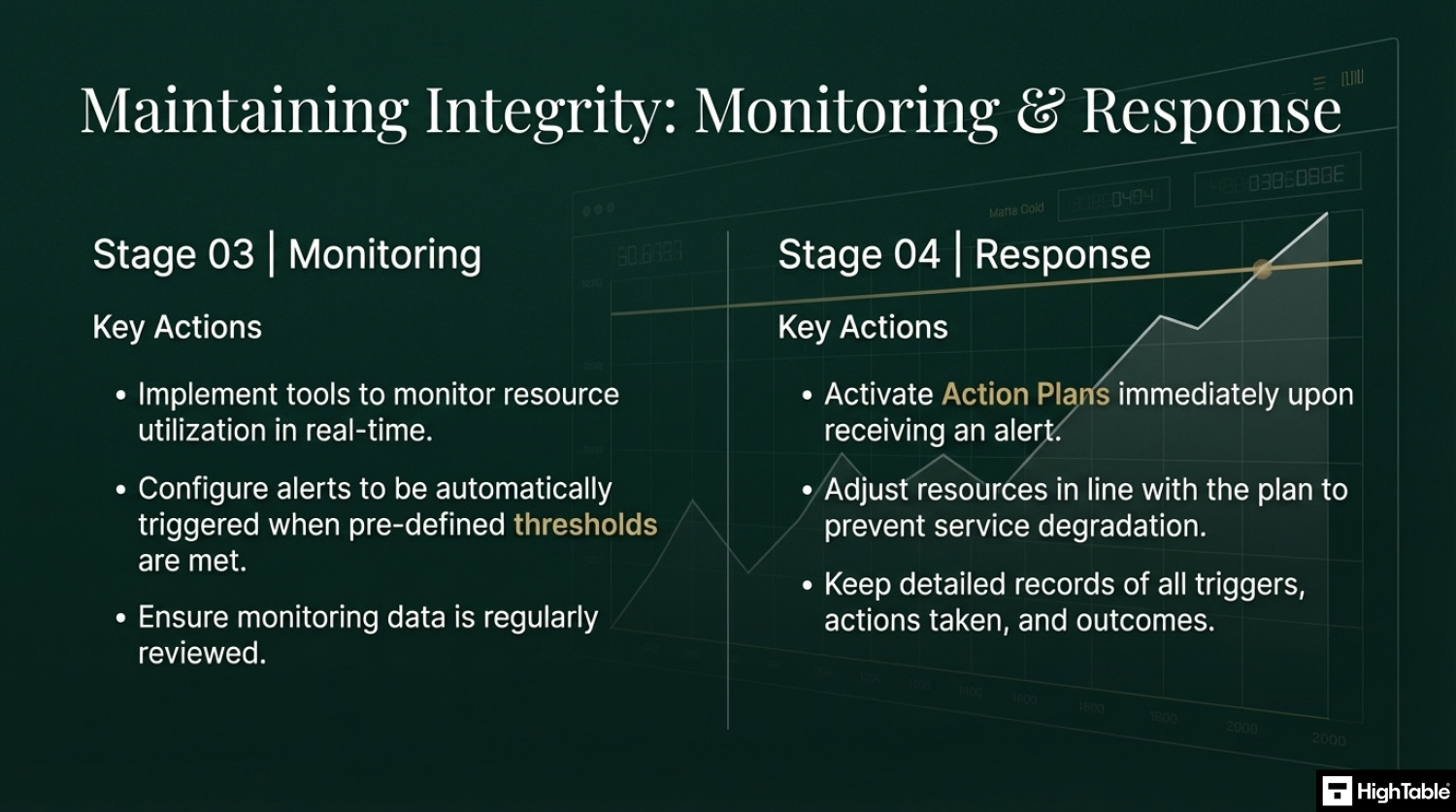
- Monitor and Alert: Implement continuous monitoring of resource use against defined thresholds and trigger automated alerts
- Adjust and Respond: Execute pre defined action plans when thresholds are reached and document all adjustements
How to implement ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6
Effective capacity management is essential for maintaining the availability and performance of information processing facilities. By following these technical implementation steps, your organisation can proactively scale resources, mitigate the risk of system outages, and satisfy the requirements of ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6.
1. Formalise Capacity Requirements and Performance Baselines
- Identify critical business applications and document their technical requirements for CPU, memory, storage, and network bandwidth.
- Establish a “Rules of Engagement” (ROE) document that defines acceptable performance thresholds and the triggers for capacity expansion.
- Result: A documented performance baseline that ensures technical resource planning is aligned with organisational service level agreements (SLAs).
2. Provision Automated Monitoring and Telemetry Tools
- Deploy infrastructure monitoring solutions to capture real-time telemetry from on-premises servers, cloud instances, and network appliances.
- Configure granular dashboards to visualise resource utilisation trends and identify potential bottlenecks before they impact operational availability.
- Result: Continuous visibility into system health, allowing for data-driven decisions regarding resource allocation and scaling.
3. Execute Trend Analysis and Forecasting Exercises
- Perform periodic reviews of historical monitoring data to identify seasonal peaks, growth patterns, and long-term capacity trajectories.
- Utilise predictive analytics or stress-testing tools to simulate high-load scenarios and verify that current infrastructure can handle future demand.
- Result: Proactive capacity planning that prevents emergency provisioning and reduces the risk of unplanned downtime during peak periods.
4. Implement Automated Scaling and Resource Quotas
- Provision auto-scaling groups within cloud environments to dynamically adjust compute resources based on real-time demand metrics.
- Enforce hard resource quotas and limits at the container or virtual machine level to prevent “noisy neighbour” effects and ensure fair resource distribution.
- Result: Technical resilience and cost optimisation through the efficient, automated management of shared processing facilities.
5. Restrict Capacity Management via IAM and MFA
- Apply the Principle of Least Privilege by assigning specific Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles to personnel authorised to modify resource limits.
- Mandate Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for any administrative actions that involve de-provisioning or significantly altering infrastructure capacity.
- Result: Protection against unauthorised or accidental resource changes that could lead to service degradation or excessive operational costs.
6. Perform Periodic Capacity Audits and Baseline Reviews
- Conduct quarterly technical audits to verify that current capacity remains sufficient for the evolving risk and demand profile of the organisation.
- Revoke or adjust resource allocations for decommissioned projects and “orphan” assets to maintain environment hygiene and technical efficiency.
- Result: Sustained compliance with ISO 27001 standards and the continuous optimisation of the information processing environment.
Capacity Monitoring Strategy Example
| Resource | Reactive (Bad) | Proactive (Good / ISO Compliant) |
| Disk Space | “The server stopped because the disk is full.” | “Alert when disk is 80% full.” |
| CPU Load | “The app is slow right now.” | “Trend analysis shows we need a CPU upgrade in 3 months.” |
| Cloud Costs | “Why is the AWS bill so high?” | “Auto-scaling limits set to prevent cost spikes.” |
| Bandwidth | “The internet is lagging.” | “Traffic shaping prioritizes Zoom calls over downloads.” |
How to pass an ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 audit
Time needed: 1 day.
How to comply with ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6
- Have procedures in place
Write, approve, implement and communicate the documentation required for capacity management.
- Assess your capacity requirements and perform a risk assessment
Conduct a risk assessment and work out what your capacity requirements are.
- Implement controls proportionate to the risk posed
Based on the risk and requirements implement the controls that are proportionate. Set upper limits for capacity, implement triggers and put in places processes to respond to those triggers and alerts.
- Keep records
For audit purposes you will keep records. Examples of the records to keep include changes, updates, monitoring, review and audits.
- Test the controls that you have to make sure they are working
Perform internal audits that include the testing of the controls to ensure that they are working.
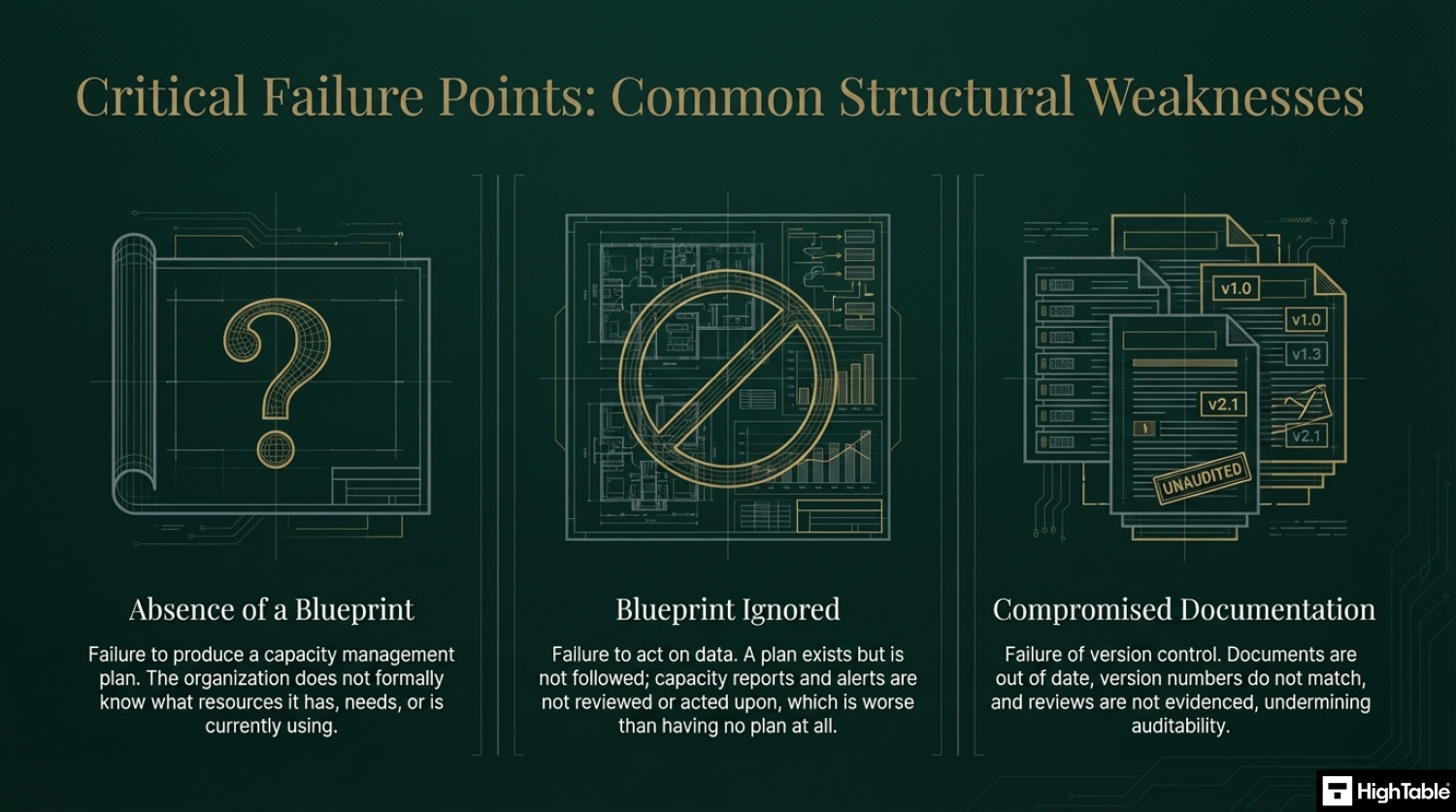
Top 3 ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 mistakes and how to avoid them
The top 3 mistakes people make for ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 are
- You have no capacity management plan: This usual things here that go wrong are when people don’t actually know what resources they need or what they are using or what they have. Identify your resource requirements, record what you are using, what you need, what the trigger thresholds are to take action.
- You have not acted on plan: Having a plan and not using it is worse than no plan at all. Be sure to follow the plan and be able to evidence that you are reviewing and acting on capacity reports.
- Your document and version control is wrong: Keeping your document version control up to date, making sure that version numbers match where used, having a review evidenced in the last 12 months, having documents that have no comments in are all good practices.
Applicability of ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 across different business models.
| Business Type | Applicability | Examples of Control Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Small Businesses | Focuses on ensuring that basic office resources like disk space, cloud storage limits, and internet bandwidth are sufficient for daily operations. The goal is to prevent sudden outages caused by running out of capacity. |
|
| Tech Startups | Essential for maintaining the availability of customer-facing applications. Compliance involves automating resource scaling in the cloud and proactively managing costs to prevent service disruptions. |
|
| AI Companies | Critical for managing high-performance computing (HPC) resources, such as GPU clusters and massive training datasets. Focus is on efficient resource allocation and forecasting for long-running training jobs. |
|
Fast Track ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Compliance with the ISO 27001 Toolkit
For ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 (Capacity management), the requirement is to ensure that the use of resources is monitored and adjusted in line with current and expected capacity requirements. Many organizations are misled into thinking they need a complex SaaS platform to “track” their server loads or bandwidth.
| Compliance Factor | SaaS Monitoring Platforms | High Table ISO 27001 Toolkit | Audit Evidence Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy Ownership | Rents your data back to you; if you cancel, you lose your capacity history and documented thresholds. | Permanent Assets: Fully editable Word/Excel Capacity Management Policies that you own forever. | A localized Capacity Plan document defining 80% utilization alerts stored on your secure internal drive. |
| Implementation | Over-engineers compliance with proprietary dashboards that often duplicate native cloud monitoring data. | Governance-First: Formalizes your existing technical telemetry (AWS/Azure) into an auditor-ready framework. | A signed capacity review meeting log proving that resource growth was forecasted and approved. |
| Cost Structure | Charges a “Growth Tax” based on the number of monitored assets, increasing your OpEx as your business scales. | One-Off Fee: A single payment covers your capacity governance for one server or a global cloud estate. | Allocating budget to actual infrastructure scaling rather than a monthly compliance “paperwork” subscription. |
| Platform Freedom | Limited by vendor integrations; struggles with serverless or hybrid models that don’t fit rigid SaaS connectors. | 100% Agnostic: Standards adapt to any environment (On-prem, Cloud, or Hybrid) without technical limits. | The ability to shift from on-premise hardware to cloud-native microservices without extra compliance fees. |
Summary: For Annex A 8.6, the auditor wants to see that you have a policy for capacity and proof that you plan for the future. The High Table ISO 27001 Toolkit provides the governance framework to satisfy this requirement immediately. It is the most direct, cost-effective way to achieve compliance using permanent documentation that you own and control.
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 FAQ
What is the primary objective of ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6?
The primary objective is to ensure system availability by monitoring and adjusting resources to meet current and future operational demands. This control shifts organizations from a “break-fix” mentality to a proactive strategy that prevents downtime caused by resource exhaustion. Key goals include:
- Preventing Bottlenecks: Identifying constraints in IT, human, or physical resources before they impact service delivery.
- Ensuring Availability: Guaranteeing that systems have the necessary “muscle” (CPU, storage, staff) to function during peak times.
- Future Proofing: Using trend analysis to predict growth and budget for upgrades months in advance.
Which specific resources must be monitored for Annex A 8.6 compliance?
Compliance requires monitoring a broad spectrum of resources, extending beyond just server hardware to include human and physical assets. Organizations must identify and track any resource whose depletion could disrupt information security or business operations. Mandatory categories typically include:
- IT Infrastructure: CPU usage, RAM, disk storage, network bandwidth, and IP address pools.
- Human Resources: Staff availability, workload capacity, and key personnel dependencies.
- Physical Facilities: Office desk space, meeting room availability, power supply capacity, and secure storage (filing cabinets).
- Cloud Quotas: API rate limits, licensed user counts, and cloud storage tiers.
What is the difference between reactive and proactive capacity management?
Proactive management anticipates resource exhaustion through forecasting, whereas reactive management only addresses issues after a failure has occurred. For ISO 27001 certification, a purely reactive approach (e.g., buying a new hard drive only after the server crashes) is often a major non-conformity. The distinction involves:
- Reactive (Audit Risk): Responding to “disk full” errors, scrambling for new hires during burnout, or investigating high AWS bills after they arrive.
- Proactive (Audit Success): Setting alerts at 80% utilization, analyzing 6-month growth trends, and configuring auto-scaling to handle traffic spikes automatically.
Does ISO 27001 capacity management apply to human resources?
Yes, human resource capacity is a critical component of Annex A 8.6 and is frequently scrutinized by auditors. You must demonstrate that you have sufficient staff to maintain security controls and operations without compromising integrity or availability. Evidence includes:
- Utilization Reports: Tracking team workload to prevent burnout and error rates.
- Succession Planning: Ensuring no single point of failure exists if a key administrator leaves.
- Recruitment Forecasting: Aligning hiring plans with projected business growth to ensure security teams are not understaffed.
What evidence do auditors require for Capacity Management compliance?
Auditors require tangible proof of the “Monitor, Alert, Act” cycle, not just a static policy document. You must demonstrate that you are actively watching your environment and making decisions based on data. Essential audit artifacts include:
- Monitoring Dashboards: Screenshots of tools like AWS CloudWatch, Datadog, or Nagios showing active tracking.
- Alert Logs: Evidence of automated triggers (e.g., “Email sent when CPU > 90%”) and the subsequent tickets raised to resolve them.
- Capacity Plans: Meeting minutes or reports reviewing usage trends and authorizing future hardware/staffing investments.
How should organizations handle cloud scaling under this control?
Cloud environments satisfy this control through “elasticity,” but organizations must configure specific constraints and alerts to remain compliant. While the cloud offers infinite theoretical capacity, your budget and configuration do not. Best practices include:
- Auto-Scaling Groups: Configuring servers to automatically spin up during high-traffic events to maintain availability.
- Cost/Usage Alerts: Setting budget alarms to detect runaway processes or denial-of-service attacks that consume resources.
- Quota Monitoring: Tracking soft and hard limits imposed by the cloud provider (e.g., maximum number of vCPUs per region).
How often should capacity projections and trend analysis be performed?
Capacity reviews should be performed at planned intervals, typically quarterly or semi-annually, or triggered by significant operational changes. The frequency depends on the volatility of your environment. Recommended review triggers include:
- Periodic Reviews: A formal quarterly meeting to analyze growth trends (e.g., “Data storage is growing 10% month-over-month”).
- Project Launches: Assessing capacity impact before deploying a new resource-intensive application.
- Major Acquisitions: Re-evaluating licensing and infrastructure needs immediately following a merger or bulk hiring event.
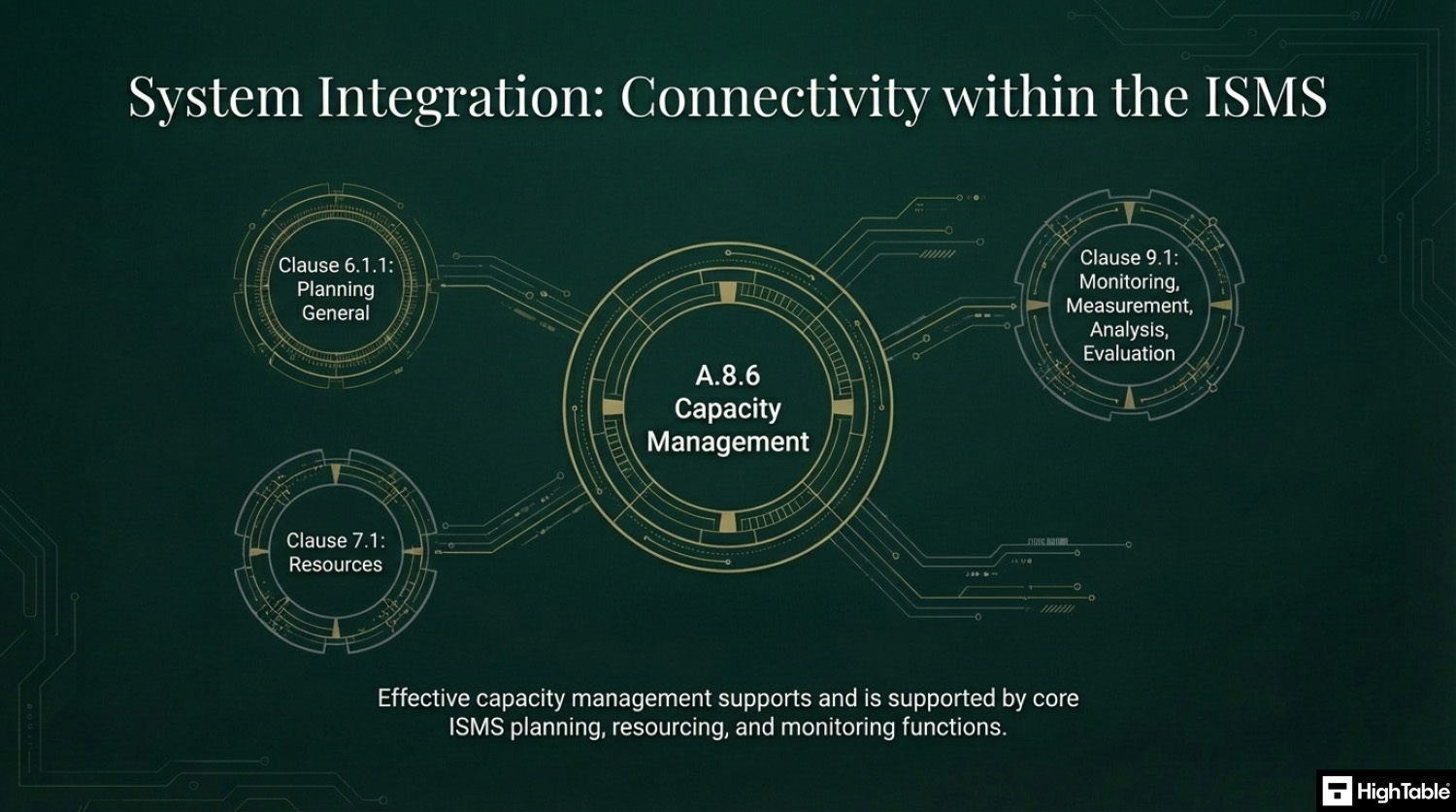
Related ISO 27001 Controls
- ISO 27001 Clause 9.1 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis, Evaluation
- ISO 27001 Clause 7.1 Resources
- ISO 27001 Clause 6.1.1 Planning General
Further Reading
ISO 27001 Controls and Attribute Values
| Control type | Information security properties | Cybersecurity concepts | Operational capabilities | Security domains |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preventive | Availability | Protect | Continuity | Protection |
| Detective | Integrity | Governance and Ecosystem | ||
ISO 27001 Annex A 8.6 Strategic Briefing Slides