Introduction
In this tutorial we will cover ISO 27001 ISO 27001 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis and Evaluation.
You will learn what it is and how to implement it.
Table of contents
Implementation Guide
The information security management system (ISMS) is a living management system. As things change then so too must the ISMS. To ensure that the ISMS is operating effectively and meetings its intended out comes we need to ensure that we
- are monitoring it for effectiveness
- measuring it which can include process and system measures
- analysing those measures
- and evaluating those measures in the context of the ensuring the effectiveness of the ISMS.
In terms of the ISO 27001 standard this approach will be applied to both the Information Security Management System (ISMS) itself and to the ISO 27001 Annex A Controls.
The ISO 27001 Annex A Controls are the controls that we choose to mitigate the risk that we have and the needs of the business and they’re documented within the ISO 27001 Statement of Applicability, the SOA.
Information Security Objectives
When it comes to the monitoring and measurement of the information security management system (ISMS), you will remember that we have in previous tutorial and previous guides and tutorials gone through how to identify our information security objectives.
You may remember this information security objectives spreadsheet that sets out what our information security objectives are and that within that we have said what we are going to be monitoring and measuring as well as how we are going to be evaluating our results.
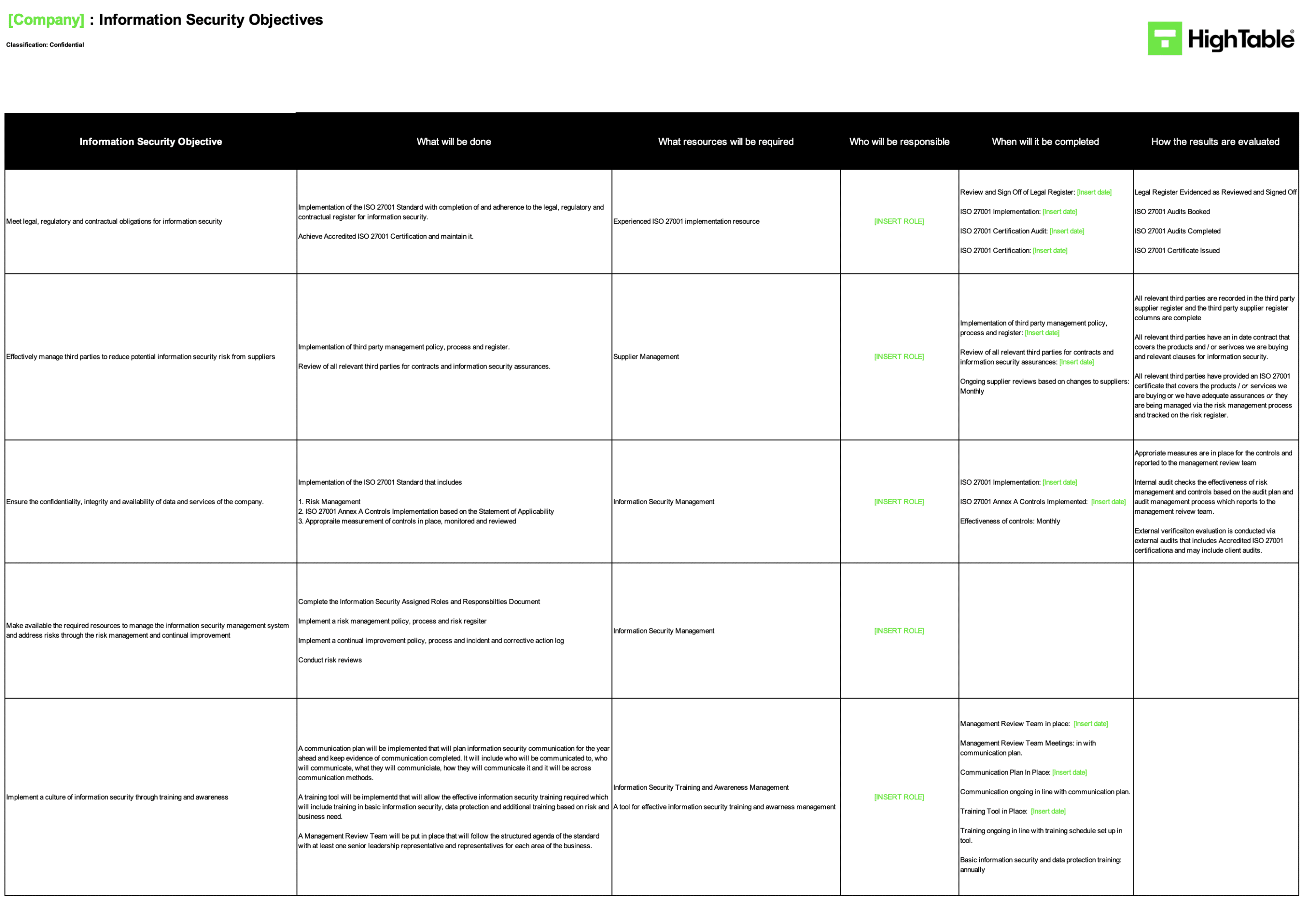
The basic way that we’re going to satisfy this for the isms is by the regular monitoring and analysis against our objectives.
Management Review
We have management reviews at least monthly up until and including our first audit and ideally for the first year after audit. Our management reviews follow a structured agenda and meet a number of requirements and one of those requirements is that we are going to review the performance against the objectives. You can learn more in How to conduct an ISO 27001 Management Review Meeting.
Internal Audit
For the information security management system we to perform our internal audit. Internal audit is going to cover the processes as well and that is touched on in the last sentence of this particular clause – the organisation shall evaluate the information security performance and the effectiveness of the management system.
We do that by conducting our ongoing internal audit. You can learn How to conduct an ISO 27001 Internal Audit
That structured internal audit process will generate reports that are fed to the continual improvement process.
Business Specific Processes
The part where it becomes a little bit more tricky and here I can only give you guidance is when it comes to the ISO 27001 Annex A Controls because the ISO 27001 Annex A Controls are going to be business specific.
These are processes that you are writing. They are how you run and operate your business.
My guidance and my advice is, every control in effect is a process or a series of processes but let’s take it at a high level logical step. If we have a process, a process will have an input, a process will have an output and a process will be able to be measured and monitored.
Operational Security Dashboard
You need to generate an operational security dashboard. What that operational security dashboard is going to cover is the metrics, the main metrics that you are measuring, at least on a monthly basis.
Examples of metrics include
- the level of patching across devices, how many devices are patched, how many patches are outstanding. Speak to your IT teams and understand the metrics that you can get around patching.
- the level of encryption that is on your devices, are devices encrypted, are they not encrypted, are there issues with encryption.
- malware, anti-malware technology, antivirus. What is the status on a monthly ongoing basis of our antivirus?
- measurement and analysis of incidents. At least that looks at the security incidents that you’ve had.
- the status of your training. How many people have completed it? How many are outstanding? How many haven’t completed it?
The things that you can measure or monitor are the processes that you have.
As you are developing your processes and documenting your processes for your controls, think about what the process does, whether or not you can measure that, what kind of a report that you can generate out of the back of that that will provide value and as a minimum share those results with the management review team.
The Process
The bigger you are the more complex that’s going to be. In a smaller organisation it’s going to be relatively straightforward. The report is going to be quite simplistic.
The process is – you’re going to share it with the management review team. Probably you’re going to have some level of recommendation that goes with it. If you require action off of the back of that and you’re then following your continual improvement process to implement that continual improvement or you’re going to update your risk register because what you’ve identified is that through analysing these processes and analysing what’s going on that a risk has occurred because something has gone wrong and something isn’t operating.
There are tutorials on continued improvement – ISO 27001 Continual Improvement Explained – and there are tutorials on risk management.
DO IT YOURSELF ISO 27001
All the templates, tools, support and knowledge you need to do it yourself.
Implementation Summary
The steps to implement are:
- write a process
- document the process
- understand what the process can measure
- measure it
- report that to the management review team
Documented information should be available as evidence of the result so keep those reports.
When it comes to the audit the auditor is going to want to see that you’ve got that.
The simplest way of doing that is to have a copy of that report alongside the minutes of your management review meeting within your folder structure so you can say
- here is the management review meeting
- here are the minutes of that meeting
- here is where that report was discussed
- this is what was discussed about that report
- and here is a copy of that report.
That is the simplest and easiest way for you to satisfy that part of this requirement.
Training Video
In this free ISO 27001 training video we look specifically at implementing ISO 27001 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis and Evaluation.


