Introduction
In this tutorial we will cover ISO 27001 Risk Treatment.
You will learn what ISO 27001 Risk Treatment is and how to implement it.
Table of contents
ISO 27001 Risk Treatment
Building on the foundation of risk management explored in previous blogs, videos, and guides, we’ll now focus specifically on risk treatment within the context of ISO 27001. This standard mandates a defined and implemented risk treatment process encompassing several key steps:
- Selecting appropriate information security risk treatment options: This involves choosing the most effective strategies to address identified risks.
- Determining necessary controls: Based on the chosen treatment options, you’ll need to identify the specific controls required for implementation.
- Mapping controls to ISO 27001 Annex A: This step involves comparing your chosen controls to the extensive list provided in the standard’s Annex A, ensuring alignment.
- Developing a Statement of Applicability: This document will outline the controls chosen to mitigate your specific organisational risks.
- Formulating a risk treatment plan: This plan will detail the actions necessary to implement the chosen controls and mitigate risks.
- Obtaining approval: Secure necessary approvals for the selected risk treatment options.
- Documenting the process: Maintaining documented information on the entire risk treatment process is crucial for ongoing monitoring and improvement.
Information Security Risk Management Procedure
The first step is to implement a risk management procedure.
The risk management procedure will cover
- how you identify risk
- how you assess risk
- how you treat risk
- how you manage risk
- the risk register
ISO 27001 Templates

DO IT YOURSELF ISO 27001
All the templates, tools, support and knowledge you need to do it yourself.
Risk Treatment Options
Risk assessment generates a risk score and based on that score we have a risk treatment option.
You can select the risk treatment options that work for you but the industry standard risk treatment options are:
- risk avoidance
- risk reduction
- risk acceptance
- risk transfer
Risk avoidance
Risk avoidance is where the failure cost is too great and therefore, the risk is not taken and we don’t accept the risk.
Risk reduction
Risk reduction is where the gross risk is high thereby reducing the probability or impact of the risk through controls.
Risk acceptance
Risk acceptance is where the gross risk is accepted as it stands.
Risk Transfer
Risk transfer is that we transfer part of a risk to a third party, for example, via insurance or outsourcing.
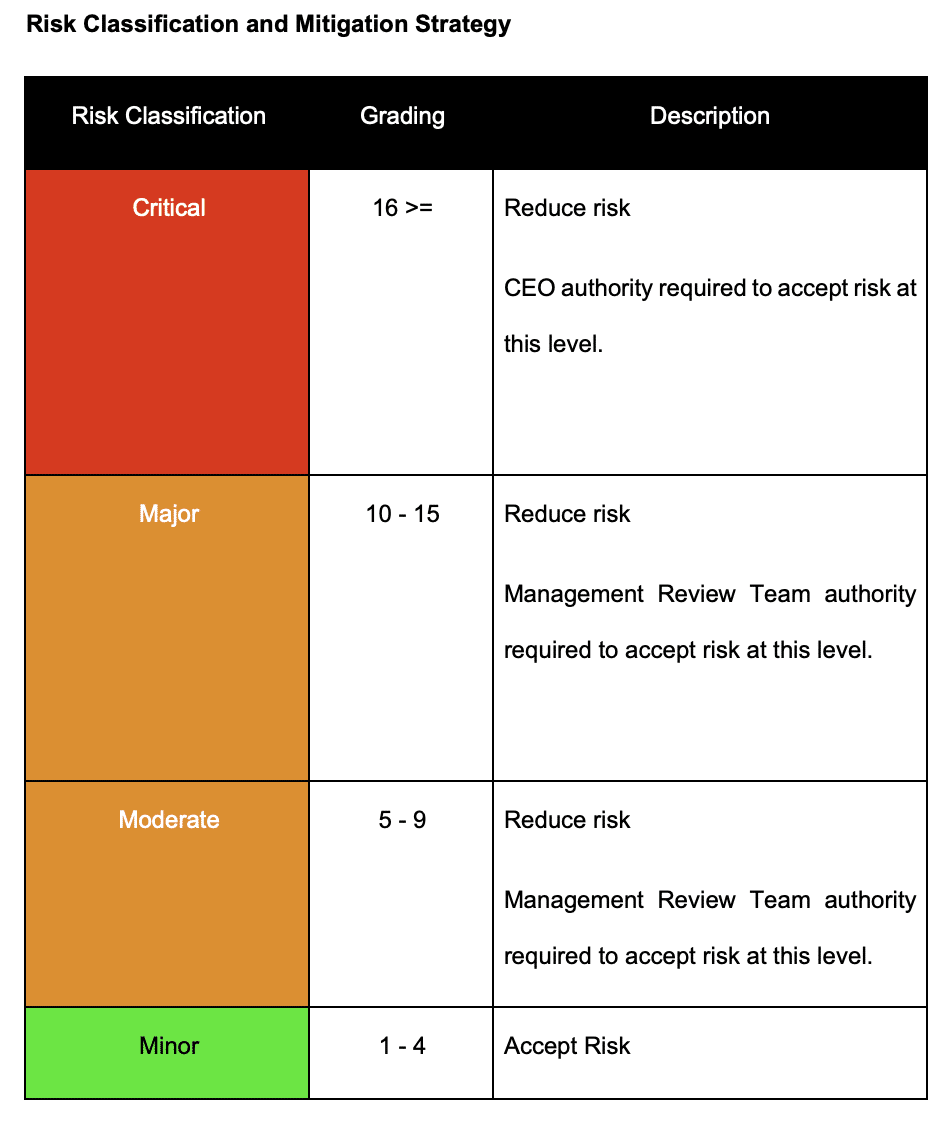
Risk Treatment Defaults
The process includes default risk treatment options based on the risk score. These can be overridden and are guidance.
Risk Treatment Plan
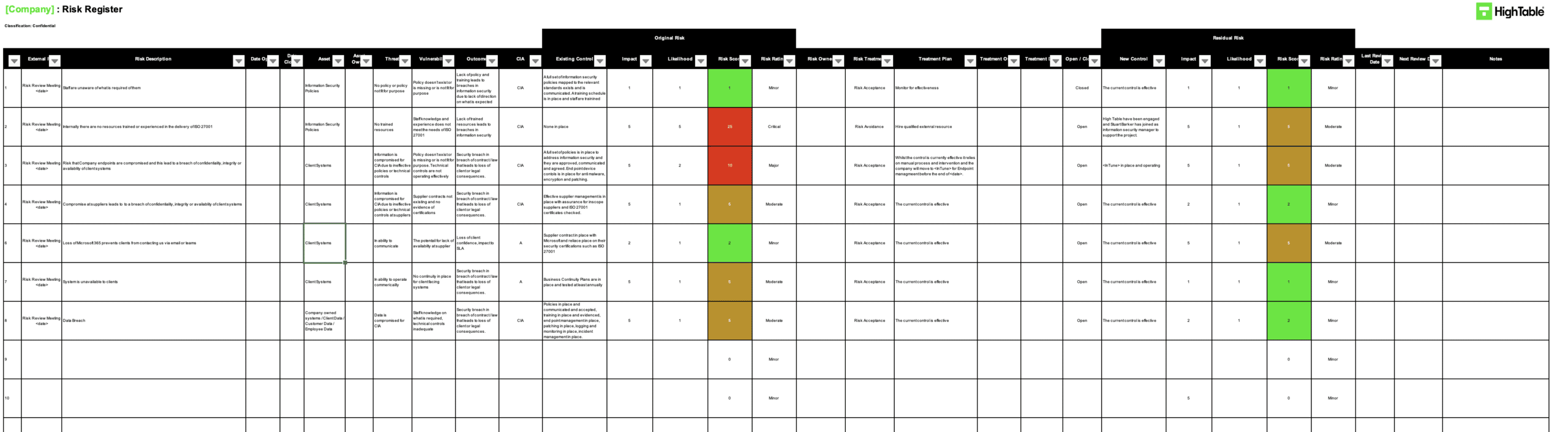
The risk treatment plan is the record and management of risk treatment.
To risk treatment plan and management of risk is via the risk register. This risk register tool is a fundamental tool when it comes to the management of risk, including risk treatment.
Risk Treatment Process
The steps in managing risk treatment are:
allocate a treatment owner
- select the risk treatment option
- set a treatment date
- record whether or not it’s open or closed
- managing the risk treatment to completion
- regularly review progress of risk treatment plans
On completion of the risk treatment the risk is rescored and this gives what is called ‘residual risk’. Residual risk is the amount of risk that still remains after a risk treatment has occurred. This is the acceptable level of risk as nothing can be risk free.
In the risk treatment plan there will now be the risk score when the risk was first identified and the residual risk score. The score should have decreased as the risk has been managed. It is not sensible to do a risk treatment that doesn’t mitigate, reduce, address, or treat a risk. The risk score should never go up.
Determining Controls To Mitigate Risks
Having identified what the risk treatments options are you are going to determine the controls that are necessary to mitigate risks.
The steps are:
- identify what the risks are to your information security management system
- identify what the risks are to your information security posture
- choose the controls from ISO 27001 Annex A that help to mitigate those risks
ISO 27001 Statement of Applicability
The ISO 27001 Statement of Applicability is a list of the ISO 27001 Annex A controls where you record if that control applies to you or not and if not why not.
The way that the statement of applicability is set out to take the annex a controls and list what those annex A controls are with their control objective and to state why it is needed. The need for the control can be
- a business need – the business has determined it needs the control
- a risk need – there is a risk that the control mitigates
- a legal need – the law requires the control to be in place
- a contractual need – a contract or client requires the control
If a control is not required for any of those reasons then a control is recorded as being not applicable and a short summary of why is provided.


