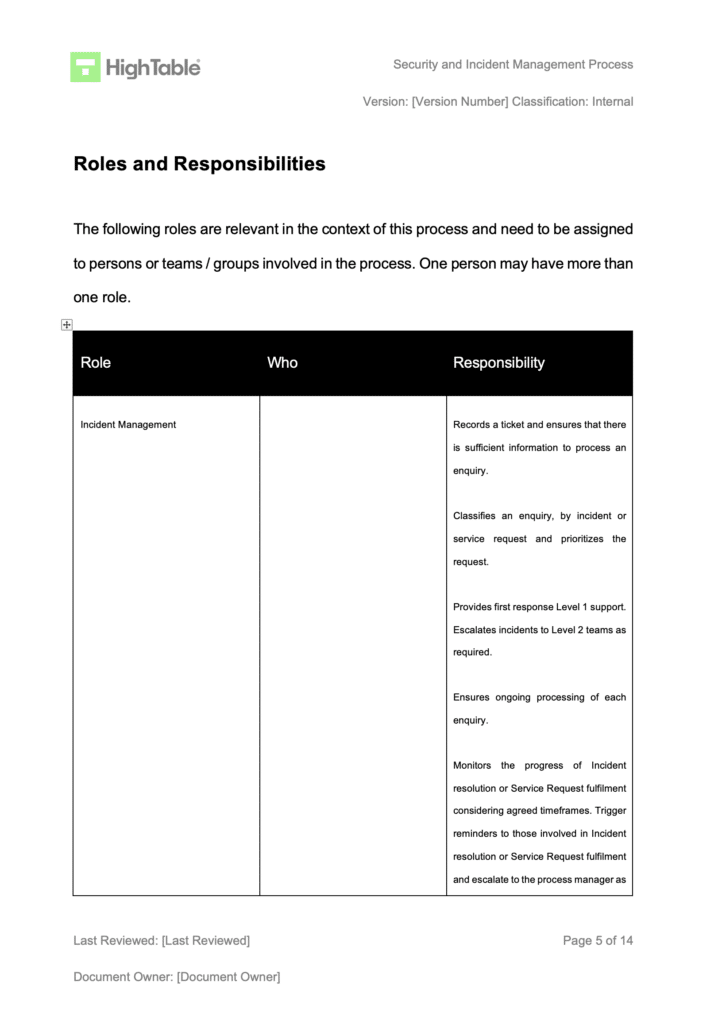
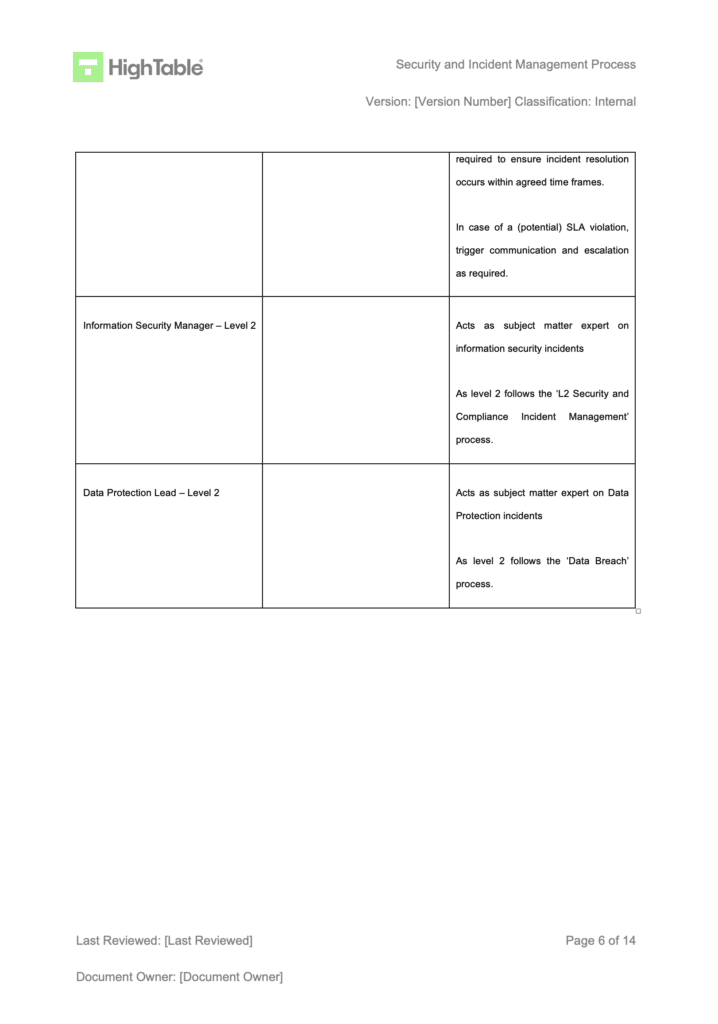
Table of contents
ISO 27001 Nonconformity and Corrective Action
I am going to show you what ISO 27001 Clause 10.2 Nonconformity and Corrective Action is, what’s new, give you ISO 27001 templates, an ISO 27001 Toolkit, show you examples, do a walkthrough and show you how to implement it.
I am Stuart Barker the ISO 27001 Ninja and using over two decades of experience on hundreds of ISO 27001 audits and ISO 27001 certifications I show you exactly what changed in the ISO27001:2022 update and exactly what you need to do for ISO 27001 certification.
Watch
What is it?
ISO 27001 Clause 10.2 Nonconformity and Corrective Action is a sub clause to ISO 27001 Clause 10 Improvement that requires us to manage nonconformities.
Nonconformities are deviations to the norm.
If a policy or process is not operating as expected, that would be classed as a nonconformity.
The clause sets out the requirement of what we do once we have identified the problem.
The ISO 27001 standard requires an organisation to manage when things go wrong.
ISO 27001 Nonconformity and Corrective Action is about effectively managing when things go wrong, correcting it and taking steps to make sure it does not happen again.
The ISO 27001 standard for ISO 27001 certification wants you to be in control of your management system and continually improve it.
Purpose
The purpose of clause 10.2 is to identify when things are not operating as expected and to make sure that when things go wrong they are corrected.
Definition
The ISO 27001 standard defined clause 10.2 as follows:
When a nonconformity occurs, the organisation shall:
React to the nonconformity, and as applicable:
– take action to control and correct it; and
– deal with the consequences;Evaluate the need for action to eliminate the causes of nonconformity, in order that it does not recur or occur elsewhere, by:
– reviewing the nonconformity;
– determining the causes of the nonconformity;and
– determining if similar nonconformities exist, or could potentially occur;Implement any action needed;
Review the effectiveness of any corrective action taken; and
Make changes to the information security management system, if necessary.
Corrective actions shall be appropriate to the effects of the nonconformities encountered.
The organisation shall retain documented information as evidence of:
– the nature of the nonconformities and any subsequent actions taken,and
– the results of any corrective action.Non conformity and corrective action falls under incident management. It can be implemented as a level 2 incident management process or a sub process. The trick is to identify that what has happened has or could impact information security and then to invoke your processes for managing the non conformity.
ISO 27001 Clause 10.2 Nonconformity and Corrective Action
ISO27001:2022 Changes
The ISO27001:2022 Changes are minor.
The 2022 update to the clause changed the numbering of the clause from ISO 27001 Clause 10.1 to ISO 27001 Clause 10.2.
In fact it just swapped the numbering of those 2 clauses to bring in line with other standards in the series.
They have removed the word ‘and‘ from the end of bullet points.
They have changed the words ‘the organisation shall retain documented information as evidence of‘ to ‘Documented Information shall be available as evidence of’.
I mean it does feel at times that people make changes just to justify their existence.
ISO 27001 Templates
ISO 27001 templates are a great way to implement your information security management system. Whilst an ISO 27001 toolkit can save you up to 30x in consulting fees and allow you to deliver up to 10x faster these individual templates help meet the specific requirements of ISO 27001 clause 10.2
Nonconformity
A nonconformity is usually identified by audit or the occurrence of incidents.
For Incidents
Our first step is to handle the incident and to manage the consequences of that incident. We document everything as we go and best practice would be to use and incident management system or a help desk system. Many of these come with capability out of the box and at worst they require some minor tweaks.
This ensures we have a record of the incident and what happened.
Once this step has completed we then do an assessment of what happened. We are looking to see if this was a one off or if there is potential that the incident could happen either again or elsewhere.
We take appropriate actions to ensure that this does not and cannot occur again. This may include risk management and accepting that it may occur, if the cost of action is too high. That would require us to follow the risk management process and seek to get approval and sign off of the management review team.
We find the use of an incident and corrective action log is ideal for managing this process. The benefits of having an effective log that meets the requirements of the ISO 27001 standard whilst also efficiently handling the process are worth it.
For Audits
When an audit results in a nonconformity we follow as similar process to handling incidents. The non conformity is recorded on the incident and corrective action log. A root cause analysis is conducted. Remediation is implemented under the guidance of the management review team.
Implementation Guide
Implement Policy
We need an ISO 27001 Continual Improvement Policy. Policies are statements of what we do, not how we do it which is covered in the process documents, but the policy sets out your approach to how you handle nonconformities and corrective actions.

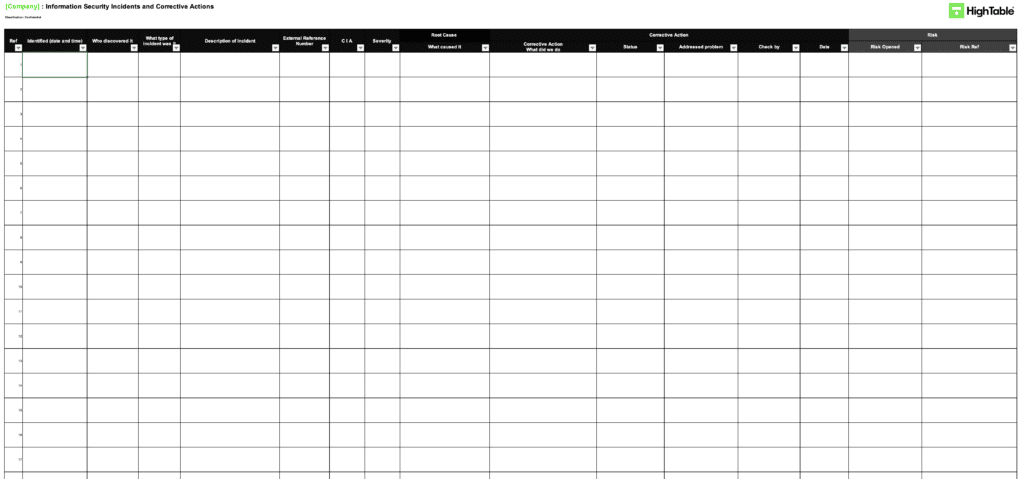
Implement an incident and corrective action log
Implement and use an incident and corrective action log that includes the required fields and allows you to manage incidents and corrective actions. This is the main tool for the management of nonconformity.

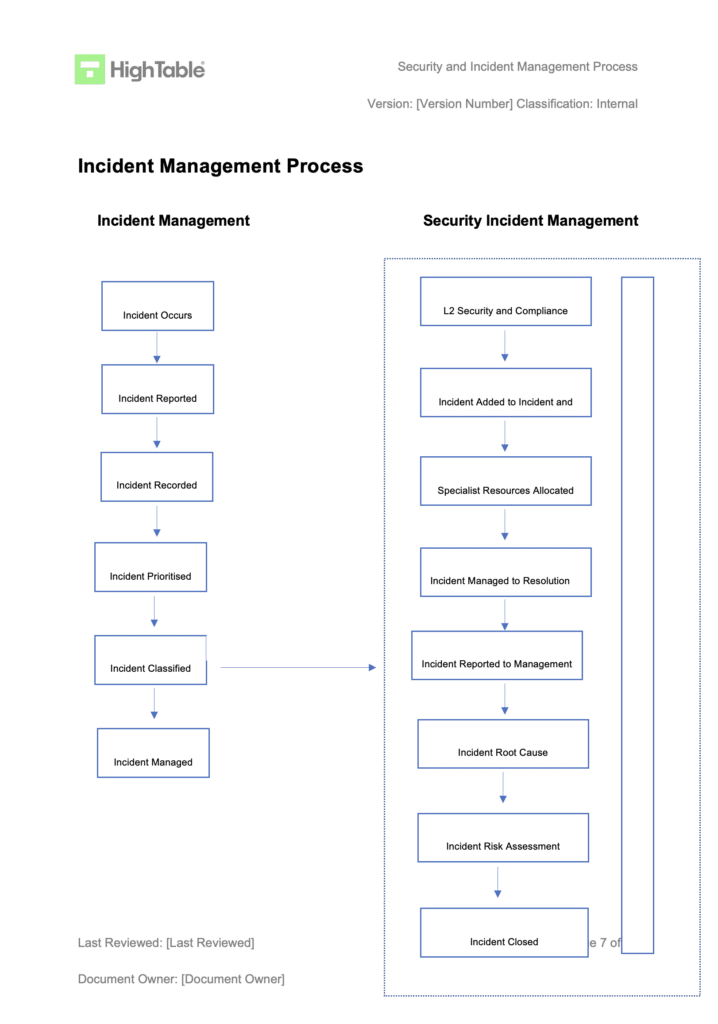
Implement an incident management process
The incident management process sets out how we deal with incidents. Incidents are one of the major sources of identifying nonconformities. The incident management process is include the ISO 27001 Toolkit but to see what it should include take a look at the following contents table:
Implement a continual improvement process
The ISO 27001 continual improvement process sets out how you make fundamental changes to prevent nonconformities from re occurring. The continual improvement process is include the ISO 27001 Toolkit but to see what it should include take a look at the following contents table:


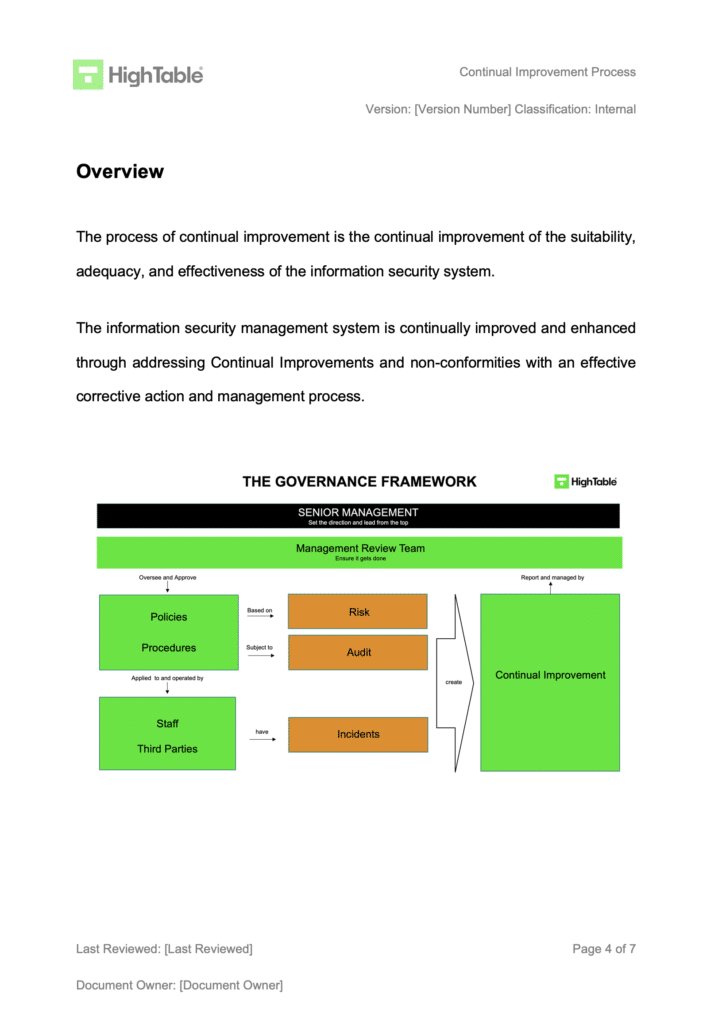
Reporting
The Management Review Team provides the management oversight and decision making body. Be sure to report to the meeting and minute the meeting minutes.
Stop Spanking £10,000s on consultants and ISMS Online tools.

How to Comply
You demonstrate compliance to ISO 27001 Clause 10.2 Nonconformity and Corrective Action by having effective policy and process in place and having documented evidence that those processes have operated effectively. What this means is that you need policy and process for the identifiers of nonconformities, being:
- Incident management
- Audit (both internal audit and external audit)
And you need policy and process to deal with the nonconformities being
To demonstrate evidence you will have a series of documents and records
- Incident tickets on your associated help desk systems
- Change tickets that support any changes that have been made
- The complete incident and corrective action log that is used to manage nonconformities
- Meeting minutes from the Management Review Team meetings where all of he above have been shared and minuted
What the auditor will check
The auditor is going to check a number of areas for compliance with Clause 10.2. Lets go through them
That you have incident management in place
When a non conformity is identified we need to be able to manage it. Incident management is required to respond to incidents and manage them through to resolution. The auditor will look at the process and a sample of recent incidents to ensure they followed the process and they were managed effectively.
That you have internal audit in place
Internal audit is the main mechanism to identify non conformity. Through the process of internal audit we identify when things are not operating as expected. The auditor will look at the process of internal audit and sample internal audits over the last 12 months. They will examine how the internal audits were reported and what happened as a result, especially in relation to any identified non conformities.
That you have corrective action in place
When a non conformity is identified something needs to happen. This is the corrective action. The auditor will want to see the corrective action process and that you have followed it. They will sample corrective actions from the last 12 months and want you to walk through them and explain how you managed them.
Top 3 Mistakes People Make
In my experience, the top 3 mistakes people make for ISO 27001 clause 10.2 are:
- Not having independent internal audits
- Not having document processes
- Not following your documented processes or not being able to evidence them in operation
ISO 27001 Clause 10.2 FAQ
The ISO 27001 standard requires that the organisation shall manage when things go wrong, manage the consequences of things going wrong, identify why it went wrong and put in place measures to stop it from happening again.
You evidence compliance to the ISO 27001 Clause 10.2 Nonconformity and Corrective Action by being able to demonstrate that you identify when things go wrong, put things right, identify why it went wrong and put in place measures so it does not happen again.
You can download ISO 27001 Clause 10.2 Nonconformity and Corrective Action templates in the ISO 27001 Toolkit.
An example of ISO 27001 Clause 10.2 Nonconformity and Corrective Action can be in the ISO 27001 Toolkit.
Yes. Senior management and leadership are informed of non conformities. This is usually via the management review team meeting.
Yes. Non conformities require a root cause analysis to identify why they happened and to help to identify what can be done to prevent it from happening again.
You can classify non conformities to help you to prioritise the order in which to tackle them and the recommended actions you should take. This would be aligned with the risk management process.
Technically yes but by doing nothing you are accepting risk and therefore you would follow your risk management process with sign off and acceptance by the management review team.
Non conformities are reported via the incident management process.
Yes you can pass the ISO 27001 certification if you have non conformities as long as they are being effectively managed and reported.