Table of contents
- Introduction
- What is ISO 27001 competence?
- What does ISO 27001 say about competence?
- What is an ISO 27001 Competency Matrix?
- ISO 27001 Competency Matrix Template
- How to create and use an ISO 27001 Competency Matrix
- ISO 27001 Competency Matrix Example
- What are the benefits of ISO 27001 Competency Matrix?
- Who is responsible for the ISO 27001 Competency Matrix?
- Who is responsible for implementing the ISO 27001 Competency Matrix?
- How do you monitor the effectiveness of the ISO 27001 Competency Matrix?
- FAQ
Introduction
In this ultimate guide I show you everything you need to know about the ISO 27001 Competency Matrix and exactly what you need to do to satisfy it to gain ISO 27001 certification.
We will get to grips with what competence is, understand why organisations need a Competency Matrix, show you how to write one, and let you in on trade secret’s that’ll save you hours of time and effort.
I am Stuart Barker: founder of High Table, Information Security expert and ISO 27001 Ninja, and this is the ISO 27001 Competency Matrix.
What is ISO 27001 competence?
The ISO 27001 standard requires us to to have the competence to effectively run the information security management system. Competence is the skills and experience that people have that evidence that they can manage and operate information security in the organisation.
Competency development requires us to identify the gaps in information security knowledge, experience and training and address those gaps.
We need to know that employees have the skills for information security.
We record it in an ISO 27001 competency matrix.
What does ISO 27001 say about competence?
ISO 27001 clause 7.2 competence addresses having the right people in place with the right skills and experience to run the information security management system. Without it you wont reach ISO 27001 certification and you wont have effective information security in place.
The standard defines competence as:
The organisation shall:
ISo 27001 Clause 7.2 competence
a) determine the necessary competence of person(s) doing work under its control that affects its information security performance;
b) ensure that these persons are competent on the basis of appropriate education, training, or experience;
c) where applicable, take actions to acquire the necessary competence, and evaluate the effectiveness of the actions taken; and
d) retain appropriate documented information as evidence of competence.
In this video we explore in more detail how to implement the full requirements of this clause of the standard.
What is an ISO 27001 Competency Matrix?
The ISO 27001 competency matrix is a requirement of ISO 27001 certification. It is also best practice management that we understand the competency of employees for information security. It forms part of the information security management system. We also use it to track, plan and manage information security training.
For a deep dive into competence you can read the Essential Guide to ISO 27001 Clause 7.2 Competence but let’s look at a summary:
It allows you to demonstrate and evidence that you have the adequate skills to operate the Information Security Management System and to identify, track and manage any training or resourcing needs.
ISO 27001 Competency Matrix Template
The competency matrix template is a simple and effective way to record and manage employee competency.
It is a record of the skills and training level of staff against information security and business technology.

DO IT YOURSELF ISO 27001
All the templates, tools, support and knowledge you need to do it yourself.
How to create and use an ISO 27001 Competency Matrix
In this tutorial video I show you how to create a competency matrix for skills in around 5 minutes.
A competency matrix shows the skills you have, the skills you need and the training requirements and is a part of of data security and many industry certifications including ISO 27001, PCI DSS, SOC and a host of others.
We cover how the it fits into the information security management system in the ISO 27001 Templates Documents Ultimate Guide.
The competency matrix doesn’t have to be hard and it really is easy to create a basic functioning competency matrix from scratch.
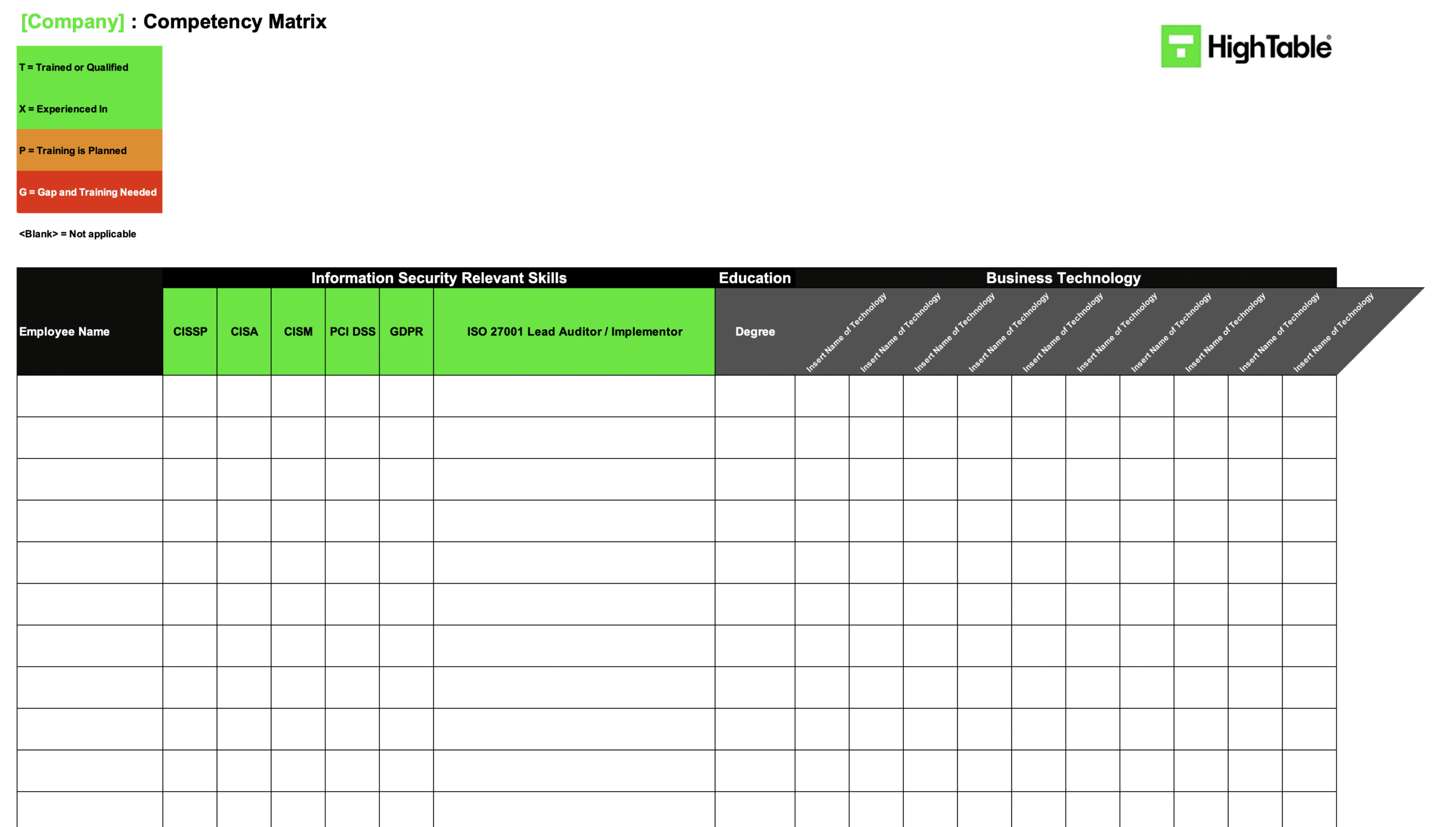
ISO 27001 Competency Matrix Example
This is an ISO 27001 Competency Matrix example and a great way to meet the requirement of the standard.
What are the benefits of ISO 27001 Competency Matrix?
Other than your ISO 27001 certification requiring it, the following are benefits of having the ISO 27001 Competency Matrix:
- Improved security: You will have the skills and experience to run an effective information security management system.
- Reduced risk: Ensuring that you have the skills and experience needed will lead to a reduction in risk to your organisation and ensure the information security goals are met and the management system runs as intended.
- Improved compliance: Standards and regulations require that you have competence for information security.
- Reputation Protection: In the event of a breach having trained, experienced and competence personnel will reduce the potential for fines and reduce the PR impact of an event
Who is responsible for the ISO 27001 Competency Matrix?
This will depend on the structure and make up of your organisation. It is usually the information security manager that takes responsibility for this working alongside the HR manager. It is also possible to be just the HR manager.
Who is responsible for implementing the ISO 27001 Competency Matrix?
The implementation is a combination of the information security manager, HR and the resources that are involved in the ISMS.
How do you monitor the effectiveness of the ISO 27001 Competency Matrix?
The approaches to monitoring the effectives of competence include:
- Internal audit of the skills and training process
- External audit of the skills and training process
- Review of training records and checks on employment history
FAQ
A trusted ISO 27001 competency matrix template can be downloaded from High Table: The ISO 27001 Company.
A competency matrix is a way to measure the skills and experience of staff against the business skill requirements.
A competency matrix is a way to measure the skills of employees against the requirements of the business. In HR they will use the matrix to align the training needs of staff for the business and allocate the training resources. They will use it to identify skills risks and skills gaps and then plan to reduce those risks.
It is easy to build a competency matrix. In a spreadsheet list your employees down the left hand side in a column. Across the top in a row list the skills that you are interested in measuring. For each employee then mark the level of skill that they have against each skill required. You can use the a simple key of Gap, Trained, Experienced. A tutorial video on how to do it can be found here on YouTube: How To Build a Competency Matrix.
Yes. It is the easiest, simplest way to understand what skills you need verses what skills you have.
Yes. Information security skills are wide and varied. Once you understand what skills you need it is important to understand what skills you have so you can address the gaps.
After any significant change that affects personnel or the roles and responsibilities of the management system and at least annually.


