Introduction
In this tutorial we will cover ISO 27001 Risk Assessment.
You will learn what ISO 27001 Risk Assessment is and how to implement it.
Table of contents
ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
So we start the process by understanding the requirement. We’re going to understand what the standard wants from us so that we can work out what we need to comply and satisfy this ISO 27001 requirement.
The information security risk assessment process should
- Establishes and maintain information security risk criteria that include the risk acceptance criteria and criteria for performing information security risk assessments.
- Ensure that repeated information security risk assessments produce consistent, valid and
comparable results. - Identifies the information security risks
- Apply the information security risk assessment process to identify risks
- Identify risk owners
- Analyses the information security risks
- Assess the potential consequences that would result if the risks were to materialise
- Assess the realistic likelihood of the occurrence of the risks identified
- Determine the levels of risk
- Evaluate the information security risks
- Compare the results of risk analysis with the risk criteria established
- Prioritise the analysed risks for risk treatment
- Keep documentation
Information Security Risk Management Procedure
The first step is to implement a risk management procedure.
The risk management procedure will cover
- how you identify risk
- how you assess risk
- how you treat risk
- how you manage risk
- the risk register
ISO 27001 Templates

DO IT YOURSELF ISO 27001
All the templates, tools, support and knowledge you need to do it yourself.
Risk Assessment
You will perform risk analysis of the risks that you identify. This analysis will create a risk score. The risk score is based on the likelihood of the risk occurring and the impact if that risk were to be realised.
Risk Likelihood
Risk likelihood is table of scores and thresholds that you can define that categorise how likely an event is to occur and in what time frame. An example risk likelihood would be:
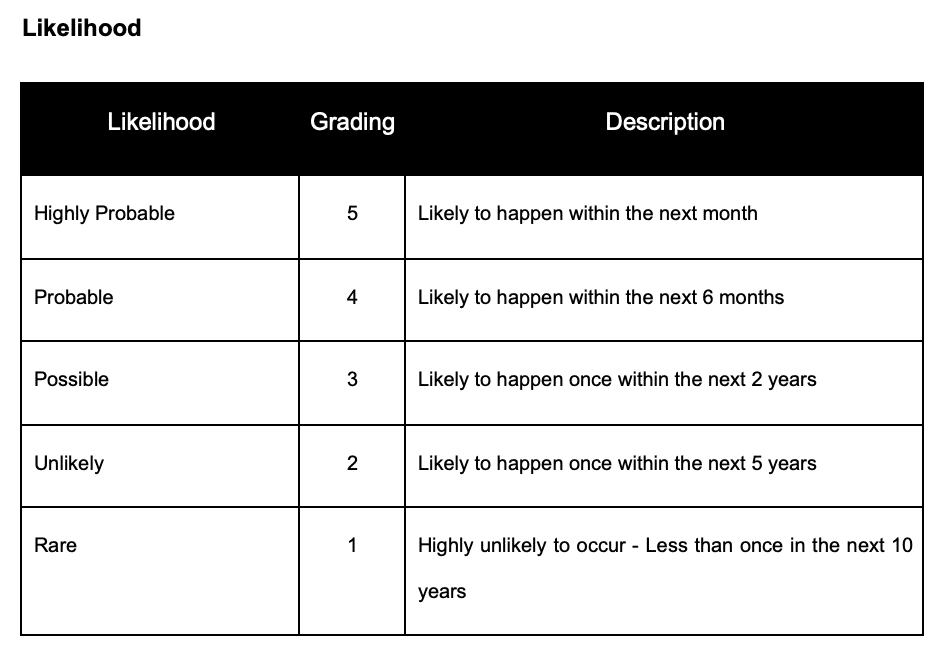
You can change the definitions of this based on your environment. For example if you’re in financial services with high transactions then ‘highly probable’ could be measured in seconds and minutes not months and years.
Risk Impact
Impact is what is the result to you if the risk happens. This can be measured based on factors such as legal impact, business impact, financial impact and an example risk impact table would be:
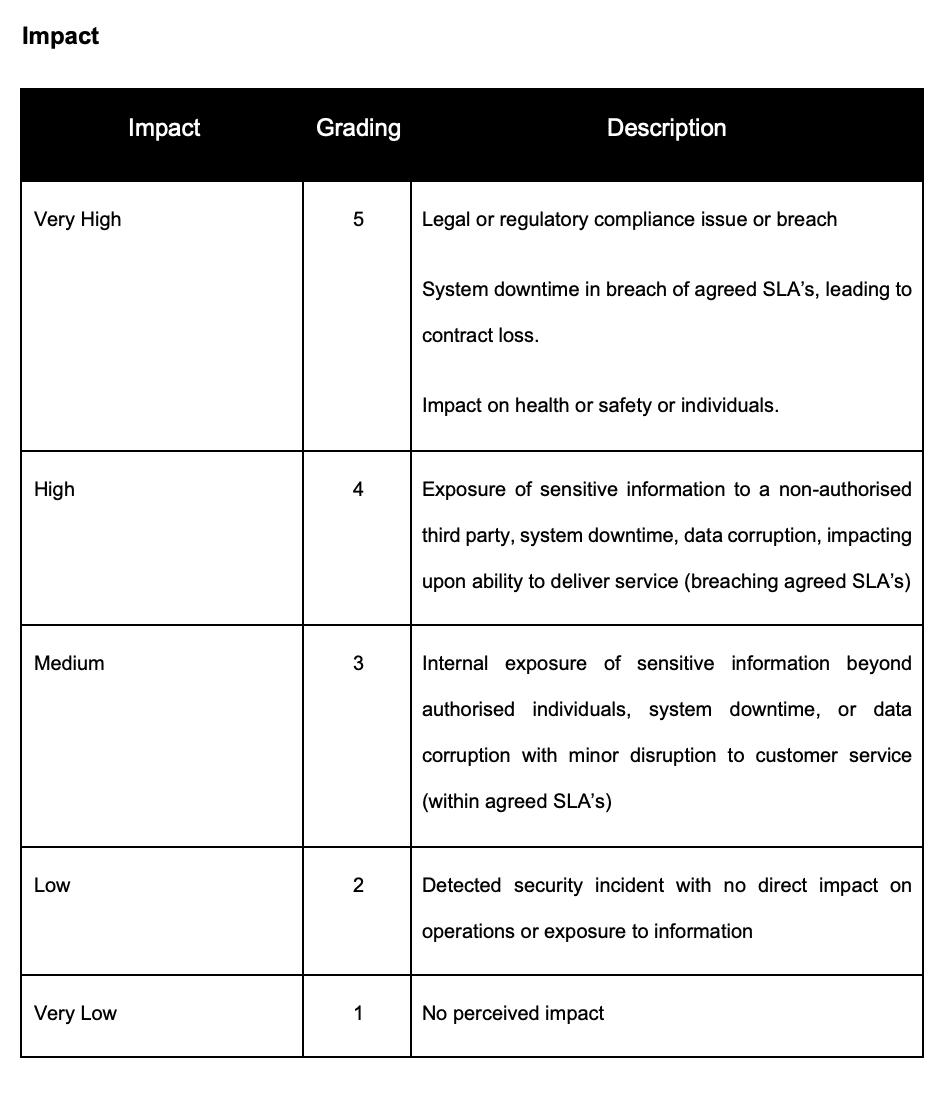
In this example you can see that ‘very low’ has no perceived impact where as ‘very high’ is a Legal and Regulatory breach or an impact on health and safety or a risk to life or it’s generating system downtime outage that leads to a contractual loss.
Risk Score Formula
To generate a risk score the formula is – you multiply the likelihood by the impact and that generates a score.
Likelihood x Impact = Risk Score
Risk Mitigation Strategy
That score will generate some default behaviour which can be overridden but what you are looking at here is an example risk mitigation strategy where a minor risk is something that we would accept, a critical risk is something that by default we would reduce and if we want to accept it it would require the sign off of the CEO to sign that off.
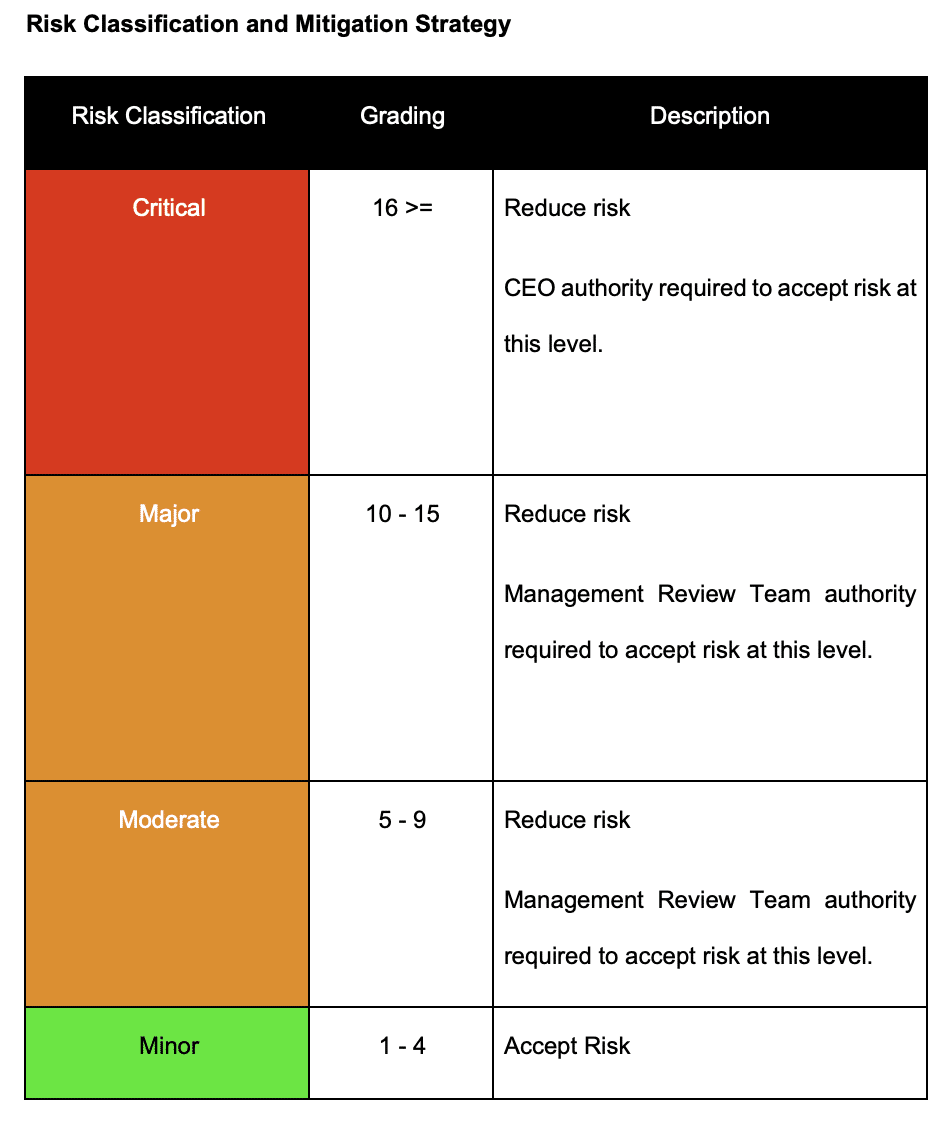
Conclusion
That is risk assessment and for further reading look at the The Ultimate Guide to the ISO 27001 Risk Register that relates to the risk register and how these informational elements transpose into the day-to-day operation of the risk register and overall risk management.


